Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are noncancerous growths that develop in the uterus.
Call us to book an appointment with the best Vascular surgeon near you.
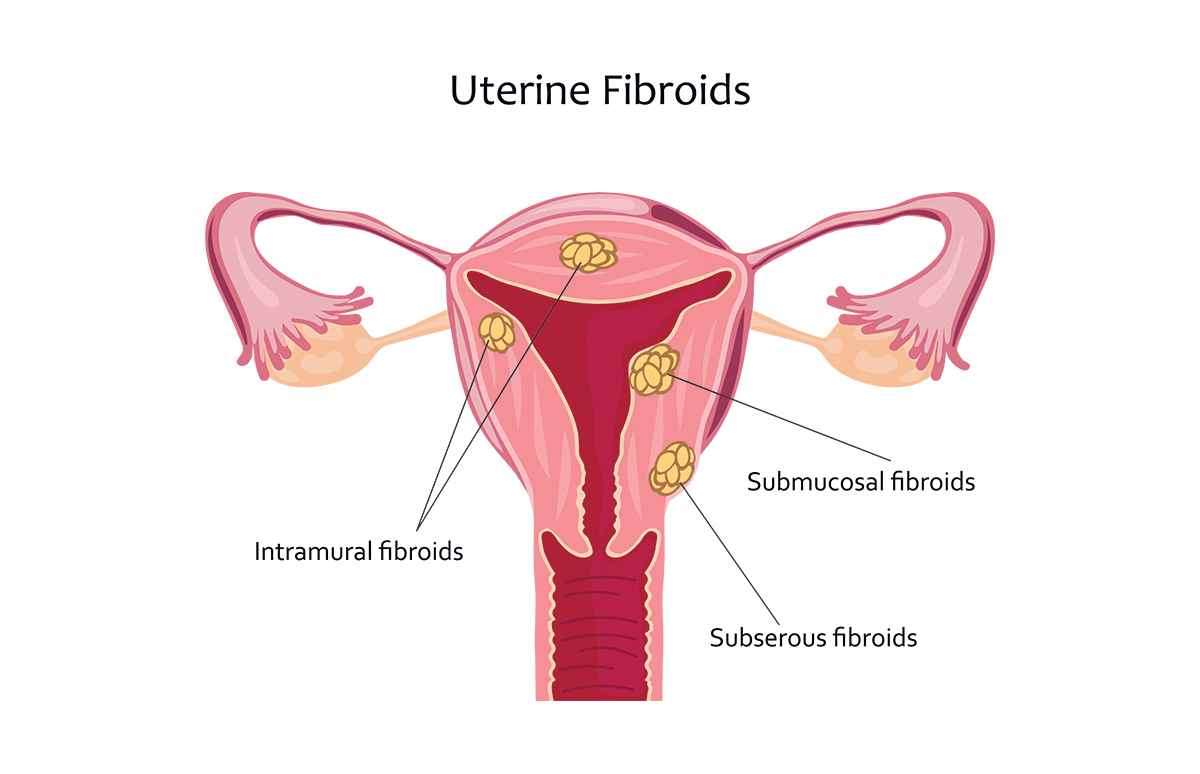
1. Subserosal Fibroids: These fibroids develop
on the outer layer of the uterus and can cause a bulging appearance. They may
press against surrounding organs, leading to discomfort or pain.
2. Intramural Fibroids: This type of fibroid
grows within the muscular wall of the uterus. Intramural fibroids can result in
a bulky uterus and may cause heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic
pain, or pressure. 3. Submucosal Fibroids: These fibroids grow
just beneath the inner lining of the uterus and can protrude into the uterine
cavity. Submucosal fibroids often lead to heavy menstrual bleeding, menstrual
cramps, and fertility issues.
