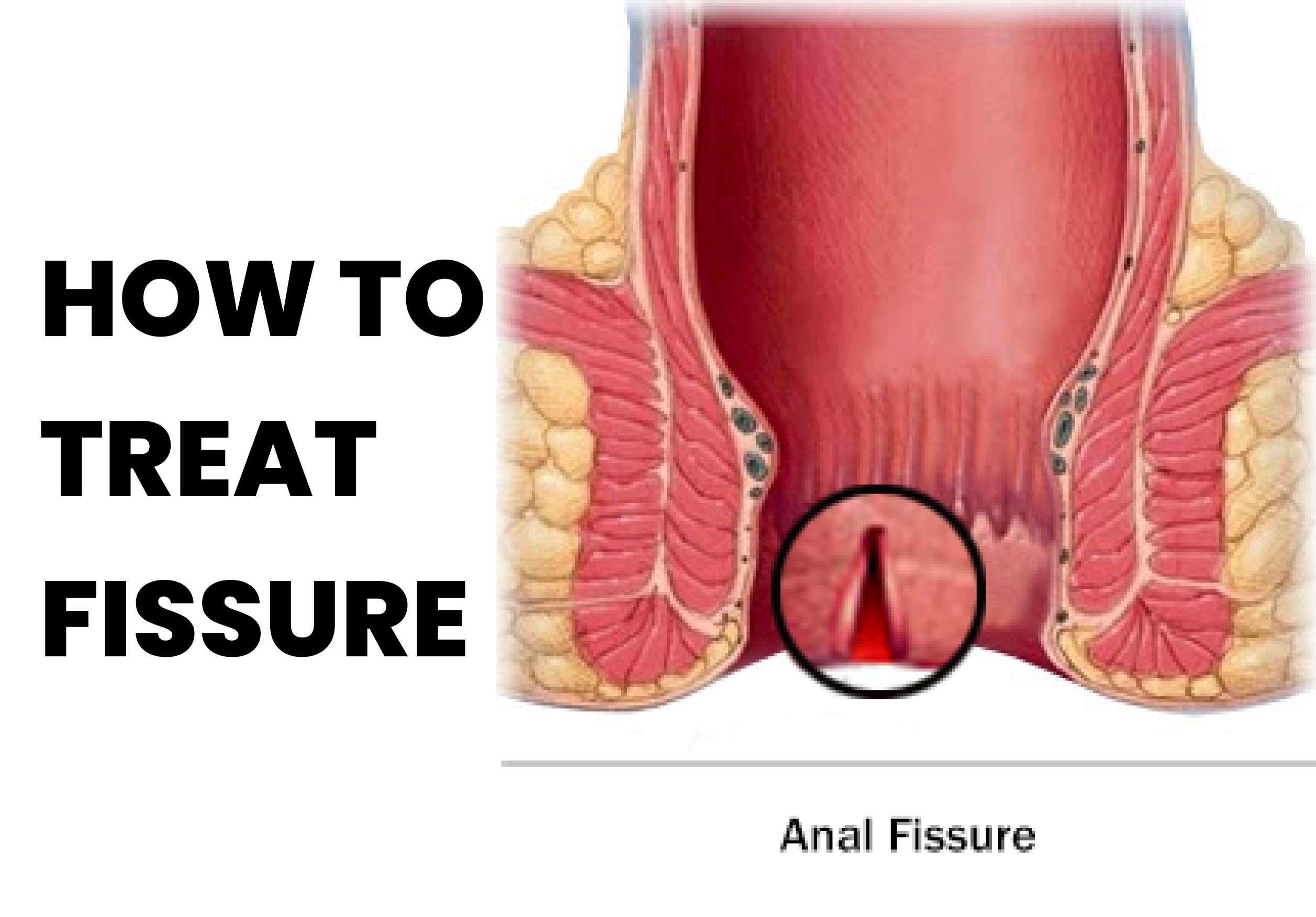
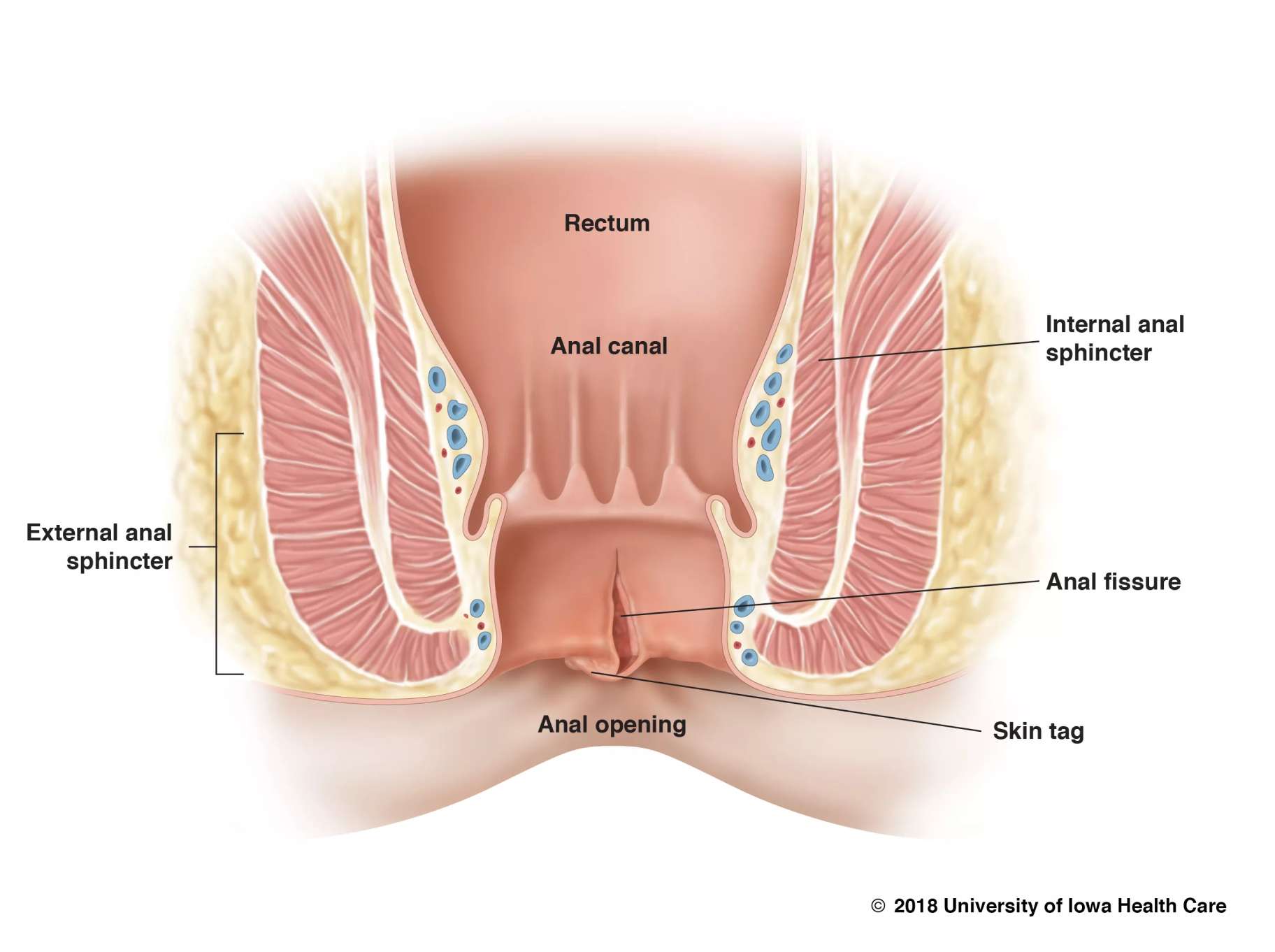
A fissure is a small, narrow crack or groove that can occur in various parts of the body, including the skin, teeth, and anus. Fissures in the anus can be painful and uncomfortable, and if left untreated, they can lead to complications such as infections, bleeding, and even anal abscesses. Fortunately, there are several effective treatments available for fissures, ranging from self-care measures to medical interventions.
Visit www.doctorsapp.in to know more.
