Adenomyosis is a condition characterized by the presence of endometrial
tissue (the tissue that lines the uterus) within the muscular wall of
the uterus.
Call us to book a appointment with the gynaecology specialist near you.
Adenomyosis is a common yet often misunderstood gynecological condition that affects many women worldwide. It is characterized by the presence of endometrial tissue, which normally lines the inside of the uterus, growing into the muscular wall of the uterus. This condition can cause significant pain and discomfort, as well as other symptoms that can greatly impact a woman's quality of life. In this article, we will explore adenomyosis in detail, including its causes, symptoms, stages, and available treatment options.
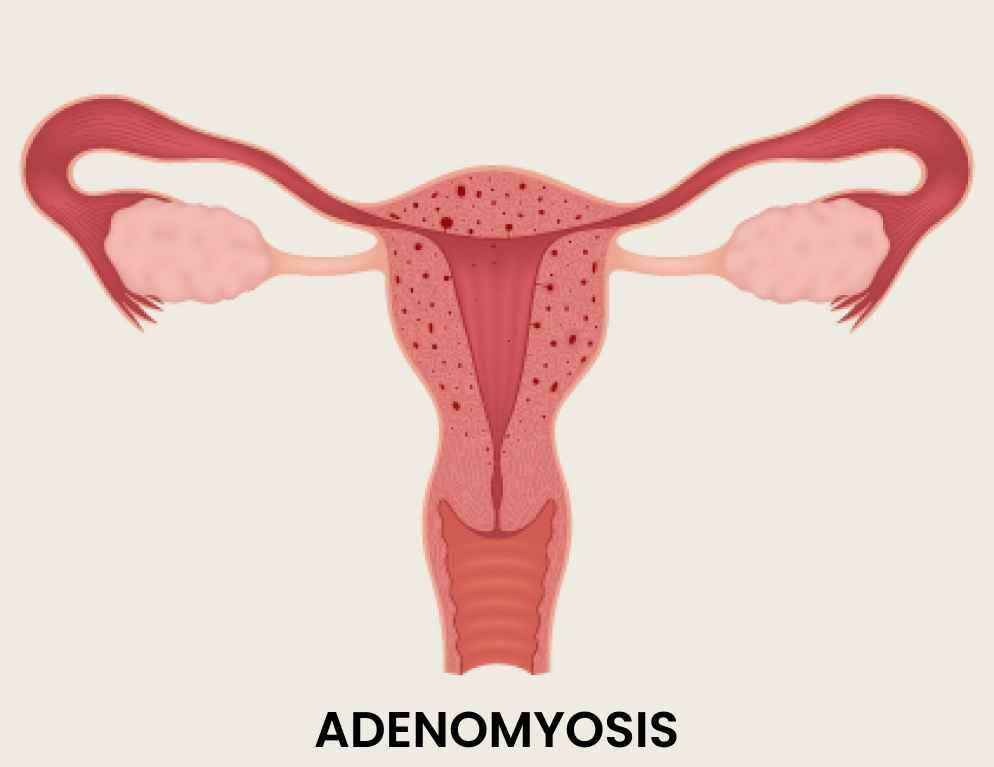
Adenomyosis is a common yet often misunderstood gynecological condition that affects many women worldwide. It is characterized by the presence of endometrial tissue, which normally lines the inside of the uterus, growing into the muscular wall of the uterus. This condition can cause significant pain and discomfort, as well as other symptoms that can greatly impact a woman's quality of life. In this article, we will explore adenomyosis in detail, including its causes, symptoms, stages, and available treatment options.
While the exact cause of adenomyosis remains unclear, several theories have been proposed by medical professionals. One possible cause is the invasion of endometrial cells into the uterine muscle due to trauma during childbirth or a surgical procedure such as a cesarean section. Hormonal imbalances, specifically an excess of estrogen relative to progesterone, have also been suggested as a contributing factor. Additionally, there is evidence to suggest that genetics and hormonal factors play a role in the development of adenomyosis.