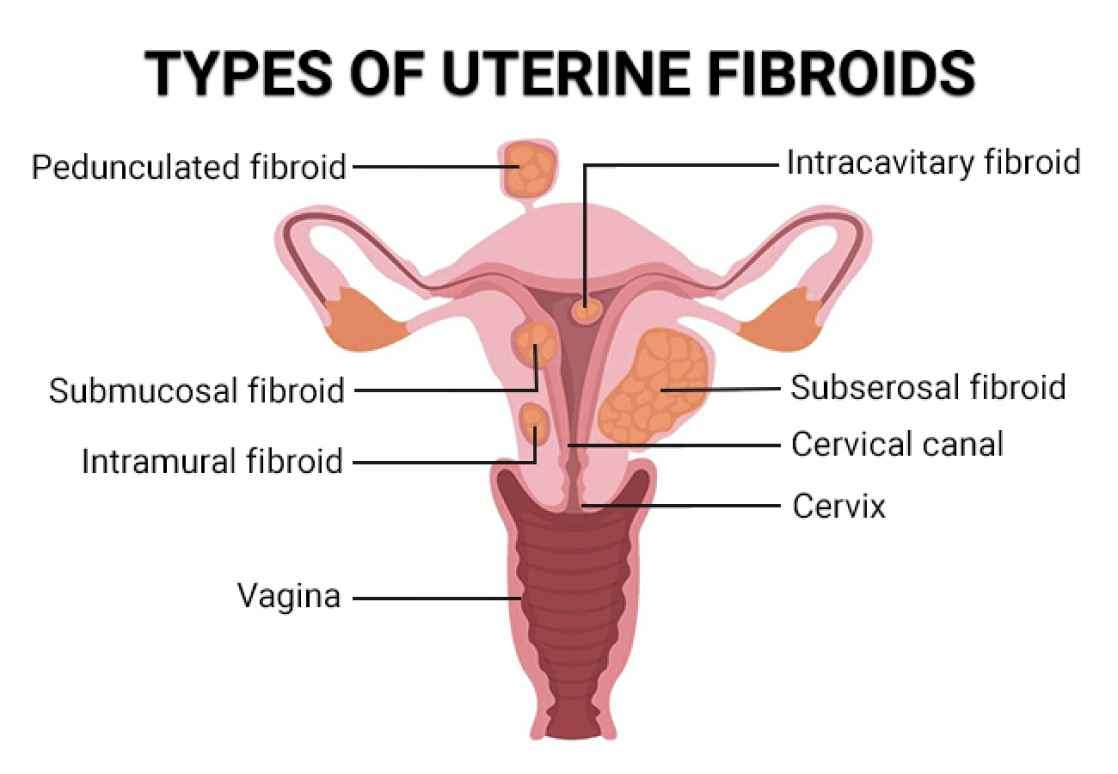
1. Subserosal Fibroids: These fibroids develop on the outer layer of the uterus and can cause a bulging appearance. They may press against surrounding organs, leading to discomfort or pain.
2. Intramural Fibroids: This type of fibroid grows within the muscular wall of the uterus. Intramural fibroids can result in a bulky uterus and may cause heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, or pressure.
3. Submucosal Fibroids: These fibroids grow just beneath the inner lining of the uterus and can protrude into the uterine cavity. Submucosal fibroids often lead to heavy menstrual bleeding, menstrual cramps, and fertility issues.
1. Observation and Monitoring: Small uterine
fibroids that are not causing significant symptoms may be monitored without
immediate intervention. Regular check-ups and imaging tests allow doctors to
track the fibroid's growth and assess the need for treatment. 2. Medications: Hormonal medications such as
gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (GnRH agonists) or oral contraceptives
may be prescribed to manage symptoms associated with fibroids, including heavy
bleeding and pain. These medications can help shrink fibroids and provide
symptom relief. 3. Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE): This
minimally invasive procedure involves blocking the blood supply to the
fibroids, causing them to shrink. UAE is performed by an interventional
radiologist and is a viable alternative to surgery for eligible patients. 4. Myomectomy Surgery: Myomectomy is a
surgical procedure aimed at removing fibroids while preserving the uterus. It
is often recommended for women who wish to maintain fertility. Myomectomy can
be performed via traditional open surgery, laparoscopy, or robotic-assisted
techniques. 5. New Treatment Options without surgery:
Recent advancements in the field of fibroid treatment have introduced
non-surgical alternatives. These include focused ultrasound surgery (FUS) and magnetic
resonance-guided focused ultrasound (MRgFUS). These techniques use focused
ultrasound waves to heat and destroy fibroid tissue without incisions or
hospital stays. 6. Hysterectomy: In cases where fibroids cause
severe symptoms or are unresponsive to other treatments, a hysterectomy may be
recommended. This surgical procedure involves the removal of the uterus and is
considered a definitive treatment for fibroids. However, it eliminates the
possibility of future pregnancies.
