Bariatric surgery is an operation on the stomach and/or intestines that helps patients with extreme obesity to lose weight. This surgery is an option for people who cannot lose weight by other means or who suffer from serious health problems related to obesity.
Bariatric surgery has emerged as a life-changing option for individuals struggling with obesity and its associated health conditions. This surgical intervention modifies the digestive system, helping patients achieve significant and sustainable weight loss.
1. Duodenal Switch: - Duodenal switch surgery, also known as biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS), is a complex procedure that combines restrictive and malabsorptive techniques. During the surgery, the surgeon removes a significant portion of the stomach and reroutes the small intestine to limit the amount of food absorbed. The duodenal switch offers substantial weight loss results and is particularly effective for individuals with a high body mass index (BMI) or severe obesity. 2. Gastric Band Surgery:- Gastric band surgery, commonly referred to as lap band surgery, involves placing an adjustable band around the upper part of the stomach, creating a small pouch. The band is adjustable and can be tightened or loosened to control food intake. By restricting the amount of food the stomach can hold, gastric band surgery promotes weight loss. This procedure is minimally invasive and reversible, making it a popular choice for individuals seeking a less invasive bariatric option. 3. Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy (VSG):-Vertical sleeve gastrectomy, also known as laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, involves removing a large portion of the stomach, leaving behind a slender, banana-shaped pouch. The reduced stomach size restricts the amount of food that can be consumed and decreases hunger-inducing hormones. VSG is a restrictive procedure that does not involve rerouting or altering the intestines. It offers excellent weight loss results and improves obesity-related comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure. 4. Gastroplasty:- Gastroplasty, also known as stomach stapling, is an older bariatric surgery procedure that is less commonly performed today. During gastroplasty, the surgeon creates a small stomach pouch by stapling a portion of the stomach, similar to gastric band surgery. However, unlike gastric band surgery, gastroplasty is not adjustable. While effective in promoting weight loss, the procedure has a higher risk of complications compared to other bariatric surgeries. 5. Gastric Balloon Surgery:- Gastric balloon surgery involves placing a deflated silicone balloon into the stomach through an endoscopic procedure. Once in place, the balloon is filled with a saline solution to occupy space within the stomach, reducing the capacity for food intake. The gastric balloon is temporary and is typically removed after six months. This procedure is suitable for individuals with a lower BMI who require short-term weight loss assistance. 6. Gastric Mini Bypass:- Gastric mini bypass, also known as mini gastric bypass, is a variation of the traditional gastric bypass surgery. The procedure involves creating a small stomach pouch and rerouting a segment of the small intestine to bypass a significant portion of the digestive system. The gastric mini bypass restricts food intake and reduces nutrient absorption, resulting in weight loss. It is less invasive than the traditional gastric bypass and offers comparable results. 7. Gastric Bypass Surgery:- Gastric bypass surgery, often referred to as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, is one of the most commonly performed bariatric procedures. During the surgery, the surgeon creates a small stomach pouch and reroutes the small intestine to bypass a portion of the digestive system. This procedure combines both restrictive and malabsorptive techniques, leading to substantial weight loss. Gastric bypass surgery has proven to be highly effective in resolving obesity-related comorbidities, such as type 2 diabetes and sleep apnea. 8. Gastric Sleeve Surgery:-Gastric sleeve surgery, also known as sleeve gastrectomy, involves removing a large portion of the stomach, leaving behind a small, sleeve-shaped pouch. The procedure restricts food intake by reducing the stomach's capacity and altering the hunger-regulating hormones. Gastric sleeve surgery has gained popularity due to its excellent weight loss outcomes and lower risk of complications compared to some other procedures. It is often performed as a standalone procedure or as the first step in a staged approach to weight loss surgery.