The first step in treating a fissure is to keep the affected area clean and dry. This can be achieved by gently washing the area with warm water and mild soap, and then patting it dry with a soft towel. Avoid using harsh soaps or wipes, as they can irritate the skin and make the fissure worse. To relieve pain and discomfort, over-the-counter painkillers can be taken. Topical creams and ointments containing local anesthetics or numbing agents can also be used to provide temporary relief. However, it's important to note that these medications only provide symptomatic relief and do not treat the underlying cause of the fissure. If self-care measures and over-the-counter medications don't provide relief, a doctor may recommend prescription medications or medical procedures. One common medication used to treat fissures is a topical nitroglycerin ointment, which helps relax the muscles around the anus and promote healing. Other medications that may be prescribed include calcium channel blockers, which help relax the sphincter muscle, and botulinum toxin injections, which can help relax the muscle and improve blood flow to the area. In cases where conservative treatments fail, surgery may be necessary. One common surgical procedure used to treat fissures is a lateral internal sphincterotomy, which involves cutting the muscle that surrounds the anus to relieve pressure on the fissure and promote healing. While surgery is generally considered a last resort, it can be highly effective in treating chronic or severe fissures.
The first step in treating a fissure is to keep the affected area clean and dry. This can be achieved by gently washing the area with warm water and mild soap, and then patting it dry with a soft towel. Avoid using harsh soaps or wipes, as they can irritate the skin and make the fissure worse.
To relieve pain and discomfort, over-the-counter painkillers can be taken. Topical creams and ointments containing local anesthetics or numbing agents can also be used to provide temporary relief. However, it's important to note that these medications only provide symptomatic relief and do not treat the underlying cause of the fissure.
If self-care measures and over-the-counter medications don't provide relief, a doctor may recommend prescription medications or medical procedures. One common medication used to treat fissures is a topical nitroglycerin ointment, which helps relax the muscles around the anus and promote healing. Other medications that may be prescribed include calcium channel blockers, which help relax the sphincter muscle, and botulinum toxin injections, which can help relax the muscle and improve blood flow to the area.
In cases where conservative treatments fail, surgery may be necessary. One common surgical procedure used to treat fissures is a lateral internal sphincterotomy, which involves cutting the muscle that surrounds the anus to relieve pressure on the fissure and promote healing. While surgery is generally considered a last resort, it can be highly effective in treating chronic or severe fissures.
