Adenoidectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the adenoids, which are
small masses of tissue located in the back of the throat, behind the
nose.
Call us to book an appointment with the best Otolaryngologist-Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) specialist or a Sinus Surgeon near you.
Adenoidectomy, also known as adenoid removal, is a surgical procedure performed to remove the adenoids—a pair of lymphoid tissues located at the back of the nasal cavity. This procedure is often done in conjunction with tonsillectomy (removal of the tonsils), known as tonsil and adenoid removal surgery. Adenoidectomy is a common surgical intervention aimed at improving breathing, alleviating chronic infections, and addressing other related health concerns.
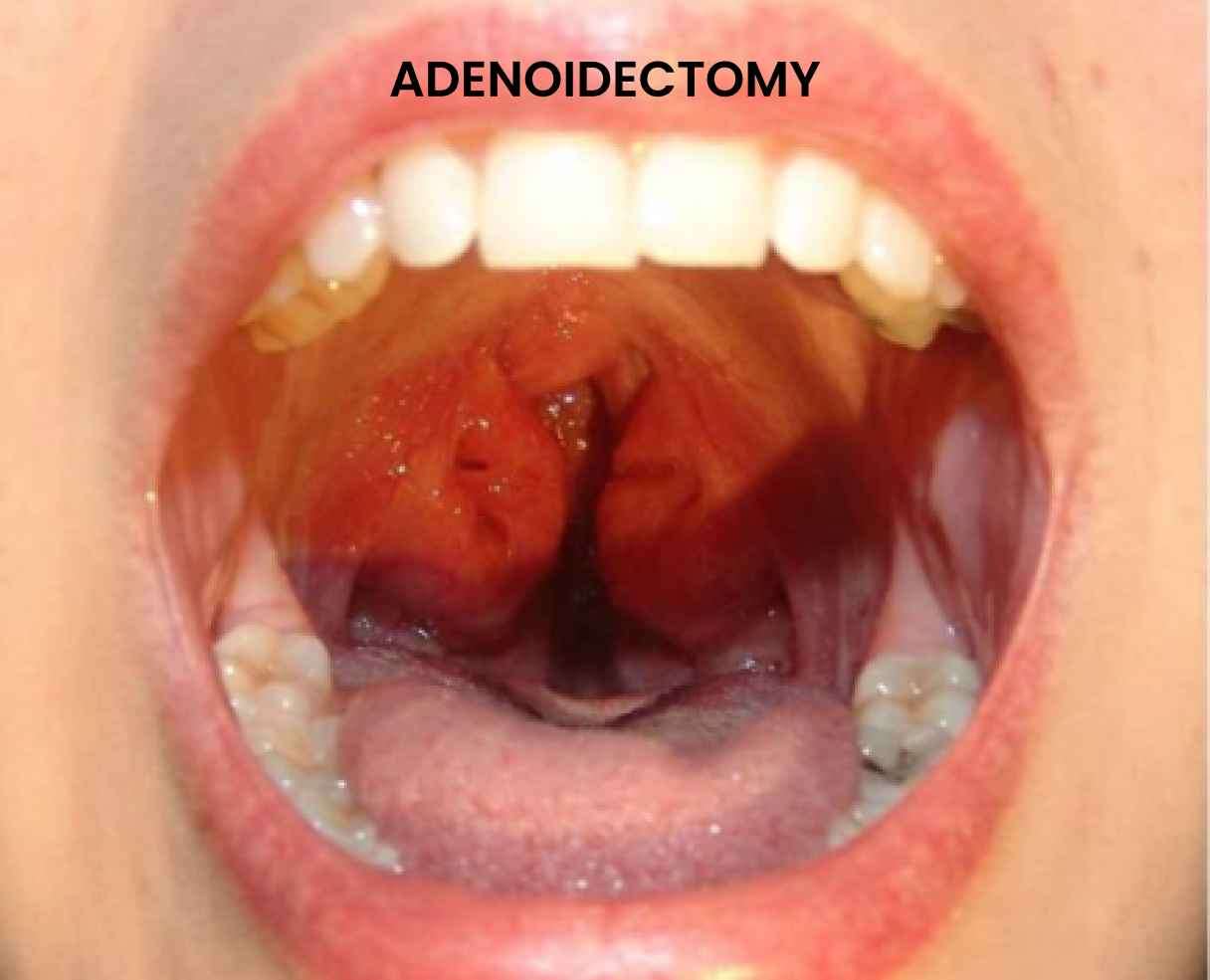
Adenoidectomy, also known as adenoid removal, is a surgical procedure performed to remove the adenoids—a pair of lymphoid tissues located at the back of the nasal cavity. This procedure is often done in conjunction with tonsillectomy (removal of the tonsils), known as tonsil and adenoid removal surgery. Adenoidectomy is a common surgical intervention aimed at improving breathing, alleviating chronic infections, and addressing other related health concerns.
