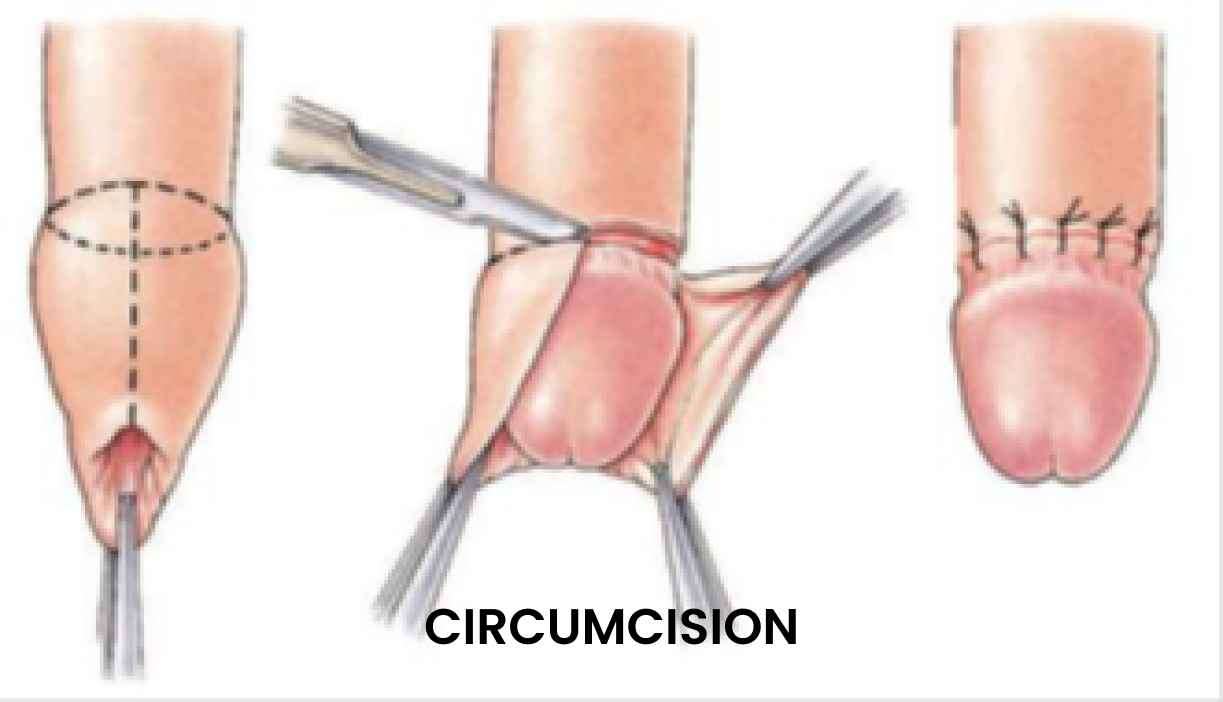
Circumcision is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the
foreskin, the fold of skin covering the head of the penis.
Call us to book an appointment with the best Urology specialist near you.
2. Reduced Urinary
Tract Infections (UTIs): Studies have indicated that circumcision in infancy
may reduce the risk of UTIs, particularly during the first year of life.
However, it's worth noting that the overall risk reduction is modest, and UTIs
can still occur in circumcised individuals. 3. Lower Risk of
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Research suggests that circumcision may
provide some protection against certain STIs, such as HIV/AIDS, herpes, and
HPV. However, it is important to note that circumcision alone is not a
foolproof method of prevention, and safe sexual practices, including condom
use, remain essential. 4. Decreased Risk
of Penile Cancer: Circumcision has been associated with a reduced risk of
penile cancer, a relatively rare form of cancer. However, the overall incidence
of penile cancer is low, and other risk factors, such as smoking and poor
hygiene, play significant roles.
5. Prevention of Phimosis and Balanitis: Circumcision
can help prevent conditions like phimosis (tight foreskin that cannot be
retracted) and balanitis (inflammation of the foreskin or head of the penis).
In cases where these conditions cause recurrent problems or discomfort,
circumcision may be recommended as a therapeutic option.

2. Reduced Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Studies have indicated that circumcision in infancy may reduce the risk of UTIs, particularly during the first year of life. However, it's worth noting that the overall risk reduction is modest, and UTIs can still occur in circumcised individuals.
3. Lower Risk of Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Research suggests that circumcision may provide some protection against certain STIs, such as HIV/AIDS, herpes, and HPV. However, it is important to note that circumcision alone is not a foolproof method of prevention, and safe sexual practices, including condom use, remain essential.
4. Decreased Risk of Penile Cancer: Circumcision has been associated with a reduced risk of penile cancer, a relatively rare form of cancer. However, the overall incidence of penile cancer is low, and other risk factors, such as smoking and poor hygiene, play significant roles.
