Enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a
common condition in which the prostate gland grows in size.
Call us to book an appointment with the best Urology specialist near you.
The prostate gland, a crucial part of the male reproductive system, plays a vital role in semen production. However, as men age, the prostate may undergo changes that result in its enlargement, leading to a condition known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or benign prostatic hypertrophy. An enlarged prostate can cause various symptoms and impact a man's quality of life.
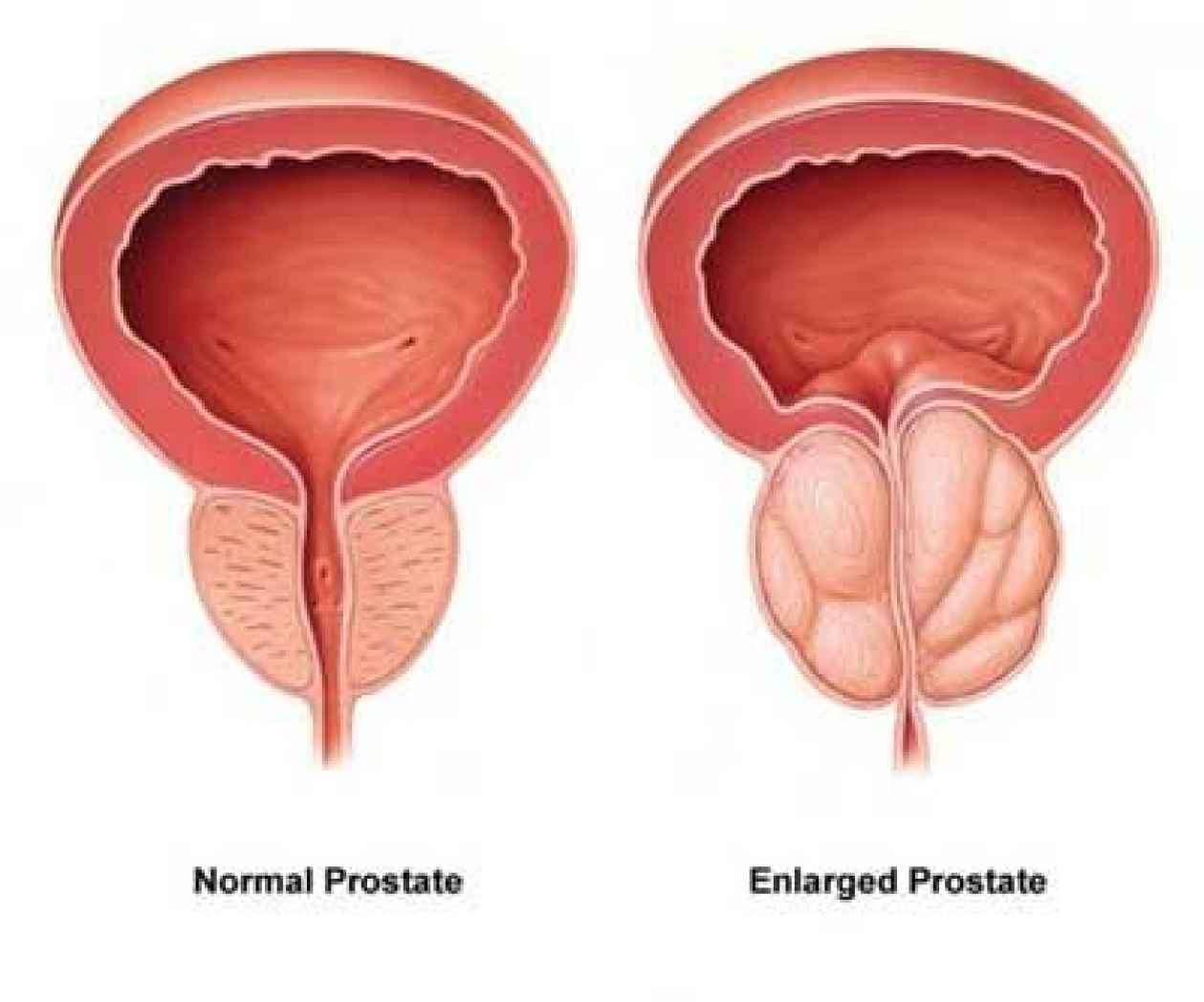
The prostate gland, a crucial part of the male reproductive system, plays a vital role in semen production. However, as men age, the prostate may undergo changes that result in its enlargement, leading to a condition known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or benign prostatic hypertrophy. An enlarged prostate can cause various symptoms and impact a man's quality of life.
Benign prostatic hypertrophy symptoms can vary from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the enlargement. Common symptoms include: 1. Increased Frequency of Urination: Men with an enlarged prostate may experience a sudden urge to urinate frequently, particularly at night (nocturia). This symptom can disrupt sleep patterns and affect overall well-being. 2. Difficulty Initiating and Maintaining Urination: A swollen prostate can obstruct the urethra, making it difficult to start urination or maintain a steady stream. This can lead to dribbling or a weak urine flow. 3. Incomplete Bladder Emptying: The obstruction caused by an enlarged prostate may prevent the bladder from fully emptying, resulting in a sensation of incomplete voiding.
4. Urinary urgency: The urge to urinate may become urgent and difficult to control. This can lead to a frequent need to rush to the restroom.
5. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): In some cases, an enlarged prostate can increase the risk of UTIs due to urine retention and incomplete bladder emptying.

Benign prostatic hypertrophy symptoms can vary from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the enlargement. Common symptoms include:
1. Increased Frequency of Urination: Men with an enlarged prostate may experience a sudden urge to urinate frequently, particularly at night (nocturia). This symptom can disrupt sleep patterns and affect overall well-being.
