General Surgeon, who can evaluate your specific condition and recommend the most appropriate treatment option for your hernia. Call us to book a appointment with the best general surgeon near you.
Hernias are a common medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. They occur when an organ or fatty tissue protrudes through a weak spot or tear in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. While hernias can cause discomfort and inconvenience, the good news is that effective treatment options are available for a speedy recovery.
Treatment options for hernia
Hernia treatment without surgery at home:
Hernia can be cured without surgery by following the following methods
Watchful Waiting and Lifestyle Modifications:
In some cases, small hernias may not require immediate surgical intervention. Your doctor may recommend a watchful waiting approach, especially if the hernia is not causing significant pain or complications. During this period, it's important to adopt certain lifestyle modifications to manage the condition effectively. These may include maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding heavy lifting, and practicing good posture.
Hernia Support Garments:
Hernia support garments, such as trusses or belts, can provide temporary relief and support for hernias. These devices are designed to hold the herniated tissue in place, reducing discomfort and preventing further protrusion. While support garments are not a cure for hernias, they can offer symptomatic relief and are particularly helpful for individuals who are not suitable candidates for surgery.
Surgical Repair: For most hernias, surgical repair is the best treatment option to treat hernias and achieve a permanent solution. The two main types of hernia surgery are open repair and laparoscopic (minimally invasive) repair. Open Hernia surgery: This traditional approach involves making an incision at the site of the hernia. The surgeon then pushes the protruding tissue back into place and reinforces the weakened muscle or tissue with sutures or a synthetic mesh. Open repair is a reliable and time-tested technique suitable for various types of hernias. Laparoscopic Repair: Laparoscopic hernia repair is a minimally invasive technique that involves making several small incisions. A laparoscope, a thin tube with a camera and specialized surgical tools, is inserted through these incisions to repair the hernia. This approach offers the advantages of smaller incisions, reduced pain, faster recovery, and potentially less scarring. Robotic-Assisted Hernia Repair: Robotic-assisted hernia repair is an innovative approach that combines the benefits of laparoscopic surgery with the precision and dexterity of robotic technology. In this procedure, the surgeon controls robotic arms to perform the surgery while viewing a 3D magnified image. Robotic-assisted hernia repair offers enhanced visualization, greater surgical precision, and faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
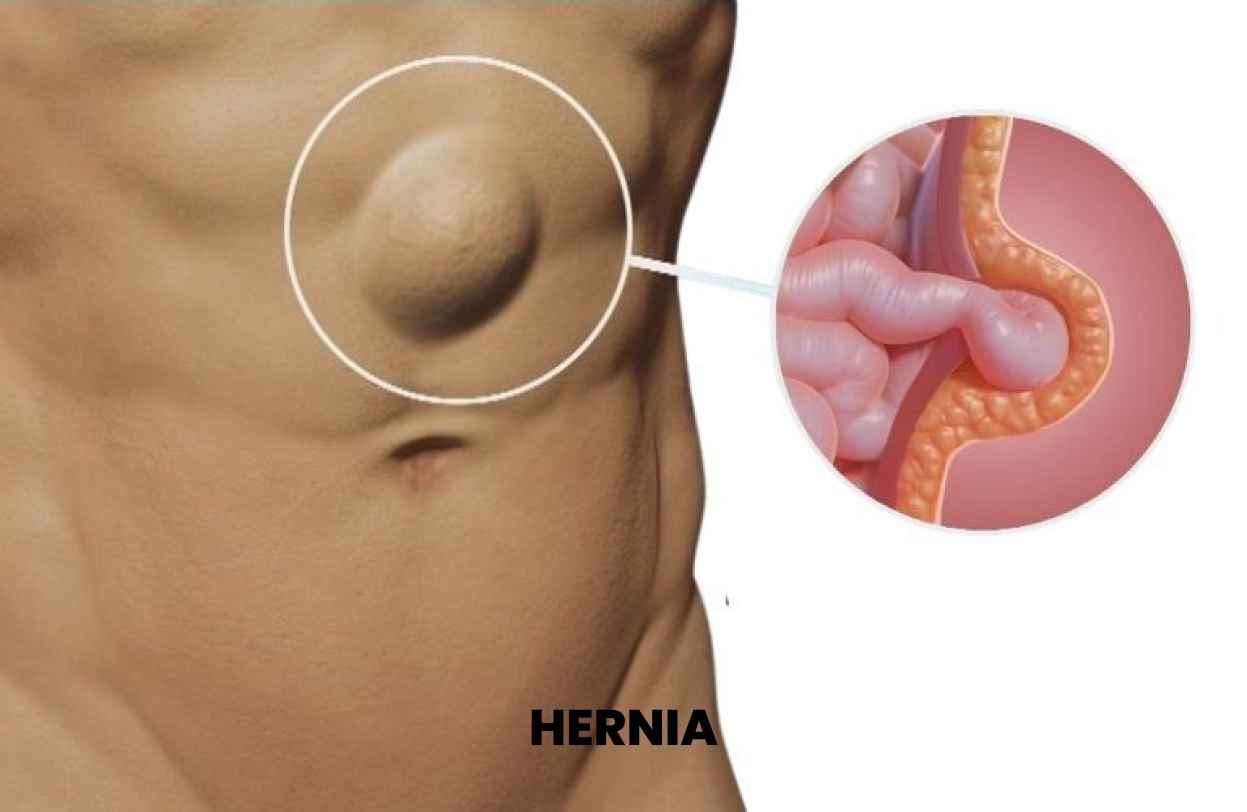
Surgical Repair:
For most hernias, surgical repair is the best treatment option to treat hernias and achieve a permanent solution. The two main types of hernia surgery are open repair and laparoscopic (minimally invasive) repair.