1. Observation and Monitoring: Small uterine fibroids that are not causing significant symptoms may be monitored without immediate intervention. Regular check-ups and imaging tests allow doctors to track the fibroid's growth and assess the need for treatment.
2. Medications: Hormonal medications such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (GnRH agonists) or oral contraceptives may be prescribed to manage symptoms associated with fibroids, including heavy bleeding and pain. These medications can help shrink fibroids and provide symptom relief.
3. Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE): This minimally invasive procedure involves blocking the blood supply to the fibroids, causing them to shrink. UAE is performed by an interventional radiologist and is a viable alternative to surgery for eligible patients.
4. Myomectomy Surgery: Myomectomy is a surgical procedure aimed at removing fibroids while preserving the uterus. It is often recommended for women who wish to maintain fertility. Myomectomy can be performed via traditional open surgery, laparoscopy, or robotic-assisted techniques.
5. New Treatment Options without surgery: Recent advancements in the field of fibroid treatment have introduced non-surgical alternatives. These include focused ultrasound surgery (FUS) and magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound (MRgFUS). These techniques use focused ultrasound waves to heat and destroy fibroid tissue without incisions or hospital stays.
6. Hysterectomy: In cases where fibroids cause severe symptoms or are unresponsive to other treatments, a hysterectomy may be recommended. This surgical procedure involves the removal of the uterus and is considered a definitive treatment for fibroids. However, it eliminates the possibility of future pregnancies.
The cost of treating uterine fibroids can vary depending on several factors, including the type and size of fibroids, the chosen treatment method, the number of fibroids being treated, the healthcare facility, and the region or city in which the treatment is sought. Here is an approximate cost range for uterine fibroid treatment in various Indian cities:
|
Serial No |
City |
Minimum Cost (INR) |
Average Cost (INR) |
|
1 |
Mumbai |
50,000 |
2,00,000 |
|
2 |
Delhi |
40,000 |
1,80,000 |
|
3 |
Bangalore |
35,000 |
1,60,000 |
|
4 |
Chennai |
30,000 |
1,40,000 |
|
5 |
Kolkata |
30,000 |
1,30,000 |
|
6 |
Hyderabad |
25,000 |
1,20,000 |
|
7 |
Pune |
25,000 |
1,10,000 |
|
8 |
Ahmedabad |
20,000 |
1,00,000 |
|
9 |
Jaipur |
18,000 |
90,000 |
|
10 |
Chandigarh |
15,000 |
80,000 |
|
11 |
Lucknow |
15,000 |
75,000 |
|
12 |
Indore |
12,000 |
70,000 |
|
13 |
Kochi |
12,000 |
65,000 |
|
14 |
Coimbatore |
10,000 |
60,000 |
|
15 |
Bhopal |
10,000 |
55,000 |
|
16 |
Nagpur |
8,000 |
50,000 |
|
17 |
Goa |
8,000 |
45,000 |
|
18 |
Mangalore |
7,000 |
40,000 |
|
19 |
Trivandrum |
7,000 |
40,000 |
|
20 |
Guwahati |
6,000 |
35,000 |
|
Serial No |
Hospital Name |
Address |
Contact Number |
|
1 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) |
Ansari Nagar, Aurobindo Marg, New Delhi - 110029 |
+91-11-26588500 |
|
2 |
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER) |
Sector-12, Chandigarh - 160012 |
+91-172-2747585 |
|
3 |
Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences (SGPGIMS) |
Rae Bareli Road, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226014 |
+91-522-2668700 |
|
4 |
JIPMER (Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research) |
Dhanvantari Nagar, Puducherry - 605006 |
+91-413-2296000 |
|
5 |
Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST) |
Medical College P.O., Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala - 695011 |
+91-471-2524266 |
|
6 |
King George's Medical University (KGMU) |
Chowk, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226003 |
+91-522-2257450 |
|
7 |
Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences (NIMS) |
Punjagutta, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500082 |
+91-40-23489000 |
|
8 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) |
Sector 32, Chandigarh - 160030 |
+91-172-2601023 |
|
9 |
Institute of Medical Sciences (IMS), Banaras Hindu University (BHU) |
Lanka, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh - 221005 |
+91-542-2367568 |
|
10 |
Osmania General Hospital |
Afzal Gunj, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500012 |
+91-40-24600146 |
Please Wait..