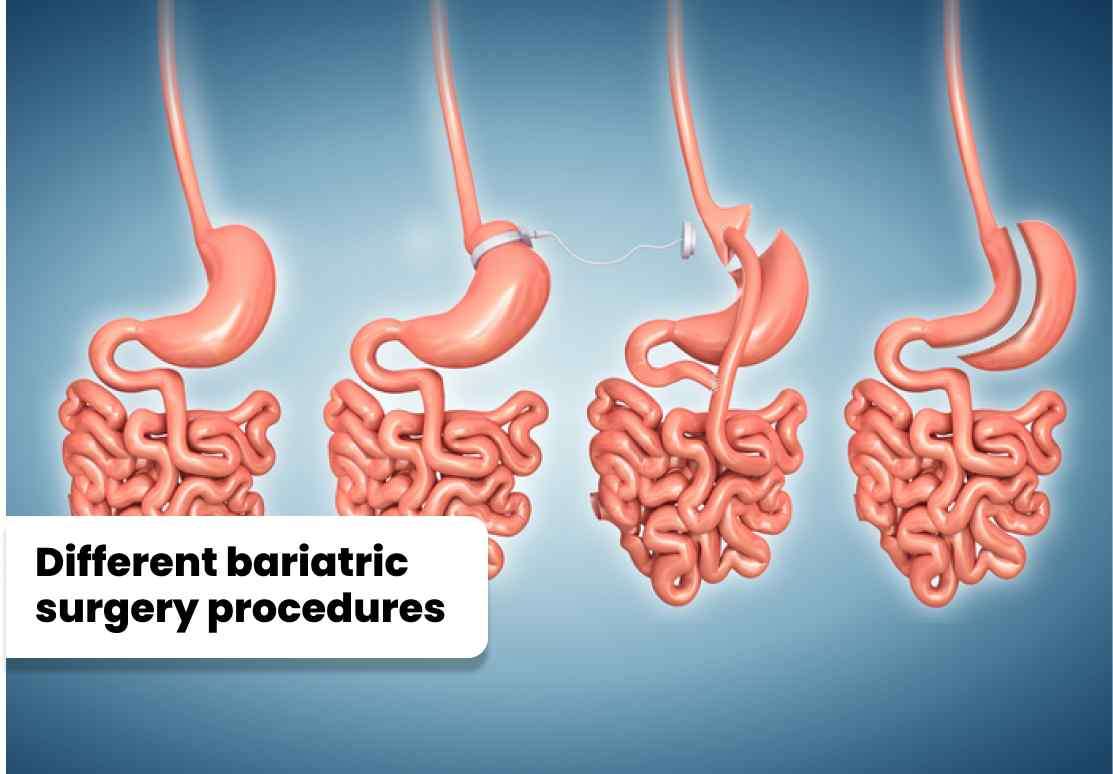
1. Duodenal Switch: - Duodenal switch surgery, also known as biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS), is a complex procedure that combines restrictive and malabsorptive techniques. During the surgery, the surgeon removes a significant portion of the stomach and reroutes the small intestine to limit the amount of food absorbed. The duodenal switch offers substantial weight loss results and is particularly effective for individuals with a high body mass index (BMI) or severe obesity.
2. Gastric Band Surgery:- Gastric band surgery, commonly referred to as lap band surgery, involves placing an adjustable band around the upper part of the stomach, creating a small pouch. The band is adjustable and can be tightened or loosened to control food intake. By restricting the amount of food the stomach can hold, gastric band surgery promotes weight loss. This procedure is minimally invasive and reversible, making it a popular choice for individuals seeking a less invasive bariatric option.
3. Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy (VSG):-Vertical sleeve gastrectomy, also known as laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, involves removing a large portion of the stomach, leaving behind a slender, banana-shaped pouch. The reduced stomach size restricts the amount of food that can be consumed and decreases hunger-inducing hormones. VSG is a restrictive procedure that does not involve rerouting or altering the intestines. It offers excellent weight loss results and improves obesity-related comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure.
