The intragastric balloon, or "weight loss balloon," is a simple, endoscopic procedure that kick-starts weight loss by inserting a soft, yet durable balloon comfortably into your stomach. By taking up space in the stomach, the weight loss balloon gives you the sensation of being full, reducing the desire to eat.
An intragastric balloon, as the name suggests, is a medical device designed to be inserted into the stomach. It is a temporary measure, typically utilized for a duration of six months. The balloon is made of a soft, expandable material that is filled with either saline solution or air. Once placed in the stomach, the balloon takes up space, creating a sensation of fullness, thereby reducing the amount of food that can be consumed.
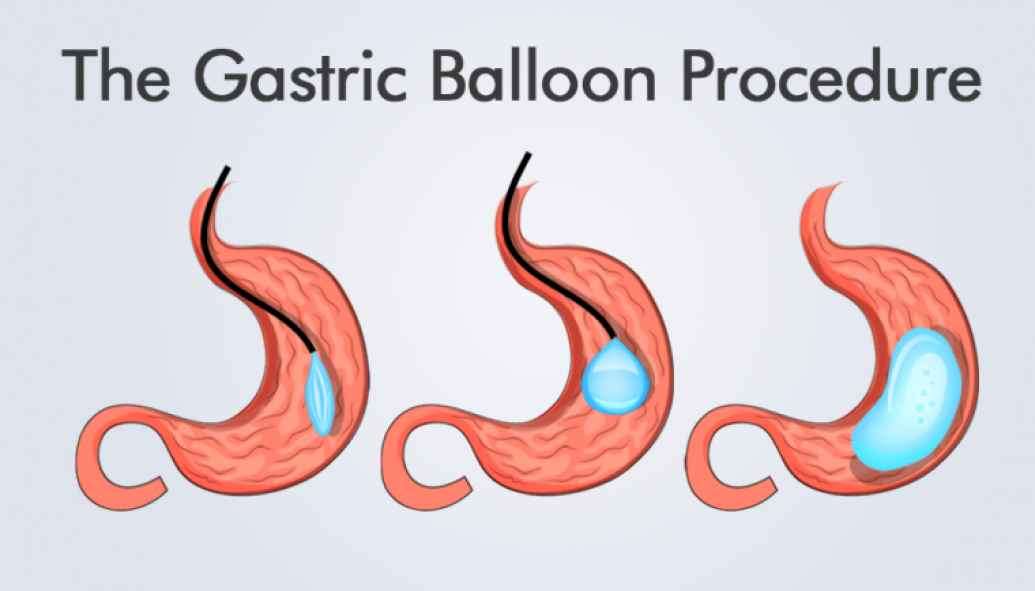
The procedure for placing an intragastric balloon is minimally invasive and does not require any incisions. It is performed endoscopically, where a thin tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth and into the stomach. Once the balloon is in position, it is filled with the desired fluid or air, after which the tube is removed. The entire process typically takes around 20 to 30 minutes and is conducted under light sedation.

The procedure for placing an intragastric balloon is minimally invasive and does not require any incisions. It is performed endoscopically, where a thin tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth and into the stomach. Once the balloon is in position, it is filled with the desired fluid or air, after which the tube is removed. The entire process typically takes around 20 to 30 minutes and is conducted under light sedation.
The primary mechanism of action of an intragastric balloon revolves around two key factors: reduced stomach capacity and delayed gastric emptying. By occupying a significant portion of the stomach, the balloon creates a feeling of fullness, allowing individuals to consume smaller portions of food. Additionally, it slows down the emptying of the stomach, leading to prolonged digestion and increased satiety.