Adenoidectomy is typically performed under general anesthesia and can be carried out using various techniques. The two main approaches to adenoidectomy surgery are:
1. Traditional Adenoidectomy:
During a traditional adenoidectomy, the surgeon uses a curette or a special instrument to scrape and remove the adenoids through the mouth. This technique has been used for many years and remains a viable option for most cases. 2. Coblation Adenoidectomy:
Coblation adenoidectomy is a newer technique that employs radiofrequency energy to remove the adenoid tissue. This method aims to minimize damage to surrounding tissues, reduce post-operative pain, and promote faster recovery.
3.Endoscopic Adenoidectomy:
In some cases, an endoscope—a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera—is used during adenoidectomy surgery. This allows the surgeon to visualize the adenoids more clearly and perform a precise removal. Endoscopic adenoidectomy may be recommended for complex cases or when there are additional concerns, such as nasal obstruction or recurrent sinus infections.
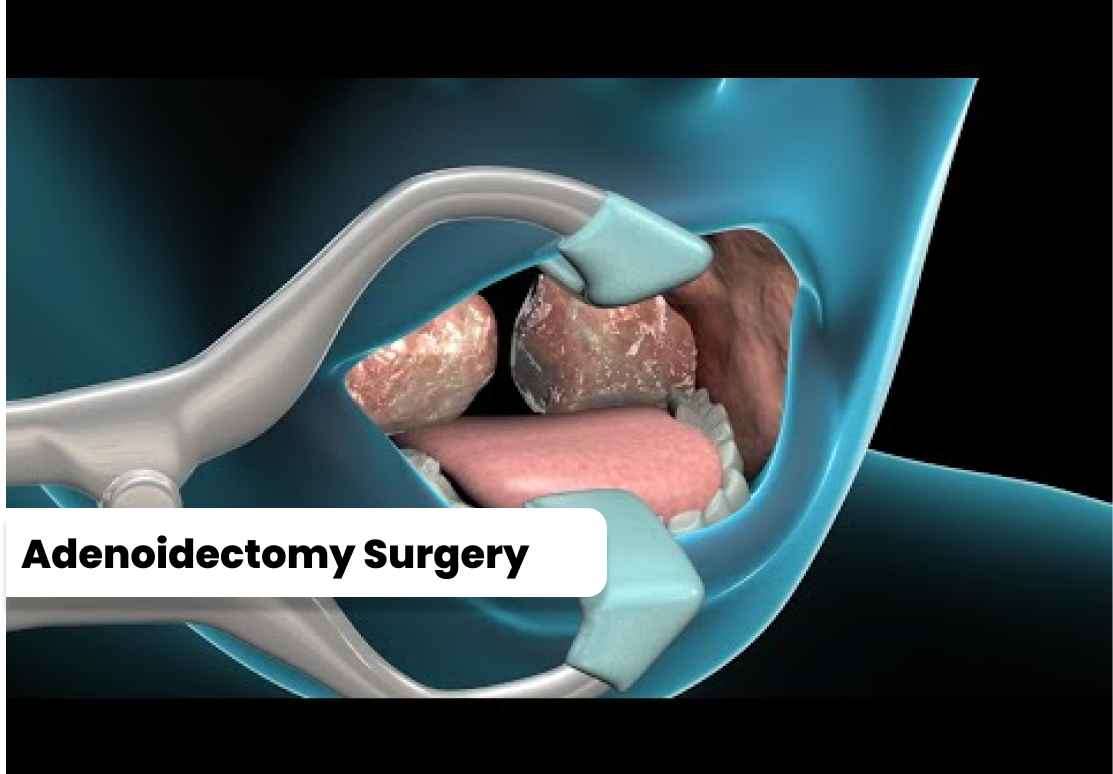
Adenoidectomy is typically performed under general anesthesia and can be carried out using various techniques. The two main approaches to adenoidectomy surgery are:
1. Traditional Adenoidectomy: During a traditional adenoidectomy, the surgeon uses a curette or a special instrument to scrape and remove the adenoids through the mouth. This technique has been used for many years and remains a viable option for most cases.