Preventing fissures from developing in the first place is the best course of action. This can be achieved by maintaining good hygiene, avoiding constipation by consuming a high-fiber diet and drinking plenty of water, and avoiding straining during bowel movements. It's also important to avoid prolonged sitting or standing, as this can put pressure on the anal area and contribute to the development of fissures.
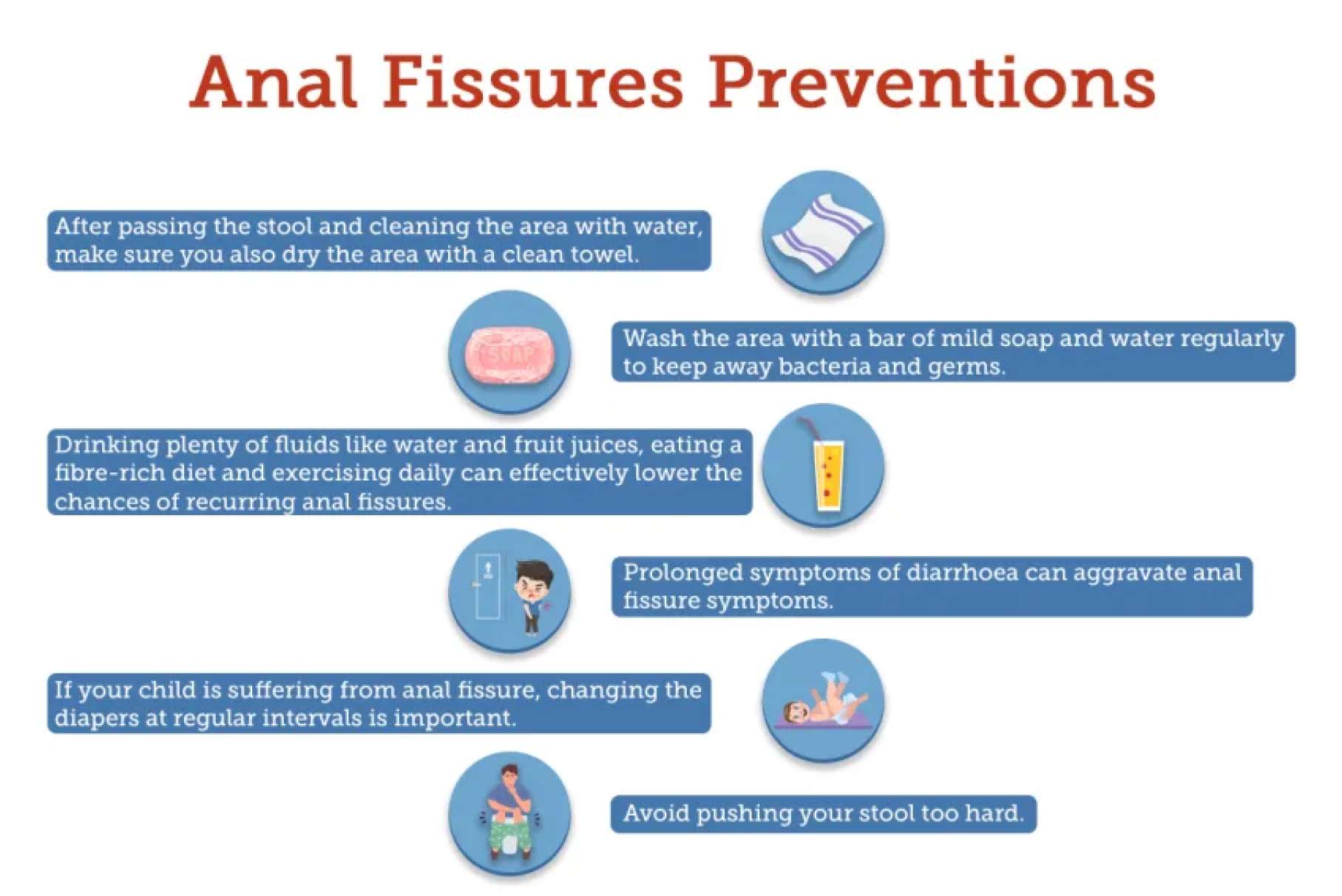
Preventing fissures from developing in the first place is the best course of action. This can be achieved by maintaining good hygiene, avoiding constipation by consuming a high-fiber diet and drinking plenty of water, and avoiding straining during bowel movements. It's also important to avoid prolonged sitting or standing, as this can put pressure on the anal area and contribute to the development of fissures.
Lateral internal sphincterotomy (LIS) surgery: Lateral internal sphincterotomy is a surgical procedure that involves cutting the internal anal sphincter muscle to reduce pressure on the fissure and promote healing. This surgery is typically done under general anesthesia. The procedure is usually effective in relieving pain and promoting healing, but there is a risk of incontinence or leakage of stool after the surgery. Anal dilation surgery: Anal dilation surgery involves widening the anal opening to reduce pressure on the fissure and promote healing. This surgery is typically done under general anesthesia. The procedure is generally safe and effective, but there is a risk of bleeding, infection, or incontinence. Fissurectomy: Fissurectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing the fissure completely. This surgery is typically done under general anesthesia. The procedure is effective in treating chronic or recurrent fissures, but there is a risk of bleeding, infection, or incontinence. Botulinum toxin injection: Botulinum toxin injection involves injecting a small amount of botulinum toxin into the anal sphincter muscle to relax it and reduce pressure on the fissure. This procedure is usually done under local anesthesia and is relatively safe and effective, but there is a risk of temporary incontinence or leakage of stool. Advancement flap surgery: Advancement flap surgery involves using nearby tissue to cover the fissure and promote healing. This surgery is typically done under general anesthesia. The procedure is generally safe and effective, but there is a risk of bleeding, infection, or incontinence. Laser surgery: Laser surgery involves using a laser to remove the fissure and promote healing. This surgery is typically done under local anesthesia and is relatively safe and effective, but there is a risk of bleeding, infection, or incontinence.
Lateral internal sphincterotomy (LIS) surgery:
Lateral internal sphincterotomy is a surgical procedure that involves cutting the internal anal sphincter muscle to reduce pressure on the fissure and promote healing. This surgery is typically done under general anesthesia. The procedure is usually effective in relieving pain and promoting healing, but there is a risk of incontinence or leakage of stool after the surgery.