4. Gastroplasty:- Gastroplasty, also known as stomach stapling, is an older bariatric surgery procedure that is less commonly performed today. During gastroplasty, the surgeon creates a small stomach pouch by stapling a portion of the stomach, similar to gastric band surgery. However, unlike gastric band surgery, gastroplasty is not adjustable. While effective in promoting weight loss, the procedure has a higher risk of complications compared to other bariatric surgeries.
5. Gastric Balloon Surgery:- Gastric balloon surgery involves placing a deflated silicone balloon into the stomach through an endoscopic procedure. Once in place, the balloon is filled with a saline solution to occupy space within the stomach, reducing the capacity for food intake. The gastric balloon is temporary and is typically removed after six months. This procedure is suitable for individuals with a lower BMI who require short-term weight loss assistance.
6. Gastric Mini Bypass:- Gastric mini bypass, also known as mini gastric bypass, is a variation of the traditional gastric bypass surgery. The procedure involves creating a small stomach pouch and rerouting a segment of the small intestine to bypass a significant portion of the digestive system. The gastric mini bypass restricts food intake and reduces nutrient absorption, resulting in weight loss. It is less invasive than the traditional gastric bypass and offers comparable results.
7. Gastric Bypass Surgery:- Gastric bypass surgery, often referred to as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, is one of the most commonly performed bariatric procedures. During the surgery, the surgeon creates a small stomach pouch and reroutes the small intestine to bypass a portion of the digestive system. This procedure combines both restrictive and malabsorptive techniques, leading to substantial weight loss. Gastric bypass surgery has proven to be highly effective in resolving obesity-related comorbidities, such as type 2 diabetes and sleep apnea.
8. Gastric Sleeve Surgery:-Gastric sleeve surgery, also known as sleeve gastrectomy, involves removing a large portion of the stomach, leaving behind a small, sleeve-shaped pouch. The procedure restricts food intake by reducing the stomach's capacity and altering the hunger-regulating hormones. Gastric sleeve surgery has gained popularity due to its excellent weight loss outcomes and lower risk of complications compared to some other procedures. It is often performed as a standalone procedure or as the first step in a staged approach to weight loss surgery.
1. Surgical Risks: Bariatric surgeries are invasive procedures that carry inherent surgical risks such as bleeding, infection, blood clots, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. These risks are relatively low but can vary depending on the specific procedure and the patient's overall health. 2. Complications: Bariatric surgery can be associated with complications, including leaks from staple lines or sutures, strictures (narrowing) in the gastrointestinal tract, hernias, and bowel obstruction. These complications may require additional procedures to correct and can lead to prolonged hospital stays or further medical intervention. 3. Nutritional Deficiencies: Malabsorptive procedures, such as duodenal switch and gastric bypass, may result in long-term nutritional deficiencies. Reduced absorption of nutrients, particularly vitamins and minerals, can lead to deficiencies in iron, calcium, vitamin B12, and folate. Lifelong monitoring and appropriate supplementation are necessary to prevent deficiencies and maintain optimal health. 4. Dumping Syndrome: Dumping syndrome is a potential complication following gastric bypass surgery. It occurs when food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine, leading to symptoms such as nausea, dizziness, sweating, and diarrhea. Adhering to dietary guidelines and eating small, frequent meals can help manage this condition. 5. Gallstones: Rapid weight loss after bariatric surgery can increase the risk of gallstone formation. Gallstones may require surgical removal if they cause symptoms or complications.

1. Surgical Risks: Bariatric surgeries are invasive procedures that carry inherent surgical risks such as bleeding, infection, blood clots, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. These risks are relatively low but can vary depending on the specific procedure and the patient's overall health.
2. Complications: Bariatric surgery can be associated with complications, including leaks from staple lines or sutures, strictures (narrowing) in the gastrointestinal tract, hernias, and bowel obstruction. These complications may require additional procedures to correct and can lead to prolonged hospital stays or further medical intervention.
3. Nutritional Deficiencies: Malabsorptive procedures, such as duodenal switch and gastric bypass, may result in long-term nutritional deficiencies. Reduced absorption of nutrients, particularly vitamins and minerals, can lead to deficiencies in iron, calcium, vitamin B12, and folate. Lifelong monitoring and appropriate supplementation are necessary to prevent deficiencies and maintain optimal health.