2. Coblation Adenoidectomy:
Coblation adenoidectomy is a newer technique that employs radiofrequency energy to remove the adenoid tissue. This method aims to minimize damage to surrounding tissues, reduce post-operative pain, and promote faster recovery.
3.Endoscopic Adenoidectomy:
In some cases, an endoscope—a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera—is used during adenoidectomy surgery. This allows the surgeon to visualize the adenoids more clearly and perform a precise removal. Endoscopic adenoidectomy may be recommended for complex cases or when there are additional concerns, such as nasal obstruction or recurrent sinus infections.
There are several reasons why a healthcare professional may recommend adenoid surgery:
1. Chronic Adenoiditis:
When the adenoids become persistently infected and inflamed, resulting in recurring or chronic sinus and ear infections, adenoidectomy may be considered. Removing the adenoids can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the frequency of infections.
2. Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA):
Adenoid enlargement can obstruct the airway during sleep, leading to breathing difficulties and disrupted sleep patterns. Adenoidectomy can be an effective treatment for children with OSA caused by enlarged adenoids. 3. Recurrent Ear Infections: 3. Recurrent Ear Infections:
Enlarged adenoids can contribute to frequent middle ear infections (otitis media). By removing the adenoids, the risk of recurrent ear infections may be reduced. 4. Nasal Obstruction:
Enlarged adenoids can cause nasal congestion, difficulty breathing through the nose, and chronic snoring. Adenoidectomy may be recommended to relieve nasal obstruction and improve breathing. 5. Abscess or Tumor:
In rare cases, adenoidectomy may be necessary to address adenoid abscesses (collection of pus) or tumors (benign or malignant growths) in the adenoid tissue.

There are several reasons why a healthcare professional may recommend adenoid surgery:
1. Chronic Adenoiditis:
When the adenoids become persistently infected and inflamed, resulting in recurring or chronic sinus and ear infections, adenoidectomy may be considered. Removing the adenoids can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the frequency of infections.
2. Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): Adenoid enlargement can obstruct the airway during sleep, leading to breathing difficulties and disrupted sleep patterns. Adenoidectomy can be an effective treatment for children with OSA caused by enlarged adenoids. 3. Recurrent Ear Infections:
3. Recurrent Ear Infections: Enlarged adenoids can contribute to frequent middle ear infections (otitis media). By removing the adenoids, the risk of recurrent ear infections may be reduced.
4. Nasal Obstruction: Enlarged adenoids can cause nasal congestion, difficulty breathing through the nose, and chronic snoring. Adenoidectomy may be recommended to relieve nasal obstruction and improve breathing.
5. Abscess or Tumor:
In rare cases, adenoidectomy may be necessary to address adenoid abscesses (collection of pus) or tumors (benign or malignant growths) in the adenoid tissue.
After adenoidectomy surgery, it is normal to experience some post-operative discomfort, including a sore throat, mild ear pain, or nasal congestion. Healthcare professionals may recommend pain medication, a soft diet, and adequate rest to aid in recovery. It is important to follow the provided aftercare instructions, which may include avoiding strenuous activities, maintaining proper oral hygiene, and attending follow-up appointments to monitor progress.

After adenoidectomy surgery, it is normal to experience some post-operative discomfort, including a sore throat, mild ear pain, or nasal congestion. Healthcare professionals may recommend pain medication, a soft diet, and adequate rest to aid in recovery. It is important to follow the provided aftercare instructions, which may include avoiding strenuous activities, maintaining proper oral hygiene, and attending follow-up appointments to monitor progress.
Tonsillectomy and
adenoidectomy, commonly referred to as "tonsil and adenoid removal
surgery," is a surgical procedure performed to remove the tonsils and
adenoids. Both the tonsils and adenoids are part of the lymphatic system
and play a role in the body's immune response. However, when they
become chronically infected or enlarged, they can cause various health
issues. Tonsil and adenoid removal surgery is a common intervention
aimed at alleviating symptoms, improving quality of life, and preventing
future complications.
Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy Procedure:
Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy are usually performed simultaneously
under general anesthesia. The surgeon accesses the tonsils through the
mouth, and the adenoids through the nose, employing specialized
instruments. There are different techniques for removing the tonsils and
adenoids, including: 1. Cold Knife (Steel) Dissection:
This traditional method involves using a scalpel or a specialized
cutting instrument to dissect and remove the tonsils and adenoids. It is
effective but may involve more post-operative pain and a longer
recovery period. 2. Electrocautery:
Electrocautery involves using a device that applies heat to the tissue
to cut, coagulate, and seal blood vessels simultaneously. It may result
in less bleeding during the procedure and a potentially faster recovery.