5. Prevention of Phimosis and Balanitis: Circumcision
can help prevent conditions like phimosis (tight foreskin that cannot be
retracted) and balanitis (inflammation of the foreskin or head of the penis).
In cases where these conditions cause recurrent problems or discomfort,
circumcision may be recommended as a therapeutic option.
2. Pain and
Psychological Factors: Circumcision can cause discomfort and pain, particularly
during infancy. Adequate pain management techniques, such as local anesthesia,
are crucial to minimize discomfort. It is also important to consider the
potential psychological impact on individuals who undergo circumcision without
their consent, emphasizing the need for sensitivity and informed
decision-making.
3. Personal
Autonomy: The ethical debate surrounding circumcision centers on the concept of
personal autonomy and the right to make decisions about one's own body. Critics
argue that performing circumcision on infants or young children raises concerns
about consent and the potential violation of bodily integrity. 4. Cultural and
Religious Considerations: The cultural and religious significance of
circumcision cannot be overlooked. For some communities, circumcision is deeply
embedded in their traditions and religious practices. Respecting cultural
diversity and religious freedoms while also prioritizing individual rights is a
complex balance that needs to be addressed.

2. Pain and Psychological Factors: Circumcision can cause discomfort and pain, particularly during infancy. Adequate pain management techniques, such as local anesthesia, are crucial to minimize discomfort. It is also important to consider the potential psychological impact on individuals who undergo circumcision without their consent, emphasizing the need for sensitivity and informed decision-making.
3. Personal Autonomy: The ethical debate surrounding circumcision centers on the concept of personal autonomy and the right to make decisions about one's own body. Critics argue that performing circumcision on infants or young children raises concerns about consent and the potential violation of bodily integrity.
4. Cultural and Religious Considerations: The cultural and religious significance of circumcision cannot be overlooked. For some communities, circumcision is deeply embedded in their traditions and religious practices. Respecting cultural diversity and religious freedoms while also prioritizing individual rights is a complex balance that needs to be addressed.
2. Anesthesia: The
circumcision procedure can be performed using various anesthesia options,
including local anesthesia, general anesthesia, or a combination of both. Local
anesthesia involves injecting numbing medication into the base of the penis to
minimize discomfort during the surgery. General anesthesia may be used for
older children or adults who require deeper sedation.
3. Techniques:
There are different techniques employed for circumcision: a. Gomco Clamp: This technique involves
using a Gomco clamp to secure the foreskin and then removing the excess tissue
with a scalpel or scissors. b. Plastibell Technique: A plastic ring
called a Plastibell is placed over the head of the penis. The foreskin is then
trimmed, and the Plastibell stays in place for several days until it falls off
naturally. c. Mogen Clamp: The Mogen clamp is a
specialized clamp used to secure the foreskin, which is then removed with a
scalpel or scissors. d. ShangRing: The ShangRing is a newer
device that clamps the foreskin, allowing for its removal without the need for
sutures. This method is often associated with shorter procedure times and
reduced bleeding.
4. Surgical
Procedure: Once the anesthesia has taken effect, the circumcision procedure
begins. The surgeon carefully removes the foreskin by following the chosen
technique. Depending on the method used, sutures may be placed to close the
incision or secure the remaining tissue.
2. Anesthesia: The circumcision procedure can be performed using various anesthesia options, including local anesthesia, general anesthesia, or a combination of both. Local anesthesia involves injecting numbing medication into the base of the penis to minimize discomfort during the surgery. General anesthesia may be used for older children or adults who require deeper sedation.
3. Techniques:
There are different techniques employed for circumcision:
a. Gomco Clamp: This technique involves
using a Gomco clamp to secure the foreskin and then removing the excess tissue
with a scalpel or scissors.
b. Plastibell Technique: A plastic ring
called a Plastibell is placed over the head of the penis. The foreskin is then
trimmed, and the Plastibell stays in place for several days until it falls off
naturally.
c. Mogen Clamp: The Mogen clamp is a
specialized clamp used to secure the foreskin, which is then removed with a
scalpel or scissors.
d. ShangRing: The ShangRing is a newer device that clamps the foreskin, allowing for its removal without the need for sutures. This method is often associated with shorter procedure times and reduced bleeding.
4. Surgical Procedure: Once the anesthesia has taken effect, the circumcision procedure begins. The surgeon carefully removes the foreskin by following the chosen technique. Depending on the method used, sutures may be placed to close the incision or secure the remaining tissue.
1. Bleeding: Some
bleeding is common immediately after the procedure. However, excessive bleeding
may occur in rare cases and require medical attention. 2. Infection:
Infection can occur at the surgical site if proper hygiene practices are not
followed. It is important to keep the area clean and follow the healthcare
provider's instructions for dressing changes and care. 3. Pain and
Discomfort: The surgical site may be tender and uncomfortable during the
healing process. Adequate pain management, such as over-the-counter pain
relievers or prescribed medication, can help alleviate discomfort. 4. Scarring and
Adhesions: In some cases, scarring or adhesions may develop, causing the
remaining foreskin to adhere to the head of the penis. These complications can
usually be resolved with proper care or additional treatment.