4. Dumping Syndrome: Dumping syndrome is a potential complication following gastric bypass surgery. It occurs when food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine, leading to symptoms such as nausea, dizziness, sweating, and diarrhea. Adhering to dietary guidelines and eating small, frequent meals can help manage this condition.
5. Gallstones: Rapid weight loss after bariatric surgery can increase the risk of gallstone formation. Gallstones may require surgical removal if they cause symptoms or complications.
1. Surgical Risks: Bariatric surgeries are invasive procedures that carry inherent surgical risks such as bleeding, infection, blood clots, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. These risks are relatively low but can vary depending on the specific procedure and the patient's overall health. 2. Complications: Bariatric surgery can be associated with complications, including leaks from staple lines or sutures, strictures (narrowing) in the gastrointestinal tract, hernias, and bowel obstruction. These complications may require additional procedures to correct and can lead to prolonged hospital stays or further medical intervention. 3. Nutritional Deficiencies: Malabsorptive procedures, such as duodenal switch and gastric bypass, may result in long-term nutritional deficiencies. Reduced absorption of nutrients, particularly vitamins and minerals, can lead to deficiencies in iron, calcium, vitamin B12, and folate. Lifelong monitoring and appropriate supplementation are necessary to prevent deficiencies and maintain optimal health. 4. Dumping Syndrome: Dumping syndrome is a potential complication following gastric bypass surgery. It occurs when food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine, leading to symptoms such as nausea, dizziness, sweating, and diarrhea. Adhering to dietary guidelines and eating small, frequent meals can help manage this condition. 5. Gallstones: Rapid weight loss after bariatric surgery can increase the risk of gallstone formation. Gallstones may require surgical removal if they cause symptoms or complications.

1. Surgical Risks: Bariatric surgeries are invasive procedures that carry inherent surgical risks such as bleeding, infection, blood clots, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. These risks are relatively low but can vary depending on the specific procedure and the patient's overall health.
2. Complications: Bariatric surgery can be associated with complications, including leaks from staple lines or sutures, strictures (narrowing) in the gastrointestinal tract, hernias, and bowel obstruction. These complications may require additional procedures to correct and can lead to prolonged hospital stays or further medical intervention.
3. Nutritional Deficiencies: Malabsorptive procedures, such as duodenal switch and gastric bypass, may result in long-term nutritional deficiencies. Reduced absorption of nutrients, particularly vitamins and minerals, can lead to deficiencies in iron, calcium, vitamin B12, and folate. Lifelong monitoring and appropriate supplementation are necessary to prevent deficiencies and maintain optimal health.
4. Dumping Syndrome: Dumping syndrome is a potential complication following gastric bypass surgery. It occurs when food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine, leading to symptoms such as nausea, dizziness, sweating, and diarrhea. Adhering to dietary guidelines and eating small, frequent meals can help manage this condition.
5. Gallstones: Rapid weight loss after bariatric surgery can increase the risk of gallstone formation. Gallstones may require surgical removal if they cause symptoms or complications.
1. Significant and Sustained Weight Loss: Bariatric surgery is the most effective treatment option for achieving substantial and sustained weight loss in individuals with severe obesity. Procedures like gastric bypass, duodenal switch, and vertical sleeve gastrectomy can result in significant weight loss, leading to improvements in obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea. 2. Resolution of Obesity-Related Comorbidities: Bariatric surgery has been shown to improve or resolve various obesity-related health conditions. Many individuals experience remission of type 2 diabetes, reduced blood pressure, improved cholesterol levels, and relief from sleep apnea after undergoing bariatric surgery. 3. Enhanced Quality of Life: Weight loss achieved through bariatric surgery often leads to an improved quality of life. Patients experience increased mobility, reduced joint pain, enhanced self-esteem, improved body image, and better overall psychological well-being. 4. Long-Term Maintenance of Weight Loss: Bariatric surgery offers a higher likelihood of long-term weight loss maintenance compared to non-surgical interventions. It helps individuals adopt healthier eating habits and lifestyles, leading to sustainable weight management. 5. Potential Reduction in Mortality: Bariatric surgery has been associated with a reduced risk of mortality in severely obese individuals, particularly in those with obesity-related health conditions. Studies have shown that bariatric surgery can significantly decrease the risk of premature death.