3. Harmonic Scalpel:
A harmonic scalpel uses ultrasonic vibrations to simultaneously cut and
seal tissue, minimizing bleeding during the surgery. This technique can
offer improved precision and may lead to reduced post-operative pain and
recovery time.
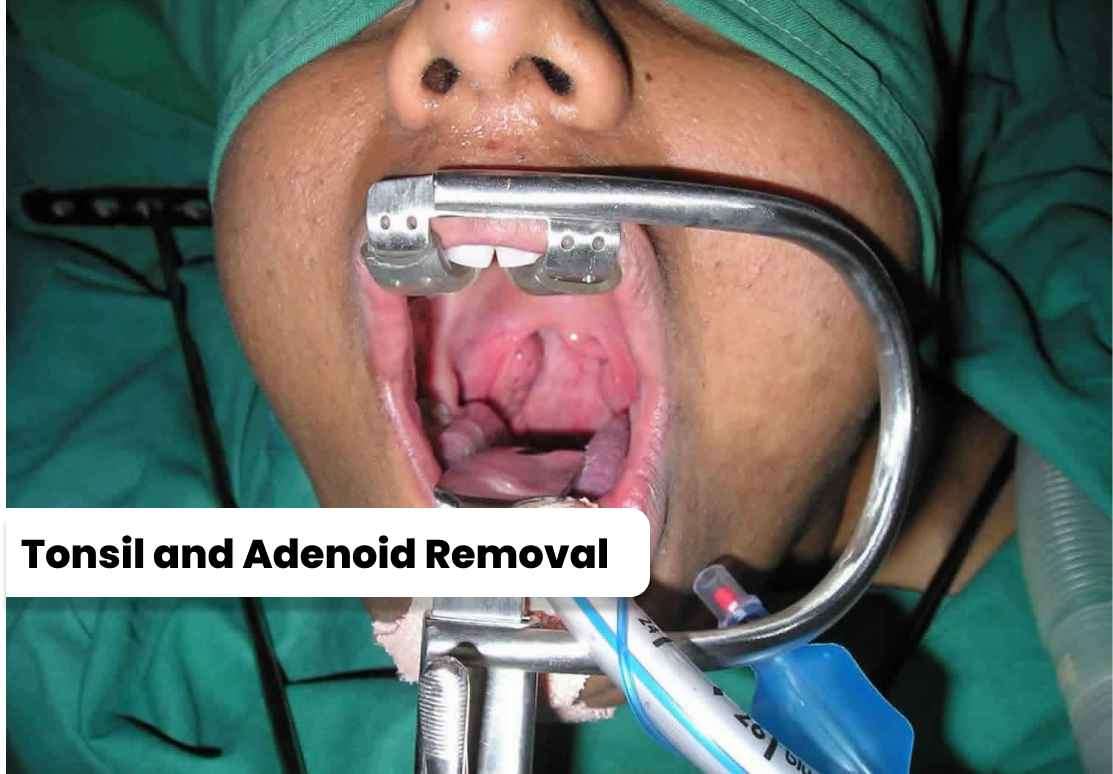
Tonsillectomy and
adenoidectomy, commonly referred to as "tonsil and adenoid removal
surgery," is a surgical procedure performed to remove the tonsils and
adenoids. Both the tonsils and adenoids are part of the lymphatic system
and play a role in the body's immune response. However, when they
become chronically infected or enlarged, they can cause various health
issues. Tonsil and adenoid removal surgery is a common intervention
aimed at alleviating symptoms, improving quality of life, and preventing
future complications.
Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy Procedure: Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy are usually performed simultaneously under general anesthesia. The surgeon accesses the tonsils through the mouth, and the adenoids through the nose, employing specialized instruments. There are different techniques for removing the tonsils and adenoids, including:
1. Cold Knife (Steel) Dissection: This traditional method involves using a scalpel or a specialized cutting instrument to dissect and remove the tonsils and adenoids. It is effective but may involve more post-operative pain and a longer recovery period.
2. Electrocautery: Electrocautery involves using a device that applies heat to the tissue to cut, coagulate, and seal blood vessels simultaneously. It may result in less bleeding during the procedure and a potentially faster recovery.
3. Harmonic Scalpel: A harmonic scalpel uses ultrasonic vibrations to simultaneously cut and seal tissue, minimizing bleeding during the surgery. This technique can offer improved precision and may lead to reduced post-operative pain and recovery time.
