Ear surgery, also known as otologic surgery or otoplasty, encompasses
various surgical procedures performed on the ear to address specific
conditions or concerns.
Call us to book an appointment with the best Otolaryngologist-Ear,
Nose, and Throat (ENT) specialist or a Sinus Surgeon near you.
Ear surgery, also known as otologic surgery, encompasses a range of procedures that aim to address various conditions affecting the ears and adjacent structures. These surgeries are performed by otolaryngologists, commonly known as ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialists. Ear operation may be recommended for a variety of reasons, such as correcting structural abnormalities, improving hearing, or treating conditions that cause pain or infections.

Ear surgery, also known as otologic surgery, encompasses a range of procedures that aim to address various conditions affecting the ears and adjacent structures. These surgeries are performed by otolaryngologists, commonly known as ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialists. Ear operation may be recommended for a variety of reasons, such as correcting structural abnormalities, improving hearing, or treating conditions that cause pain or infections.
1. Tympanoplasty: Tympanoplasty is a procedure performed to repair a perforated eardrum or to reconstruct the middle ear structures. It involves grafting tissue onto the eardrum to close the hole and restore its function. Tympanoplasty can improve hearing, prevent recurring ear infections, and alleviate symptoms like ear pain or discharge. 2. Myringotomy with grommet insertion: Myringotomy is a surgical procedure that involves creating a small incision in the eardrum to drain fluid or relieve pressure from chronic ear infections or middle ear effusion. In some cases, tiny tubes called tympanostomy tubes are inserted into the eardrum to ventilate the middle ear and prevent fluid accumulation.
3. Cochlear Implant Surgery: Cochlear implant surgery is performed to restore hearing in individuals with severe to profound hearing loss who do not benefit from conventional hearing aids. It involves the surgical implantation of a device that bypasses damaged parts of the inner ear and stimulates the auditory nerve directly.
4. Mastoidectomy: Mastoidectomy is a procedure performed to treat infections or complications in the mastoid bone, located behind the ear. It involves the removal of infected or damaged tissue and can be necessary in cases of chronic mastoiditis or cholesteatoma (a noncancerous growth in the middle ear).
5. Stapedectomy: Stapedectomy is a surgical procedure aimed at improving hearing in individuals with otosclerosis, a condition in which abnormal bone growth in the middle ear interferes with sound transmission. The surgery involves removing part of the stapes bone and replacing it with a prosthesis to restore proper sound conduction.

1. Tympanoplasty: Tympanoplasty is a procedure performed to repair a perforated eardrum or to reconstruct the middle ear structures. It involves grafting tissue onto the eardrum to close the hole and restore its function. Tympanoplasty can improve hearing, prevent recurring ear infections, and alleviate symptoms like ear pain or discharge.
2. Myringotomy with grommet insertion: Myringotomy is a surgical procedure that involves creating a small incision in the eardrum to drain fluid or relieve pressure from chronic ear infections or middle ear effusion. In some cases, tiny tubes called tympanostomy tubes are inserted into the eardrum to ventilate the middle ear and prevent fluid accumulation.
3. Cochlear Implant Surgery: Cochlear implant surgery is performed to restore hearing in individuals with severe to profound hearing loss who do not benefit from conventional hearing aids. It involves the surgical implantation of a device that bypasses damaged parts of the inner ear and stimulates the auditory nerve directly.
4. Mastoidectomy: Mastoidectomy is a procedure performed to treat infections or complications in the mastoid bone, located behind the ear. It involves the removal of infected or damaged tissue and can be necessary in cases of chronic mastoiditis or cholesteatoma (a noncancerous growth in the middle ear).
5. Stapedectomy: Stapedectomy is a surgical procedure aimed at improving hearing in individuals with otosclerosis, a condition in which abnormal bone growth in the middle ear interferes with sound transmission. The surgery involves removing part of the stapes bone and replacing it with a prosthesis to restore proper sound conduction.
Ear surgery offers several benefits for individuals experiencing ear-related conditions. Some advantages include: 1. Improved Hearing: Many ear surgeries are performed with the goal of improving hearing or restoring it entirely. Procedures such as cochlear implant surgery or tympanoplasty can significantly enhance a person's ability to hear and communicate. 2. Relief from Pain and Infections: Ear surgeries can alleviate chronic ear pain and recurrent infections, providing relief and improving overall comfort. 3. Prevention of Complications: Surgical interventions can prevent potential complications arising from chronic ear infections, such as hearing loss, mastoiditis, or damage to the middle ear structures. 4. Enhanced Quality of Life: By addressing ear-related issues, surgery can improve an individual's quality of life, allowing them to participate fully in conversations, enjoy music, and engage in social activities.