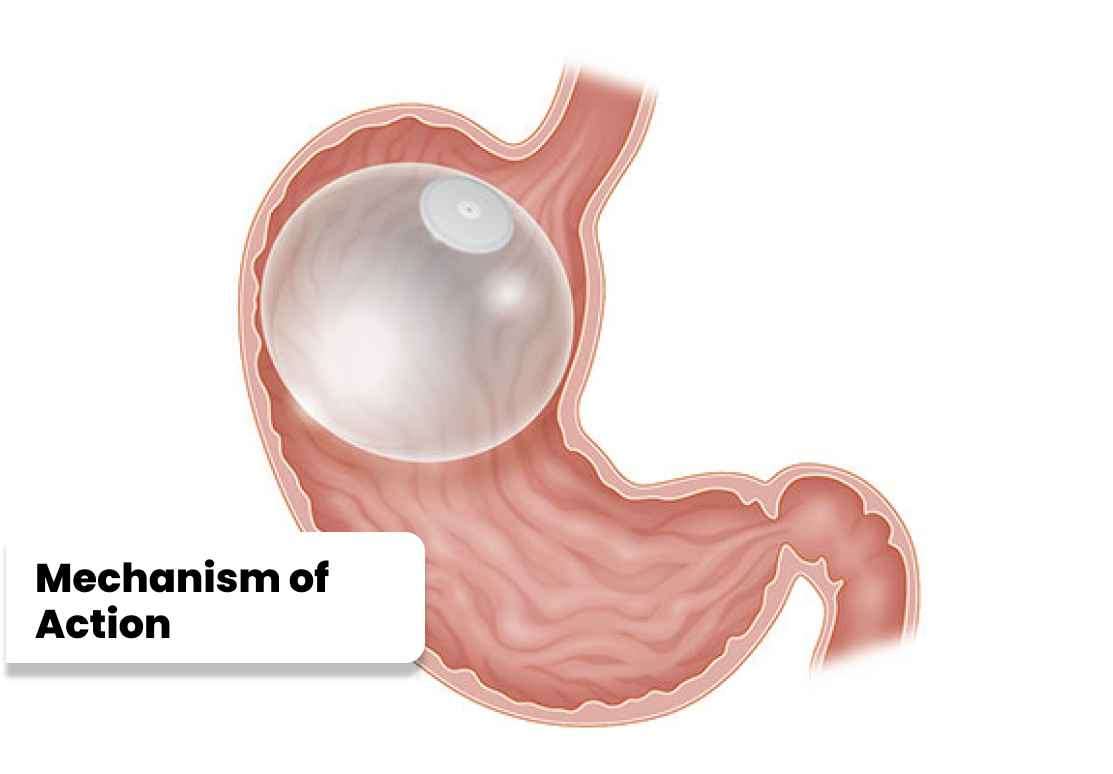
The primary mechanism of action of an intragastric balloon revolves around two key factors: reduced stomach capacity and delayed gastric emptying. By occupying a significant portion of the stomach, the balloon creates a feeling of fullness, allowing individuals to consume smaller portions of food. Additionally, it slows down the emptying of the stomach, leading to prolonged digestion and increased satiety.
The intragastric balloon offers several advantages for individuals struggling with weight loss. Firstly, it is a reversible procedure, and the balloon can be easily removed once the desired weight loss has been achieved. This aspect provides flexibility and eliminates the concerns associated with irreversible surgical interventions. Furthermore, studies have shown that the intragastric balloon can lead to significant weight loss, typically ranging from 10% to 15% of the total body weight. However, it is important to note that the degree of weight loss varies among individuals, and the success of the procedure also depends on the commitment to adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise.

The intragastric balloon offers several advantages for individuals struggling with weight loss. Firstly, it is a reversible procedure, and the balloon can be easily removed once the desired weight loss has been achieved. This aspect provides flexibility and eliminates the concerns associated with irreversible surgical interventions. Furthermore, studies have shown that the intragastric balloon can lead to significant weight loss, typically ranging from 10% to 15% of the total body weight. However, it is important to note that the degree of weight loss varies among individuals, and the success of the procedure also depends on the commitment to adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise.
While the intragastric balloon is generally considered safe, it is crucial to understand the associated risks. Some common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort during the initial period after balloon placement. In rare cases, complications such as balloon deflation, gastric ulcers, or bowel obstruction may occur. Therefore, it is imperative to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before considering this procedure. The Role of Intragastric Balloons in Weight Management: Intragastric balloons stomach are not meant to be standalone solutions for weight loss. They are most effective when used as part of a comprehensive weight management program, including dietary modifications, physical activity, and behavioral counseling. The balloon serves as a tool to facilitate the adoption of healthier habits and provides a jumpstart to achieving weight loss goals.
While the intragastric balloon is generally considered safe, it is crucial to understand the associated risks. Some common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort during the initial period after balloon placement. In rare cases, complications such as balloon deflation, gastric ulcers, or bowel obstruction may occur. Therefore, it is imperative to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before considering this procedure.
The Role of Intragastric Balloons in Weight Management:
Intragastric balloons stomach are not meant to be standalone solutions for weight loss. They are most effective when used as part of a comprehensive weight management program, including dietary modifications, physical activity, and behavioral counseling. The balloon serves as a tool to facilitate the adoption of healthier habits and provides a jumpstart to achieving weight loss goals.
Hospital Name | Address | Contact Number |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) | Ansari Nagar, Aurobindo Marg, New Delhi - 110029 | +91-11-26588500 |
Safdarjung Hospital | Safdarjung Campus, Ansari Nagar, New Delhi - 110029 | +91-11-26165060 |
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER) | Sector-12, Chandigarh - 160012 | +91-172-2747585 |
King George's Medical University (KGMU) | Chowk, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226003 | +91-522-2257450 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) | Saket Nagar, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh - 462020 | +91-755-2672355 |
Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences (NIMS) | Punjagutta, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500082 | +91-40-23489000 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) | Sector 32, Chandigarh - 160030 | +91-172-2601023 |
Institute of Medical Sciences (IMS), Banaras Hindu University (BHU) | Lanka, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh - 221005 | +91-542-2367568 |
Osmania General Hospital | Afzal Gunj, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500012 | +91-40-24600146 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) | Sector 32, Chandigarh - 160030 | +91-172-2601023 |
Please Wait..