While the exact cause of adenomyosis remains unclear, several theories have been proposed by medical professionals. One possible cause is the invasion of endometrial cells into the uterine muscle due to trauma during childbirth or a surgical procedure such as a cesarean section. Hormonal imbalances, specifically an excess of estrogen relative to progesterone, have also been suggested as a contributing factor. Additionally, there is evidence to suggest that genetics and hormonal factors play a role in the development of adenomyosis.
The symptoms of adenomyosis can vary from woman to woman and may range from mild to severe. Some common symptoms include: 1. Menstrual cramps: Women with adenomyosis often experience more intense and prolonged menstrual cramps compared to those without the condition. 2. Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding: Excessive or prolonged bleeding during menstruation is a common symptom of adenomyosis. 3. Pelvic pain: Many women with adenomyosis experience chronic pelvic pain, which may be dull, aching, or sharp in nature. 4. Painful intercourse: Adenomyosis can cause pain during sexual intercourse, known as dyspareunia. 5. Blood clots: Passing blood clots during menstruation is another symptom that may indicate the presence of adenomyosis.
6. Enlarged uterus: Adenomyosis can lead to a bulky uterus, which may be detected during a physical examination or ultrasound.

The symptoms of adenomyosis can vary from woman to woman and may range from mild to severe. Some common symptoms include:
1. Menstrual cramps: Women with adenomyosis often experience more intense and prolonged menstrual cramps compared to those without the condition.
2. Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding: Excessive or prolonged bleeding during menstruation is a common symptom of adenomyosis.
3. Pelvic pain: Many women with adenomyosis experience chronic pelvic pain, which may be dull, aching, or sharp in nature.
4. Painful intercourse: Adenomyosis can cause pain during sexual intercourse, known as dyspareunia.
5. Blood clots: Passing blood clots during menstruation is another symptom that may indicate the presence of adenomyosis.
6. Enlarged uterus: Adenomyosis can lead to a bulky uterus, which may be detected during a physical examination or ultrasound.
Diagnosing adenomyosis typically involves a combination of medical history assessment, pelvic examination, and imaging techniques. Adenomyosis Ultrasound is commonly used to visualize the uterus and identify any abnormalities. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may also be employed to provide more detailed information about the extent and location of adenomyotic lesions.
Adenomyosis is categorized into different stages based on the depth of penetration of the endometrial tissue into the uterine wall. These stages are: 1. Focal Adenomyosis: In this stage, only a small area of the uterus is affected by adenomyosis. 2. Adenomyoma: This stage refers to the formation of a localized adenomyotic mass within the uterine wall. 3. Diffuse Adenomyosis: The entire uterus is affected in this stage, with widespread infiltration of endometrial tissue into the uterine muscle.

Diagnosing adenomyosis typically involves a combination of medical history assessment, pelvic examination, and imaging techniques. Adenomyosis Ultrasound is commonly used to visualize the uterus and identify any abnormalities. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may also be employed to provide more detailed information about the extent and location of adenomyotic lesions. Adenomyosis is categorized into different stages based on the depth of penetration of the endometrial tissue into the uterine wall. These stages are:
1. Focal Adenomyosis: In this stage, only a small area of the uterus is affected by adenomyosis.
2. Adenomyoma: This stage refers to the formation of a localized adenomyotic mass within the uterine wall.
3. Diffuse Adenomyosis: The entire uterus is affected in this stage, with widespread infiltration of endometrial tissue into the uterine muscle.
The treatment approach for adenomyosis depends on the severity of symptoms, a woman's desire for future fertility, and her overall health. Several treatment options are available, including medication, hormonal therapy, and surgery. 1. Adenomyosis Medication: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain and reduce inflammation associated with adenomyosis. Hormonal birth control methods such as oral contraceptives or intrauterine devices (IUDs) may also be prescribed to control heavy bleeding and alleviate symptoms. 2. Adenomyosis Hormonal Treatment: Hormonal therapies that aim to regulate estrogen and progesterone levels can be effective in reducing symptoms. These may include the use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, which induce a temporary menopausal state, or progestin-only therapies. 3. Adenomyosis Surgery: In cases where conservative measures are ineffective or for women who have completed childbearing, surgical intervention may be recommended. Procedures such as endometrial ablation, uterine artery embolization, or even hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be considered.