Open Hernia surgery: This traditional approach involves making an incision at the site of the hernia. The surgeon then pushes the protruding tissue back into place and reinforces the weakened muscle or tissue with sutures or a synthetic mesh. Open repair is a reliable and time-tested technique suitable for various types of hernias.
Laparoscopic Repair: Laparoscopic hernia repair is a minimally invasive technique that involves making several small incisions. A laparoscope, a thin tube with a camera and specialized surgical tools, is inserted through these incisions to repair the hernia. This approach offers the advantages of smaller incisions, reduced pain, faster recovery, and potentially less scarring.
Robotic-Assisted Hernia Repair: Robotic-assisted hernia repair is an innovative approach that combines the benefits of laparoscopic surgery with the precision and dexterity of robotic technology. In this procedure, the surgeon controls robotic arms to perform the surgery while viewing a 3D magnified image. Robotic-assisted hernia repair offers enhanced visualization, greater surgical precision, and faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
Symptom Relief: Treating a hernia can help alleviate the discomfort and pain associated with the condition. Hernias often cause a bulge or swelling in the affected area, and treating the hernia can help reduce or eliminate this symptom. Prevention of Complications: Hernias have the potential to lead to complications, such as strangulation or obstruction, where the herniated tissue becomes trapped and its blood supply is cut off. By treating the hernia, these complications can be prevented or minimized. Improved Quality of Life: Hernias can limit physical activities and cause discomfort in daily life. Treating the hernia can restore mobility, allowing individuals to participate in activities they may have previously avoided due to pain or risk of complications. Lower Risk of Emergency Surgery: If a hernia becomes incarcerated or strangulated, emergency surgery may be required. By opting for elective hernia treatment, the risk of an emergency situation can be minimized, allowing for a planned procedure with better outcomes. Reduced Risk of Recurrence: Surgical repair of a hernia aims to strengthen the weakened area and reduce the chances of recurrence. This can provide long-term relief and decrease the likelihood of future hernias.
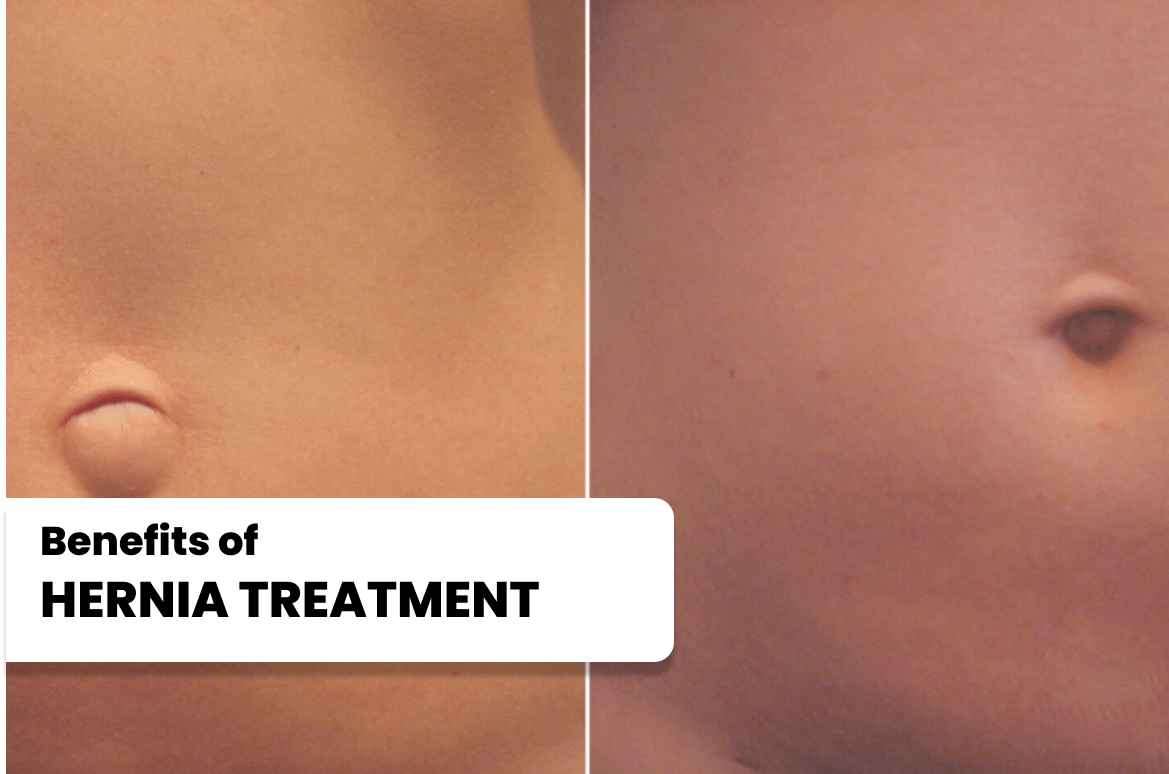
Symptom Relief: Treating a hernia can help alleviate the discomfort and pain associated with the condition. Hernias often cause a bulge or swelling in the affected area, and treating the hernia can help reduce or eliminate this symptom.