1. Significant and Sustained Weight Loss: Bariatric surgery is the most effective treatment option for achieving substantial and sustained weight loss in individuals with severe obesity. Procedures like gastric bypass, duodenal switch, and vertical sleeve gastrectomy can result in significant weight loss, leading to improvements in obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea.
2. Resolution of Obesity-Related Comorbidities: Bariatric surgery has been shown to improve or resolve various obesity-related health conditions. Many individuals experience remission of type 2 diabetes, reduced blood pressure, improved cholesterol levels, and relief from sleep apnea after undergoing bariatric surgery.
3. Enhanced Quality of Life: Weight loss achieved through bariatric surgery often leads to an improved quality of life. Patients experience increased mobility, reduced joint pain, enhanced self-esteem, improved body image, and better overall psychological well-being.
4. Long-Term Maintenance of Weight Loss: Bariatric surgery offers a higher likelihood of long-term weight loss maintenance compared to non-surgical interventions. It helps individuals adopt healthier eating habits and lifestyles, leading to sustainable weight management.
5. Potential Reduction in Mortality: Bariatric surgery has been associated with a reduced risk of mortality in severely obese individuals, particularly in those with obesity-related health conditions. Studies have shown that bariatric surgery can significantly decrease the risk of premature death.
1. Surgical Risks: Bariatric surgeries are invasive procedures that carry inherent surgical risks such as bleeding, infection, blood clots, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. These risks are relatively low but can vary depending on the specific procedure and the patient's overall health. 2. Complications: Bariatric surgery can be associated with complications, including leaks from staple lines or sutures, strictures (narrowing) in the gastrointestinal tract, hernias, and bowel obstruction. These complications may require additional procedures to correct and can lead to prolonged hospital stays or further medical intervention. 3. Nutritional Deficiencies: Malabsorptive procedures, such as duodenal switch and gastric bypass, may result in long-term nutritional deficiencies. Reduced absorption of nutrients, particularly vitamins and minerals, can lead to deficiencies in iron, calcium, vitamin B12, and folate. Lifelong monitoring and appropriate supplementation are necessary to prevent deficiencies and maintain optimal health. 4. Dumping Syndrome: Dumping syndrome is a potential complication following gastric bypass surgery. It occurs when food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine, leading to symptoms such as nausea, dizziness, sweating, and diarrhea. Adhering to dietary guidelines and eating small, frequent meals can help manage this condition. 5. Gallstones: Rapid weight loss after bariatric surgery can increase the risk of gallstone formation. Gallstones may require surgical removal if they cause symptoms or complications.

1. Surgical Risks: Bariatric surgeries are invasive procedures that carry inherent surgical risks such as bleeding, infection, blood clots, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. These risks are relatively low but can vary depending on the specific procedure and the patient's overall health. 2. Complications: Bariatric surgery can be associated with complications, including leaks from staple lines or sutures, strictures (narrowing) in the gastrointestinal tract, hernias, and bowel obstruction. These complications may require additional procedures to correct and can lead to prolonged hospital stays or further medical intervention. 3. Nutritional Deficiencies: Malabsorptive procedures, such as duodenal switch and gastric bypass, may result in long-term nutritional deficiencies. Reduced absorption of nutrients, particularly vitamins and minerals, can lead to deficiencies in iron, calcium, vitamin B12, and folate. Lifelong monitoring and appropriate supplementation are necessary to prevent deficiencies and maintain optimal health. 4. Dumping Syndrome: Dumping syndrome is a potential complication following gastric bypass surgery. It occurs when food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine, leading to symptoms such as nausea, dizziness, sweating, and diarrhea. Adhering to dietary guidelines and eating small, frequent meals can help manage this condition. 5. Gallstones: Rapid weight loss after bariatric surgery can increase the risk of gallstone formation. Gallstones may require surgical removal if they cause symptoms or complications.
