Hip replacement surgery, also known as hip arthroplasty, is a surgical
procedure performed to replace a damaged or diseased hip joint with an
artificial implant. It is commonly performed to relieve pain, improve
mobility, and restore function in individuals with severe hip joint
conditions.
Call us to book a appointment with the best Ortho specialist near you.
Hip replacement surgery, also known as total hip arthroplasty, is a procedure performed to replace a damaged hip joint with an artificial joint called a prosthesis. Here are the stages involved in this surgery, including the surgical options, alternatives, and post-operative care
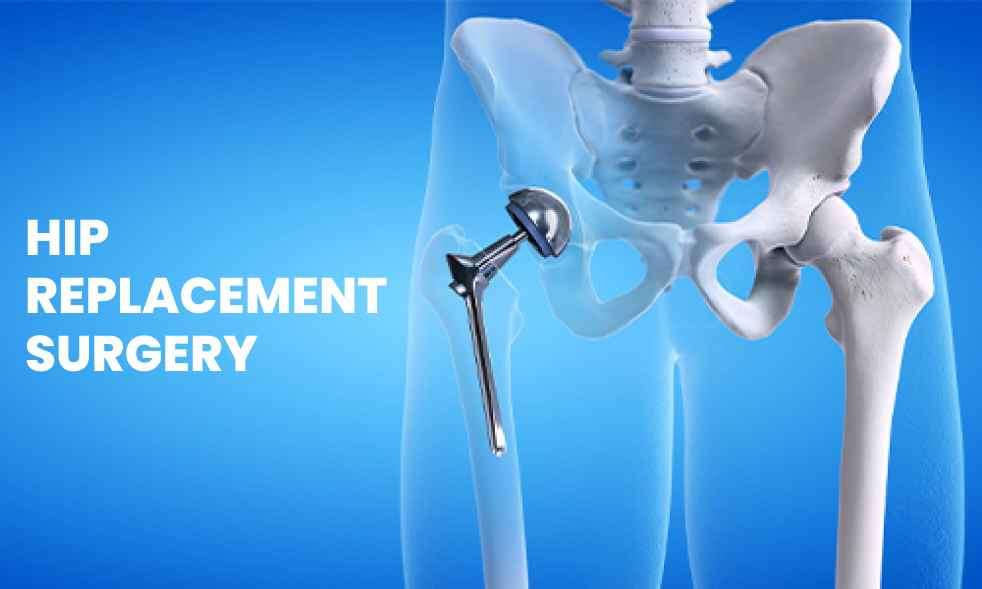
Hip replacement surgery, also known as total hip arthroplasty, is a procedure performed to replace a damaged hip joint with an artificial joint called a prosthesis. Here are the stages involved in this surgery, including the surgical options, alternatives, and post-operative care
1. The orthopedic surgeon examines the
patient's medical history, performs a physical examination, and reviews