Ear surgery offers several benefits for individuals experiencing ear-related conditions. Some advantages include:
1. Improved Hearing: Many ear surgeries are performed with the goal of improving hearing or restoring it entirely. Procedures such as cochlear implant surgery or tympanoplasty can significantly enhance a person's ability to hear and communicate.
2. Relief from Pain and Infections: Ear surgeries can alleviate chronic ear pain and recurrent infections, providing relief and improving overall comfort.
3. Prevention of Complications: Surgical interventions can prevent potential complications arising from chronic ear infections, such as hearing loss, mastoiditis, or damage to the middle ear structures.
4. Enhanced Quality of Life: By addressing ear-related issues, surgery can improve an individual's quality of life, allowing them to participate fully in conversations, enjoy music, and engage in social activities.
The recovery process following ear surgery varies depending on the specific procedure performed. However, here are some general guidelines: 1. Postoperative Care: Proper wound care is essential after ear surgery. Patients may need to keep the surgical site dry and clean, follow any prescribed medication regimen, and avoid activities that could damage the healing process. 2. Rest and Recovery: It is crucial to allow the body to heal properly. Patients may need to take time off work or school and avoid strenuous activities as recommended by their surgeon. 3. Follow-up Appointments: Regular follow-up visits with the surgeon are essential to monitor the healing process, remove any packing or sutures if necessary, and evaluate the outcomes of the surgery. 4. Auditory Rehabilitation: In cases of hearing restoration procedures like cochlear implants, patients may require auditory rehabilitation to adapt to the new hearing experience. This may involve working with audiologists or speech-language pathologists.
The recovery process following ear surgery varies depending on the specific procedure performed. However, here are some general guidelines:
1. Postoperative Care: Proper wound care is essential after ear surgery. Patients may need to keep the surgical site dry and clean, follow any prescribed medication regimen, and avoid activities that could damage the healing process.
2. Rest and Recovery: It is crucial to allow the body to heal properly. Patients may need to take time off work or school and avoid strenuous activities as recommended by their surgeon.
3. Follow-up Appointments: Regular follow-up visits with the surgeon are essential to monitor the healing process, remove any packing or sutures if necessary, and evaluate the outcomes of the surgery.
4. Auditory Rehabilitation: In cases of hearing restoration procedures like cochlear implants, patients may require auditory rehabilitation to adapt to the new hearing experience. This may involve working with audiologists or speech-language pathologists.
1. Prominent Ears: Otoplasty can correct ears
that stick out prominently from the sides of the head. This procedure involves
reshaping the cartilage and positioning the ears closer to the head, creating a
more balanced and natural appearance. 2. Oversized Ears: In cases where the size of
the ears is a concern, otoplasty can reduce the size and reshape the ear lobes
or other areas of the ear to achieve better proportionality.
3. Ear Asymmetry: Otoplasty can also address
asymmetry, where one ear may be noticeably different from the other in terms of
size, shape, or position. The
Otoplasty Procedure: During an otoplasty procedure, the surgeon
will typically follow these steps: 1. Anesthesia: Otoplasty is commonly performed
under local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia. The choice of
anesthesia depends on the patient's preferences and the surgeon's recommendation. 2. Incision Placement: The surgeon will make
incisions discreetly behind the ear, within the natural creases, to minimize
visible scarring. 3. Cartilage Reshaping: The surgeon will
access the underlying ear cartilage and reshape it as needed. Techniques may
involve suturing or removing excess cartilage to create the desired ear shape
and projection. 4. Ear Positioning: If the goal is to correct
prominent ears, the surgeon will carefully reposition the ears closer to the
head using sutures, creating a more balanced appearance. 5. Closure and Dressing: Once the desired
changes have been made, the surgeon will close the incisions with sutures and
apply a protective dressing or bandages to support the newly shaped ears during
the initial healing phase.