1. Bleeding: Some bleeding is common immediately after the procedure. However, excessive bleeding may occur in rare cases and require medical attention.
2. Infection: Infection can occur at the surgical site if proper hygiene practices are not followed. It is important to keep the area clean and follow the healthcare provider's instructions for dressing changes and care.
3. Pain and Discomfort: The surgical site may be tender and uncomfortable during the healing process. Adequate pain management, such as over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medication, can help alleviate discomfort.
4. Scarring and Adhesions: In some cases, scarring or adhesions may develop, causing the remaining foreskin to adhere to the head of the penis. These complications can usually be resolved with proper care or additional treatment.
1. Dressing and
Wound Care: The healthcare provider will provide instructions on how to clean
and care for the surgical site. This typically involves keeping the area clean,
applying petroleum jelly or prescribed ointments to promote healing, and
avoiding activities that may cause irritation or trauma to the area. 2. Pain Management:
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, may be
recommended to manage any post-operative discomfort. However, it is important
to follow the healthcare provider's guidance and avoid certain medications,
such as aspirin, which can increase the risk of bleeding. 3. Follow-up Visits: A follow-up appointment will be
scheduled to monitor the healing progress and address any concerns or
complications that may arise. It is important to attend these appointments and
communicate any changes or issues experienced during the recovery period.

1. Dressing and Wound Care: The healthcare provider will provide instructions on how to clean and care for the surgical site. This typically involves keeping the area clean, applying petroleum jelly or prescribed ointments to promote healing, and avoiding activities that may cause irritation or trauma to the area.
2. Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, may be recommended to manage any post-operative discomfort. However, it is important to follow the healthcare provider's guidance and avoid certain medications, such as aspirin, which can increase the risk of bleeding.
3. Follow-up Visits: A follow-up appointment will be scheduled to monitor the healing progress and address any concerns or complications that may arise. It is important to attend these appointments and communicate any changes or issues experienced during the recovery period.
|
Serial No |
City |
Minimum Cost (INR) |
Average Cost (INR) |
|
1 |
Mumbai |
5,000 |
10,000 |
|
2 |
Delhi |
4,000 |
8,000 |
|
3 |
Bangalore |
3,500 |
7,000 |
|
4 |
Chennai |
3,500 |
7,000 |
|
5 |
Kolkata |
3,000 |
6,000 |
|
6 |
Hyderabad |
3,000 |
6,000 |
|
7 |
Pune |
3,000 |
6,000 |
|
8 |
Ahmedabad |
2,500 |
5,000 |
|
9 |
Jaipur |
2,500 |
5,000 |
|
10 |
Chandigarh |
2,000 |
4,000 |
|
11 |
Lucknow |
2,000 |
4,000 |
|
12 |
Indore |
2,000 |
4,000 |
|
13 |
Kochi |
2,000 |
4,000 |
|
14 |
Coimbatore |
1,500 |
3,000 |
|
15 |
Bhopal |
1,500 |
3,000 |
|
16 |
Nagpur |
1,500 |
3,000 |
|
17 |
Goa |
1,500 |
3,000 |
|
18 |
Mangalore |
1,000 |
2,500 |
|
19 |
Trivandrum |
1,000 |
2,500 |
|
20 |
Guwahati |
1,000 |
2,000 |
Please note that these costs are approximate and can vary depending on factors such as the age of the patient, the type of circumcision (conventional, laser, or plastibell), the location and reputation of the clinic or hospital, and any additional charges for anesthesia or post-operative care.
|
Serial No |
Hospital Name |
Address |
Contact Number |
|
1 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) |
Ansari Nagar, Aurobindo Marg, New Delhi - 110029 |
+91-11-26588500 |
|
2 |
Safdarjung Hospital |
Safdarjung Campus, Ansari Nagar, New Delhi - 110029 |
+91-11-26165060 |
|
3 |
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER) |
Sector-12, Chandigarh - 160012 |
+91-172-2747585 |
|
4 |
King George's Medical University (KGMU) |
Chowk, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226003 |
+91-522-2257450 |
|
5 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) |
Saket Nagar, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh - 462020 |
+91-755-2672355 |
|
6 |
Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences (NIMS) |
Punjagutta, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500082 |
+91-40-23489000 |
|
7 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) |
Sector 32, Chandigarh - 160030 |
+=91-172-2601023 |
|
8 |
Institute of Medical Sciences (IMS), Banaras Hindu University (BHU) |
Lanka, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh - 221005 |
+91-542-2367568 |
|
9 |
Osmania General Hospital |
Afzal Gunj, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500012 |
+91-40-24600146 |
|
10 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) |
Sector 32, Chandigarh - 160030 |
+91-172-2601023 |
Please Wait..