diagnostic tests like X-rays and MRI scans. 2. The severity of hip joint damage, pain level, and functional
limitations are assessed to determine if the patient is a suitable
candidate for the surgery.
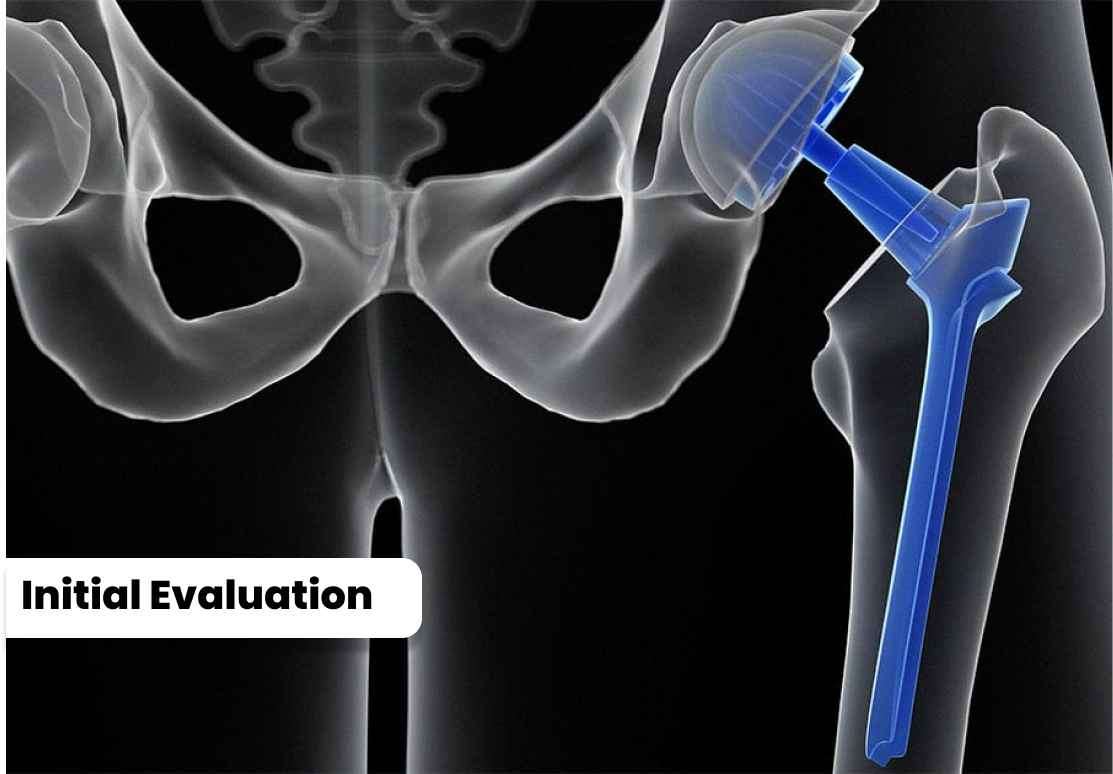
1. The orthopedic surgeon examines the patient's medical history, performs a physical examination, and reviews diagnostic tests like X-rays and MRI scans.
2. The severity of hip joint damage, pain level, and functional
limitations are assessed to determine if the patient is a suitable
candidate for the surgery.
1. The patient may be asked to stop taking certain medications, like blood thinners, before the surgery. 2. Additional tests, such as blood tests and electrocardiogram (ECG), may be conducted to assess the patient's overall health. 3. The surgeon provides instructions regarding fasting, medication use, and what to expect on the day of surgery.
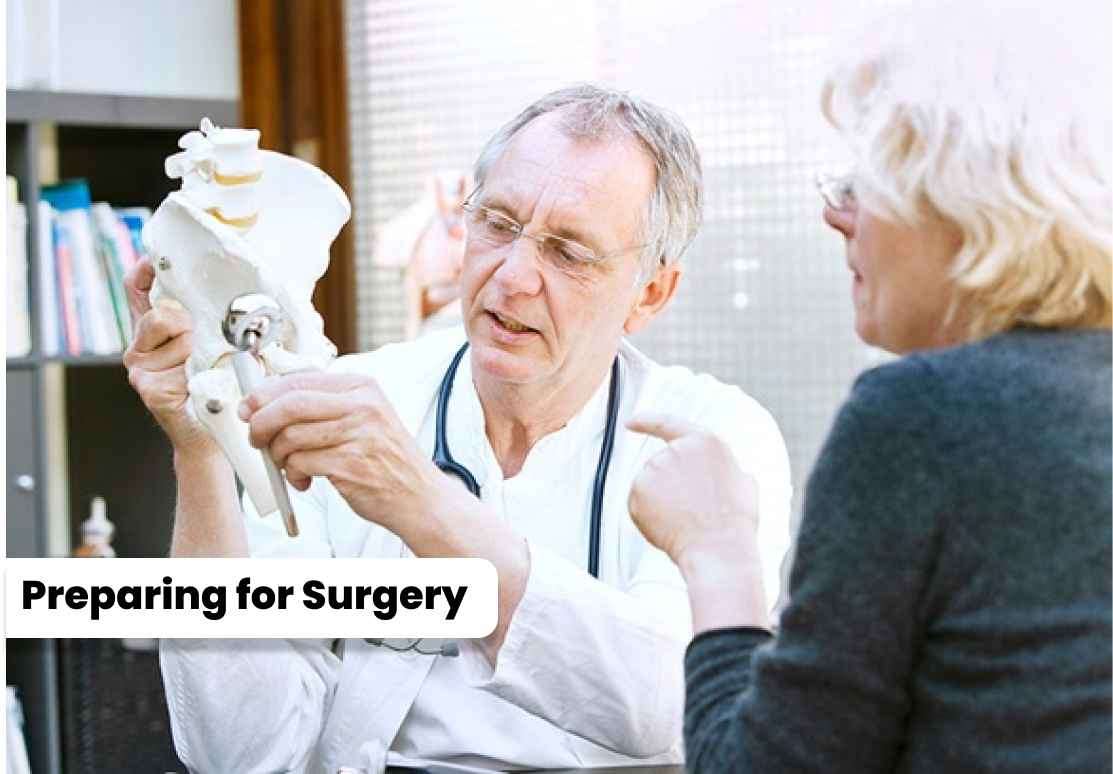
1. The patient may be asked to stop taking certain medications, like blood thinners, before the surgery.
2. Additional tests, such as blood tests and electrocardiogram (ECG), may be conducted to assess the patient's overall health.