Benefits
and Considerations: Otoplasty offers several benefits for
individuals seeking to improve the appearance of their ears: 1. Enhanced Aesthetics: Otoplasty can bring
the ears into better proportion with the rest of the face, resulting in
improved facial harmony and overall aesthetic appeal. 2. Increased Self-Confidence: Many individuals
with prominent or asymmetrical ears may feel self-conscious or experience
social discomfort. Otoplasty can boost self-confidence and improve self-esteem,
allowing individuals to feel more comfortable in social and professional
settings. 3. Permanent Results: Otoplasty provides
long-lasting results. Once the ears have healed fully, the new shape and
position are generally maintained over time. Recovery
Process: Following otoplasty, patients can expect the
following during the recovery period: 1. Bandages and Dressings: The surgeon will
apply a dressing or bandages to protect the ears and help maintain their new
position. These may be worn for a few days or weeks. 2. Swelling and Discomfort: Swelling and mild
discomfort around the ears are common after otoplasty. The surgeon may
prescribe pain medication to manage any discomfort during the initial healing
phase. 3. Activity Restrictions: Patients are
generally advised to avoid strenuous activities, especially those that could
risk injury to the ears, for several weeks following surgery. 4. Follow-up Appointments: Regular follow-up
visits with the surgeon are crucial to monitor the healing process, remove any
sutures if necessary, and ensure the desired results are being achieved.
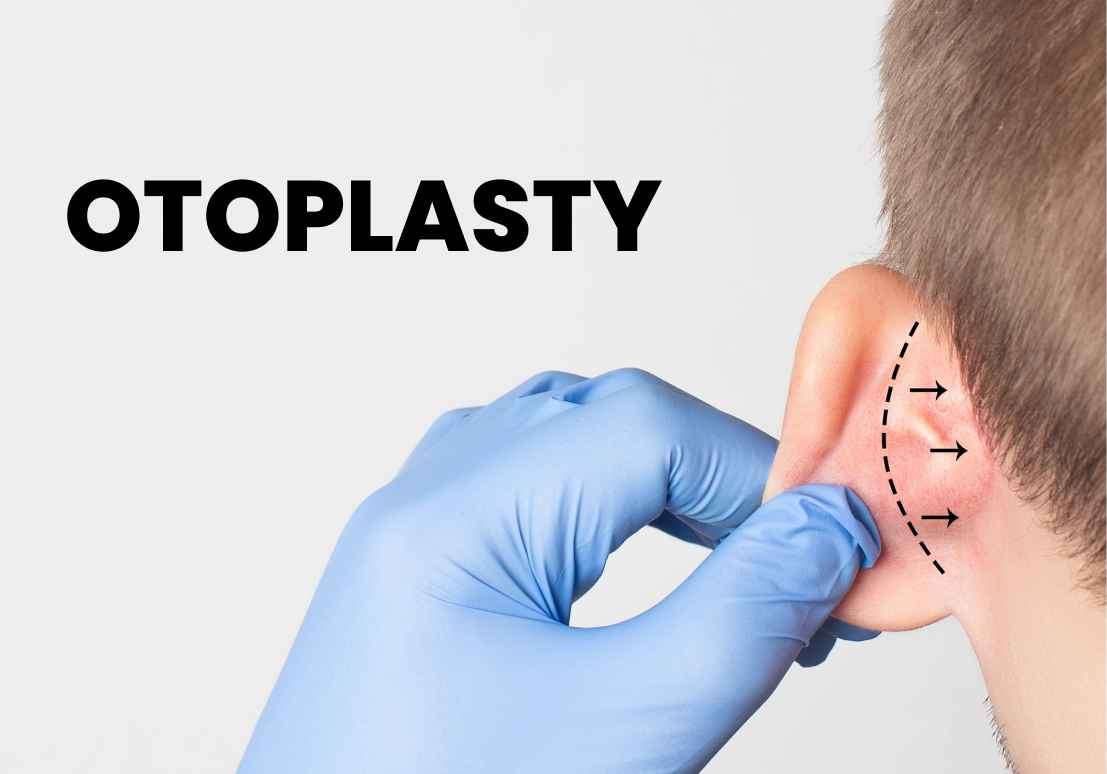
1. Prominent Ears: Otoplasty can correct ears that stick out prominently from the sides of the head. This procedure involves reshaping the cartilage and positioning the ears closer to the head, creating a more balanced and natural appearance.
2. Oversized Ears: In cases where the size of the ears is a concern, otoplasty can reduce the size and reshape the ear lobes or other areas of the ear to achieve better proportionality.
3. Ear Asymmetry: Otoplasty can also address asymmetry, where one ear may be noticeably different from the other in terms of size, shape, or position.