1. Surgical Risks: Bariatric surgeries are invasive procedures that carry inherent surgical risks such as bleeding, infection, blood clots, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. These risks are relatively low but can vary depending on the specific procedure and the patient's overall health. 2. Complications: Bariatric surgery can be associated with complications, including leaks from staple lines or sutures, strictures (narrowing) in the gastrointestinal tract, hernias, and bowel obstruction. These complications may require additional procedures to correct and can lead to prolonged hospital stays or further medical intervention. 3. Nutritional Deficiencies: Malabsorptive procedures, such as duodenal switch and gastric bypass, may result in long-term nutritional deficiencies. Reduced absorption of nutrients, particularly vitamins and minerals, can lead to deficiencies in iron, calcium, vitamin B12, and folate. Lifelong monitoring and appropriate supplementation are necessary to prevent deficiencies and maintain optimal health. 4. Dumping Syndrome: Dumping syndrome is a potential complication following gastric bypass surgery. It occurs when food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine, leading to symptoms such as nausea, dizziness, sweating, and diarrhea. Adhering to dietary guidelines and eating small, frequent meals can help manage this condition. 5. Gallstones: Rapid weight loss after bariatric surgery can increase the risk of gallstone formation. Gallstones may require surgical removal if they cause symptoms or complications.

1. Surgical Risks: Bariatric surgeries are invasive procedures that carry inherent surgical risks such as bleeding, infection, blood clots, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. These risks are relatively low but can vary depending on the specific procedure and the patient's overall health. 2. Complications: Bariatric surgery can be associated with complications, including leaks from staple lines or sutures, strictures (narrowing) in the gastrointestinal tract, hernias, and bowel obstruction. These complications may require additional procedures to correct and can lead to prolonged hospital stays or further medical intervention. 3. Nutritional Deficiencies: Malabsorptive procedures, such as duodenal switch and gastric bypass, may result in long-term nutritional deficiencies. Reduced absorption of nutrients, particularly vitamins and minerals, can lead to deficiencies in iron, calcium, vitamin B12, and folate. Lifelong monitoring and appropriate supplementation are necessary to prevent deficiencies and maintain optimal health. 4. Dumping Syndrome: Dumping syndrome is a potential complication following gastric bypass surgery. It occurs when food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine, leading to symptoms such as nausea, dizziness, sweating, and diarrhea. Adhering to dietary guidelines and eating small, frequent meals can help manage this condition. 5. Gallstones: Rapid weight loss after bariatric surgery can increase the risk of gallstone formation. Gallstones may require surgical removal if they cause symptoms or complications.
Hospital Name | Address | Contact Number |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) | Ansari Nagar, Aurobindo Marg, New Delhi - 110029 | +91-11-26588500 |
Safdarjung Hospital | Safdarjung Campus, Ansari Nagar, New Delhi - 110029 | +91-11-26165060 |
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER) | Sector-12, Chandigarh - 160012 | +91-172-2747585 |
King George's Medical University (KGMU) | Chowk, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226003 | +91-522-2257450 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) | Saket Nagar, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh - 462020 | +91-755-2672355 |
Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences (NIMS) | Punjagutta, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500082 | +91-40-23489000 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) | Sector 32, Chandigarh - 160030 | +91-172-2601023 |
Institute of Medical Sciences (IMS), Banaras Hindu University (BHU) | Lanka, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh - 221005 | +91-542-2367568 |
Osmania General Hospital | Afzal Gunj, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500012 | +91-40-24600146 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) | Sector 32, Chandigarh - 160030 | +91-172-2601023 |
Please Wait..