Tonsil and adenoid removal surgery can provide several benefits, including: 1. Reduction in Infections:
Enlarged or infected tonsils and adenoids can lead to frequent bouts of tonsillitis, adenoiditis, or recurring ear infections. Removing these structures can significantly decrease the occurrence of these infections, leading to improved overall health and well-being. 2. Improved Breathing:
Enlarged tonsils and adenoids can obstruct the airway, causing breathing difficulties, particularly during sleep. Tonsil and adenoid removal can alleviate airway obstruction, improve nasal airflow, and enhance breathing patterns, leading to better sleep quality and reduced snoring. 3. Resolution of Sleep-Related Disorders:
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and related sleep-disordered breathing can be caused or exacerbated by enlarged tonsils and adenoids. By removing these structures, the airway is cleared, reducing episodes of interrupted breathing during sleep and potentially resolving sleep-related issues. 4. Enhanced Quality of Life:
Relief from chronic infections, improved breathing, and better sleep can greatly enhance a person's quality of life. Removal of the tonsils and adenoids can lead to increased energy levels, improved concentration, and reduced absenteeism from school or work.

Tonsil and adenoid removal surgery can provide several benefits, including:
1. Reduction in Infections: Enlarged or infected tonsils and adenoids can lead to frequent bouts of tonsillitis, adenoiditis, or recurring ear infections. Removing these structures can significantly decrease the occurrence of these infections, leading to improved overall health and well-being.
2. Improved Breathing:
Enlarged tonsils and adenoids can obstruct the airway, causing breathing difficulties, particularly during sleep. Tonsil and adenoid removal can alleviate airway obstruction, improve nasal airflow, and enhance breathing patterns, leading to better sleep quality and reduced snoring.
3. Resolution of Sleep-Related Disorders:
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and related sleep-disordered breathing can be caused or exacerbated by enlarged tonsils and adenoids. By removing these structures, the airway is cleared, reducing episodes of interrupted breathing during sleep and potentially resolving sleep-related issues.
4. Enhanced Quality of Life:
Relief from chronic infections, improved breathing, and better sleep can greatly enhance a person's quality of life. Removal of the tonsils and adenoids can lead to increased energy levels, improved concentration, and reduced absenteeism from school or work.
|
Serial No |
City |
Minimum Cost (INR) |
Average Cost (INR) |
|
1 |
Mumbai |
15,000 |
45,000 |
|
2 |
Delhi |
12,000 |
40,000 |
|
3 |
Bangalore |
10,000 |
35,000 |
|
4 |
Chennai |
9,000 |
30,000 |
|
5 |
Kolkata |
8,000 |
25,000 |
|
6 |
Hyderabad |
7,000 |
22,000 |
|
7 |
Pune |
6,000 |
20,000 |
|
8 |
Ahmedabad |
5,000 |
18,000 |
|
9 |
Jaipur |
5,000 |
18,000 |
|
10 |
Chandigarh |
4,000 |
15,000 |
|
11 |
Lucknow |
4,000 |
15,000 |
|
12 |
Indore |
3,500 |
12,000 |
|
13 |
Kochi |
3,500 |
12,000 |
|
14 |
Coimbatore |
3,000 |
10,000 |
|
15 |
Bhopal |
3,000 |
10,000 |
|
16 |
Nagpur |
2,500 |
8,000 |
|
17 |
Goa |
2,500 |
8,000 |
|
18 |
Mangalore |
2,000 |
6,000 |
|
19 |
Trivandrum |
2,000 |
6,000 |
|
20 |
Guwahati |
1,500 |
5,000 |
|
Serial No |
College/Institution |
City |
Contact Number |
|
1 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) |
Multiple Cities |
+91-11-26588500 |
|
2 |
Maulana Azad Medical College |
Delhi |
+91-11-2323-9277 |
|
3 |
Lady Hardinge Medical College and Associated Hospitals |
Delhi |
+91-11-2336-3728 |
|
4 |
King George's Medical University (KGMU) |
Lucknow |
+91-522-2257450 |
|
5 |
Madras Medical College |
Chennai |
+91-44-2530-5000 |
|
6 |
Grant Medical College and Sir JJ Group of Hospitals |
Mumbai |
+91-22-2373-5555 |
|
7 |
Christian Medical College (CMC) |
Vellore |
+91-416-228-1000 |
|
8 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) |
Chandigarh |
+91-172-260-1023 |
|
9 |
Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University |
Varanasi |
+91-542-236-7568 |
|
10 |
Osmania Medical College |
Hyderabad |
+91-40-2465-1533 |
Please Wait..