The Otoplasty Procedure:
During an otoplasty procedure, the surgeon will typically follow these steps:
1. Anesthesia: Otoplasty is commonly performed under local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia. The choice of anesthesia depends on the patient's preferences and the surgeon's recommendation.
2. Incision Placement: The surgeon will make incisions discreetly behind the ear, within the natural creases, to minimize visible scarring.
3. Cartilage Reshaping: The surgeon will access the underlying ear cartilage and reshape it as needed. Techniques may involve suturing or removing excess cartilage to create the desired ear shape and projection.
4. Ear Positioning: If the goal is to correct prominent ears, the surgeon will carefully reposition the ears closer to the head using sutures, creating a more balanced appearance.
5. Closure and Dressing: Once the desired changes have been made, the surgeon will close the incisions with sutures and apply a protective dressing or bandages to support the newly shaped ears during the initial healing phase.
Benefits
and Considerations:
Otoplasty offers several benefits for individuals seeking to improve the appearance of their ears:
1. Enhanced Aesthetics: Otoplasty can bring the ears into better proportion with the rest of the face, resulting in improved facial harmony and overall aesthetic appeal.
2. Increased Self-Confidence: Many individuals with prominent or asymmetrical ears may feel self-conscious or experience social discomfort. Otoplasty can boost self-confidence and improve self-esteem, allowing individuals to feel more comfortable in social and professional settings.
3. Permanent Results: Otoplasty provides long-lasting results. Once the ears have healed fully, the new shape and position are generally maintained over time.
Recovery Process:
Following otoplasty, patients can expect the following during the recovery period:
1. Bandages and Dressings: The surgeon will apply a dressing or bandages to protect the ears and help maintain their new position. These may be worn for a few days or weeks.
2. Swelling and Discomfort: Swelling and mild discomfort around the ears are common after otoplasty. The surgeon may prescribe pain medication to manage any discomfort during the initial healing phase.
3. Activity Restrictions: Patients are generally advised to avoid strenuous activities, especially those that could risk injury to the ears, for several weeks following surgery.
4. Follow-up Appointments: Regular follow-up visits with the surgeon are crucial to monitor the healing process, remove any sutures if necessary, and ensure the desired results are being achieved.
|
Serial No |
City |
Minimum Cost (INR) |
Average Cost (INR) |
|
1 |
Mumbai |
10,000 |
40,000 |
|
2 |
Delhi |
8,000 |
35,000 |
|
3 |
Bangalore |
7,000 |
30,000 |
|
4 |
Chennai |
6,000 |
25,000 |
|
5 |
Kolkata |
5,000 |
22,000 |
|
6 |
Hyderabad |
5,000 |
22,000 |
|
7 |
Pune |
4,500 |
18,000 |
|
8 |
Ahmedabad |
4,000 |
16,000 |
|
9 |
Jaipur |
4,000 |
16,000 |
|
10 |
Chandigarh |
3,500 |
14,000 |
|
11 |
Lucknow |
3,500 |
14,000 |
|
12 |
Indore |
3,000 |
12,000 |
|
13 |
Kochi |
3,000 |
12,000 |
|
14 |
Coimbatore |
2,500 |
10,000 |
|
15 |
Bhopal |
2,500 |
10,000 |
|
16 |
Nagpur |
2,000 |
8,000 |
|
17 |
Goa |
2,000 |
8,000 |
|
18 |
Mangalore |
1,800 |
6,000 |
|
19 |
Trivandrum |
1,800 |
6,000 |
|
20 |
Guwahati |
1,500 |
5,000 |
|
Serial No |
Hospital Name |
City |
Contact Number |
|
1 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) |
Multiple Cities |
+91-11-26588500 |
|
2 |
Safdarjung Hospital |
Delhi |
+91-11-2673-0000 |
|
3 |
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research |
Chandigarh |
+91-172-275-6565 |
|
4 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) |
Nagpur |
+91-712-270-1646 |
|
5 |
King George's Medical University (KGMU) |
Lucknow |
+91-522-2257450 |
|
6 |
Madras Medical College |
Chennai |
+91-44-2530-5000 |
|
7 |
Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research |
Kolkata |
+91-33-2204-1000 |
|
8 |
SMS Medical College |
Jaipur |
+91-141-251-8121 |
|
9 |
Government General Hospital |
Vijayawada |
+91-866-257-6000 |
Please Wait..