3. The surgeon provides instructions regarding fasting, medication use, and what to expect on the day of surgery.
1. Traditional Total Hip Replacement: The surgeon makes an incision, removes the damaged hip joint components, and replaces them with artificial components made of metal or ceramic. The artificial joint is fixed in place using cement or bone ingrowth. 2. Minimally Invasive Total Hip Replacement: This technique uses smaller incisions and specialized instruments, potentially leading to a shorter recovery time and less tissue damage. 3. Anterior Approach Total Hip Replacement: The surgeon accesses the hip joint through a small incision at the front of the hip, which may result in reduced muscle damage and potentially faster recovery.
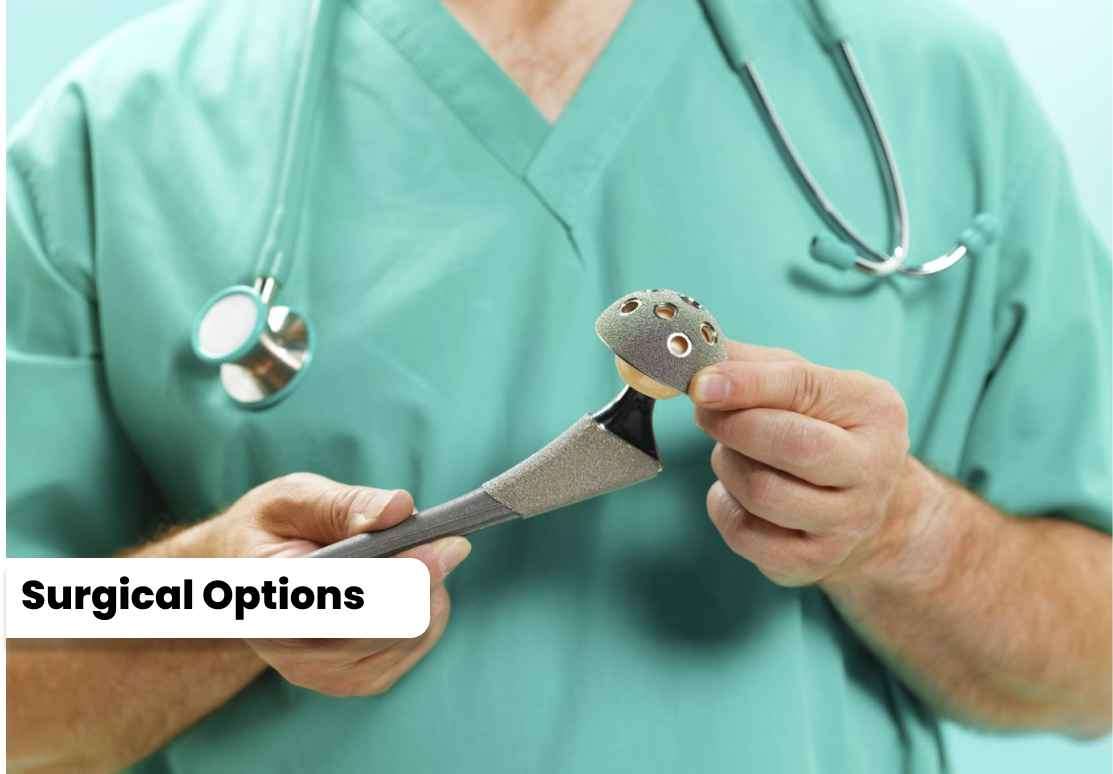
1. Traditional Total Hip Replacement: The surgeon makes an incision, removes the damaged hip joint components, and replaces them with artificial components made of metal or ceramic. The artificial joint is fixed in place using cement or bone ingrowth.
2. Minimally Invasive Total Hip Replacement: This technique uses smaller incisions and specialized instruments, potentially leading to a shorter recovery time and less tissue damage.
3. Anterior Approach Total Hip Replacement: The surgeon accesses the hip joint through a small incision at the front of the hip, which may result in reduced muscle damage and potentially faster recovery.
1. Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage hip pain and inflammation. 2. Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches can improve hip joint strength and flexibility. 3. Assistive Devices: Canes, crutches, or walkers may provide support and alleviate pressure on the hip joint. 4. Injections: Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections can reduce inflammation and pain in the hip joint.
1. Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage hip pain and inflammation.
2. Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches can improve hip joint strength and flexibility.
3. Assistive Devices: Canes, crutches, or walkers may provide support and alleviate pressure on the hip joint.
4. Injections: Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections can reduce inflammation and pain in the hip joint.
1. The patient receives anaesthesia for comfort during the surgery. 2. The surgeon makes an incision, removes the damaged bone and cartilage, and replaces them with artificial components. 3. The artificial joint is securely fixed in place using cement or bone ingrowth. 4. The incision is closed, and a drain may be used to remove excess fluid.
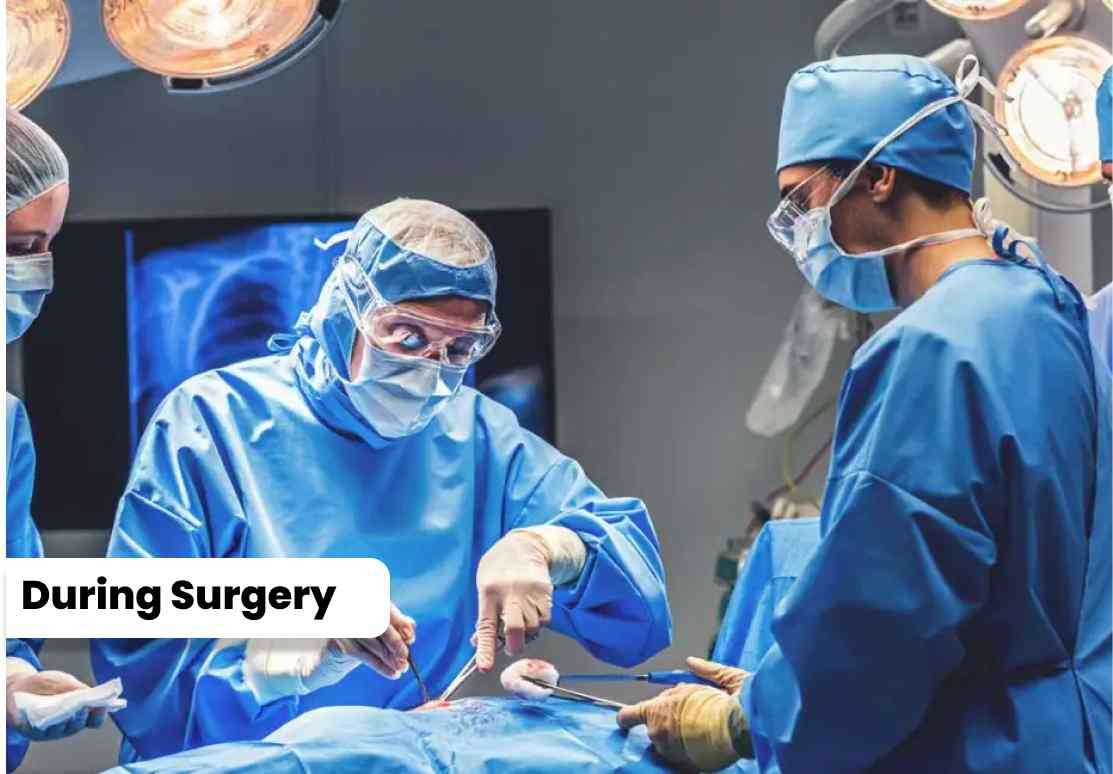
1. The patient receives anaesthesia for comfort during the surgery.
2. The surgeon makes an incision, removes the damaged bone and cartilage, and replaces them with artificial components.
3. The artificial joint is securely fixed in place using cement or bone ingrowth.
4. The incision is closed, and a drain may be used to remove excess fluid.
1. Pain Management: Medications are prescribed to control pain and discomfort.
2. Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation exercises are initiated to improve mobility and strength. They may begin shortly after the surgery.
3. Weight-Bearing and Walking: The surgeon provides instructions on weight-bearing restrictions and when it is safe to start walking with the help of assistive devices.
4. Monitoring and Follow-up: Regular check-ups and X-rays are scheduled to monitor the healing process and assess the functioning of the artificial joint.

1. Pain Management: Medications are prescribed to control pain and discomfort.
2. Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation exercises are initiated to improve mobility and strength. They may begin shortly after the surgery.
3. Weight-Bearing and Walking: The surgeon provides instructions on weight-bearing restrictions and when it is safe to start walking with the help of assistive devices.
4. Monitoring and Follow-up: Regular check-ups and X-rays are scheduled to monitor the healing process and assess the functioning of the artificial joint.
Please Wait..