Anal dilation surgery:
Anal dilation surgery involves widening the anal opening to reduce pressure on the fissure and promote healing. This surgery is typically done under general anesthesia. The procedure is generally safe and effective, but there is a risk of bleeding, infection, or incontinence.
Fissurectomy:
Fissurectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing the fissure completely. This surgery is typically done under general anesthesia. The procedure is effective in treating chronic or recurrent fissures, but there is a risk of bleeding, infection, or incontinence.
Botulinum toxin injection:
Botulinum toxin injection involves injecting a small amount of botulinum toxin into the anal sphincter muscle to relax it and reduce pressure on the fissure. This procedure is usually done under local anesthesia and is relatively safe and effective, but there is a risk of temporary incontinence or leakage of stool.
Advancement flap surgery:
Advancement flap surgery involves using nearby tissue to cover the fissure and promote healing. This surgery is typically done under general anesthesia. The procedure is generally safe and effective, but there is a risk of bleeding, infection, or incontinence.
Laser surgery:
Laser surgery involves using a laser to remove the fissure and promote healing. This surgery is typically done under local anesthesia and is relatively safe and effective, but there is a risk of bleeding, infection, or incontinence.
Visit www.doctorsapp.in to know more.
Before undergoing fissure surgery, there are certain pre-surgical requirements that need to be fulfilled. These requirements may vary depending on the type of surgery and the healthcare provider's instructions. Here are some common pre-surgical requirements for fissure surgery: Medical History: The healthcare provider will take a detailed medical history of the patient, including any past surgeries, current medications, and medical conditions. Physical Examination: A physical examination will be conducted to assess the patient's overall health and to check for any underlying medical conditions. Fasting: The patient may be required to fast for several hours before the surgery, as instructed by the healthcare provider. This is to ensure that the stomach is empty and reduce the risk of complications during the surgery. Bowel Preparation: The patient may be instructed to undergo bowel preparation before the surgery. This involves using laxatives or enemas to empty the bowel and reduce the risk of infection during the surgery. Blood Tests: The patient may be required to undergo blood tests to assess their blood count and to check for any underlying medical conditions. Medication Adjustments: The healthcare provider may advise the patient to stop taking certain medications before the surgery, such as blood thinners or aspirin, to reduce the risk of bleeding during the surgery.

Before undergoing fissure surgery, there are certain pre-surgical requirements that need to be fulfilled. These requirements may vary depending on the type of surgery and the healthcare provider's instructions. Here are some common pre-surgical requirements for fissure surgery:
Medical History: The healthcare provider will take a detailed medical history of the patient, including any past surgeries, current medications, and medical conditions.
Physical Examination: A physical examination will be conducted to assess the patient's overall health and to check for any underlying medical conditions.
Fasting: The patient may be required to fast for several hours before the surgery, as instructed by the healthcare provider. This is to ensure that the stomach is empty and reduce the risk of complications during the surgery.
Bowel Preparation: The patient may be instructed to undergo bowel preparation before the surgery. This involves using laxatives or enemas to empty the bowel and reduce the risk of infection during the surgery.
Blood Tests: The patient may be required to undergo blood tests to assess their blood count and to check for any underlying medical conditions.
Medication Adjustments: The healthcare provider may advise the patient to stop taking certain medications before the surgery, such as blood thinners or aspirin, to reduce the risk of bleeding during the surgery.
The cost of fissure surgery in India can vary depending on several factors, such as the type of surgery, the location of the hospital, the surgeon's fees, and the hospital facilities.
On average, the cost of fissure surgery in India can range from Rs.20,000 to Rs.80,000. Lateral internal sphincterotomy (LIS) surgery is typically more expensive than other types of fissure surgeries.
The cost of fissure surgery may also depend on the hospital's location and the facilities provided. Hospitals in metropolitan cities such as Mumbai, Delhi, or Bangalore may charge more for surgery than hospitals in smaller cities.
It is important to note that health insurance may cover the cost of fissure surgery, depending on the policy's terms and conditions.
Overall, the cost of fissure surgery in India can be relatively affordable compared to other countries.
Visit www.doctorsapp.in to book an appointment today.
Given below are costs of fissure anal surgery, an affordable and cheap fissure surgery option
All prices are in INR
Please Wait..