2. Difficulty Initiating and Maintaining Urination: A swollen prostate can obstruct the urethra, making it difficult to start urination or maintain a steady stream. This can lead to dribbling or a weak urine flow.
3. Incomplete Bladder Emptying: The obstruction caused by an enlarged prostate may prevent the bladder from fully emptying, resulting in a sensation of incomplete voiding.
4. Urinary urgency: The urge to urinate may become urgent and difficult to control. This can lead to a frequent need to rush to the restroom.
5. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): In some cases, an enlarged prostate can increase the risk of UTIs due to urine retention and incomplete bladder emptying.
While the exact reason for prostate gland enlargement is not fully understood, several factors are believed to contribute to the development of BPH. Age is considered the primary risk factor, as the prevalence of an enlarged prostate increases with advancing age. Hormonal imbalances, particularly changes in testosterone and estrogen levels, may also play a role. Other factors that can contribute to prostate enlargement include obesity, family history, and certain genetic factors. When a man experiences symptom of an enlarged prostate, it is essential to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional will perform a thorough evaluation, including a physical examination, medical history review, and possibly additional tests such as a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test or a digital rectal examination (DRE).
While the exact reason for prostate gland enlargement is not fully understood, several factors are believed to contribute to the development of BPH. Age is considered the primary risk factor, as the prevalence of an enlarged prostate increases with advancing age. Hormonal imbalances, particularly changes in testosterone and estrogen levels, may also play a role. Other factors that can contribute to prostate enlargement include obesity, family history, and certain genetic factors.
When a man experiences symptom of an enlarged prostate, it is essential to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional will perform a thorough evaluation, including a physical examination, medical history review, and possibly additional tests such as a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test or a digital rectal examination (DRE).
Treatment options for an enlarged prostate range from watchful waiting to medical interventions or surgical procedures, depending on the severity of symptoms and their impact on the patient's quality of life. In cases where symptoms are mild, a doctor may recommend monitoring the condition without immediate intervention. Lifestyle modifications, such as limiting caffeine and alcohol consumption, and practicing bladder training exercises, may also help manage mild symptoms. If symptoms are moderate to severe, various medications can be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and reduce the size of the prostate. These medications can help relax the muscles of the prostate and bladder neck or inhibit the growth of prostate tissue. Alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors are commonly prescribed medications for BPH. In cases where medications do not provide sufficient relief or if the prostate is significantly enlarged, surgical procedures may be considered. Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is a common surgical technique used to remove excess prostate tissue, relieving urinary obstruction. Other minimally invasive procedures, such as laser ablation or microwave therapy, may also be options for certain patients. It is important to note that not all cases of an enlarged prostate require treatment, and decisions should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional. Regular monitoring of symptoms and routine check-ups can help ensure timely intervention if necessary.
Treatment options for an enlarged prostate range from watchful waiting to medical interventions or surgical procedures, depending on the severity of symptoms and their impact on the patient's quality of life. In cases where symptoms are mild, a doctor may recommend monitoring the condition without immediate intervention. Lifestyle modifications, such as limiting caffeine and alcohol consumption, and practicing bladder training exercises, may also help manage mild symptoms.
If symptoms are moderate to severe, various medications can be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and reduce the size of the prostate. These medications can help relax the muscles of the prostate and bladder neck or inhibit the growth of prostate tissue. Alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors are commonly prescribed medications for BPH.
In cases where medications do not provide sufficient relief or if the prostate is significantly enlarged, surgical procedures may be considered. Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is a common surgical technique used to remove excess prostate tissue, relieving urinary obstruction. Other minimally invasive procedures, such as laser ablation or microwave therapy, may also be options for certain patients.
It is important to note that not all cases of an enlarged prostate require treatment, and decisions should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional. Regular monitoring of symptoms and routine check-ups can help ensure timely intervention if necessary.
Here are the approximate cost ranges for some common treatments for an enlarged prostate in various Indian cities:
1. Medication Therapy:
Cost range: INR 500 to INR 2,000 per month (depending on the specific medications prescribed)
2. Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP):
Minimum Cost: INR 80,000
Average Cost: INR 1,50,000
Maximum Cost: INR 3,00,000
3. GreenLight Laser Surgery:
Minimum Cost:
INR 1,20,000
Average Cost:
INR 2,50,000
Maximum Cost: INR 4,50,000
4. Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP):
Minimum Cost:
INR 1,50,000
Average Cost:
INR 3,00,000
Maximum Cost: INR 5,00,000
5. Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE):
Minimum Cost:
INR 1,50,000
Average Cost:
INR 3,50,000
Maximum Cost: INR 6,00,000
|
Serial No |
Hospital Name |
City |
Contact Number |
|
1 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) |
Multiple Cities |
+91-11-26588500 |
|
2 |
Safdarjung Hospital |
Delhi |
+91-11-2673-0000 |
|
3 |
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research |
Chandigarh |
+91-172-275-6565 |
|
4 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) |
Nagpur |
+91-712-270-1646 |
|
5 |
King George's Medical University (KGMU) |
Lucknow |
+91-522-2257450 |
|
6 |
Madras Medical College |
Chennai |
+91-44-2530-5000 |
|
7 |
Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research |
Kolkata |
+91-33-2204-1000 |
|
8 |
SMS Medical College |
Jaipur |
+91-141-251-8121 |
|
9 |
Government General Hospital |
Vijayawada |
+91-866-257-6000 |
Please Wait..