The treatment approach for adenomyosis depends on the severity of symptoms, a woman's desire for future fertility, and her overall health. Several treatment options are available, including medication, hormonal therapy, and surgery.
1. Adenomyosis Medication: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain and reduce inflammation associated with adenomyosis. Hormonal birth control methods such as oral contraceptives or intrauterine devices (IUDs) may also be prescribed to control heavy bleeding and alleviate symptoms.
2. Adenomyosis Hormonal Treatment: Hormonal therapies that aim to regulate estrogen and progesterone levels can be effective in reducing symptoms. These may include the use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, which induce a temporary menopausal state, or progestin-only therapies.
3. Adenomyosis Surgery: In cases where conservative measures are ineffective or for women who have completed childbearing, surgical intervention may be recommended. Procedures such as endometrial ablation, uterine artery embolization, or even hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be considered.
|
Serial No |
City |
Minimum Cost (INR) |
Average Cost (INR) |
|
1 |
Mumbai |
1,00,000 |
3,50,000 |
|
2 |
Delhi |
80,000 |
3,00,000 |
|
3 |
Bangalore |
70,000 |
2,80,000 |
|
4 |
Chennai |
60,000 |
2,50,000 |
|
5 |
Kolkata |
50,000 |
2,20,000 |
|
6 |
Hyderabad |
50,000 |
2,20,000 |
|
7 |
Pune |
40,000 |
2,00,000 |
|
8 |
Ahmedabad |
35,000 |
1,80,000 |
|
9 |
Jaipur |
35,000 |
1,80,000 |
|
10 |
Chandigarh |
30,000 |
1,60,000 |
|
11 |
Lucknow |
30,000 |
1,60,000 |
|
12 |
Indore |
25,000 |
1,40,000 |
|
13 |
Kochi |
25,000 |
1,40,000 |
|
14 |
Coimbatore |
20,000 |
1,20,000 |
|
15 |
Bhopal |
20,000 |
1,20,000 |
|
16 |
Nagpur |
18,000 |
1,00,000 |
|
17 |
Goa |
18,000 |
1,00,000 |
|
18 |
Mangalore |
15,000 |
80,000 |
|
19 |
Trivandrum |
15,000 |
80,000 |
|
20 |
Guwahati |
12,000 |
70,000 |
|
Serial No |
Hospital Name |
Address |
Contact Number |
|
1 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) |
Ansari Nagar, Aurobindo Marg, New Delhi - 110029 |
+91-11-26588500 |
|
2 |
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER) |
Sector-12, Chandigarh - 160012 |
+91-172-2747585 |
|
3 |
Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences (SGPGIMS) |
Rae Bareli Road, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226014 |
+91-522-2668700 |
|
4 |
JIPMER (Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research) |
Dhanvantari Nagar, Puducherry - 605006 |
+91-413-2296000 |
|
5 |
Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST) |
Medical College P.O., Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala - 695011 |
+91-471-2524266 |
|
6 |
King George's Medical University (KGMU) |
Chowk, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226003 |
+91-522-2257450 |
|
7 |
Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences (NIMS) |
Punjagutta, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500082 |
+91-40-23489000 |
|
8 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) |
Sector 32, Chandigarh - 160030 |
+91-172-2601023 |
|
9 |
Institute of Medical Sciences (IMS), Banaras Hindu University (BHU) |
Lanka, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh - 221005 |
+91-542-2367568 |
|
10 |
Osmania General Hospital |
Afzal Gunj, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500012 |
+91-40-24600146 |
Please Wait..