Prevention of Complications: Hernias have the potential to lead to complications, such as strangulation or obstruction, where the herniated tissue becomes trapped and its blood supply is cut off. By treating the hernia, these complications can be prevented or minimized.
Improved Quality of Life: Hernias can limit physical activities and cause discomfort in daily life. Treating the hernia can restore mobility, allowing individuals to participate in activities they may have previously avoided due to pain or risk of complications.
Lower Risk of Emergency Surgery: If a hernia becomes incarcerated or strangulated, emergency surgery may be required. By opting for elective hernia treatment, the risk of an emergency situation can be minimized, allowing for a planned procedure with better outcomes.
Reduced Risk of Recurrence: Surgical repair of a hernia aims to strengthen the weakened area and reduce the chances of recurrence. This can provide long-term relief and decrease the likelihood of future hernias.
Surgical Risks: Surgical hernia repair carries potential risks associated with anesthesia, bleeding, infection, damage to surrounding tissues or organs, and adverse reactions to medications. Complications can include wound infection, blood clots, chronic pain, nerve damage, or hernia recurrence. General Anesthesia Risks: Anesthesia is typically used during surgical hernia repair. While it is generally safe, there are inherent risks, such as allergic reactions, adverse effects on the respiratory or cardiovascular systems, and rare instances of complications resulting in injury or death. Non-Surgical Risks: Non-surgical methods, such as watchful waiting or the use of supportive devices like hernia trusses, may not provide a permanent solution and can have limitations in terms of symptom relief and prevention of complications. Recovery and Downtime: Hernia treatment, particularly surgical repair, requires a recovery period during which physical activity may be limited. This can impact daily routines, work, and other commitments. Individual Factors: The risks and benefits of hernia treatment may vary depending on the individual's overall health, age, the size and type of hernia, and the chosen treatment approach. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help assess the specific risks and benefits in individual cases.

Surgical Risks: Surgical hernia repair carries potential risks associated with anesthesia, bleeding, infection, damage to surrounding tissues or organs, and adverse reactions to medications. Complications can include wound infection, blood clots, chronic pain, nerve damage, or hernia recurrence.
General Anesthesia Risks: Anesthesia is typically used during surgical hernia repair. While it is generally safe, there are inherent risks, such as allergic reactions, adverse effects on the respiratory or cardiovascular systems, and rare instances of complications resulting in injury or death.
Non-Surgical Risks: Non-surgical methods, such as watchful waiting or the use of supportive devices like hernia trusses, may not provide a permanent solution and can have limitations in terms of symptom relief and prevention of complications.
Recovery and Downtime: Hernia treatment, particularly surgical repair, requires a recovery period during which physical activity may be limited. This can impact daily routines, work, and other commitments.
Individual Factors: The risks and benefits of hernia treatment may vary depending on the individual's overall health, age, the size and type of hernia, and the chosen treatment approach. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help assess the specific risks and benefits in individual cases.
After hernia surgery, proper post-operative care is crucial for a successful recovery. This typically includes following the surgeon's instructions, taking prescribed medications, and gradually returning to normal activities as advised. It's important to listen to your body and avoid strenuous activities that could strain the surgical site. Maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and attending follow-up appointments are also essential for monitoring progress and addressing any concerns.

After hernia surgery, proper post-operative care is crucial for a successful recovery. This typically includes following the surgeon's instructions, taking prescribed medications, and gradually returning to normal activities as advised. It's important to listen to your body and avoid strenuous activities that could strain the surgical site. Maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and attending follow-up appointments are also essential for monitoring progress and addressing any concerns.
Visit www.doctorsapp.in to book an appointment today
Please Wait..