Balanitis is a common condition characterized by inflammation of the head of the penis (glans) and the foreskin.
Call us to book an appointment with the best Urology specialist near you.
Balanitis is a common condition characterized by the inflammation and swelling of the head of the penis (glans) and the foreskin. It can cause discomfort and various symptoms that may affect the quality of life.
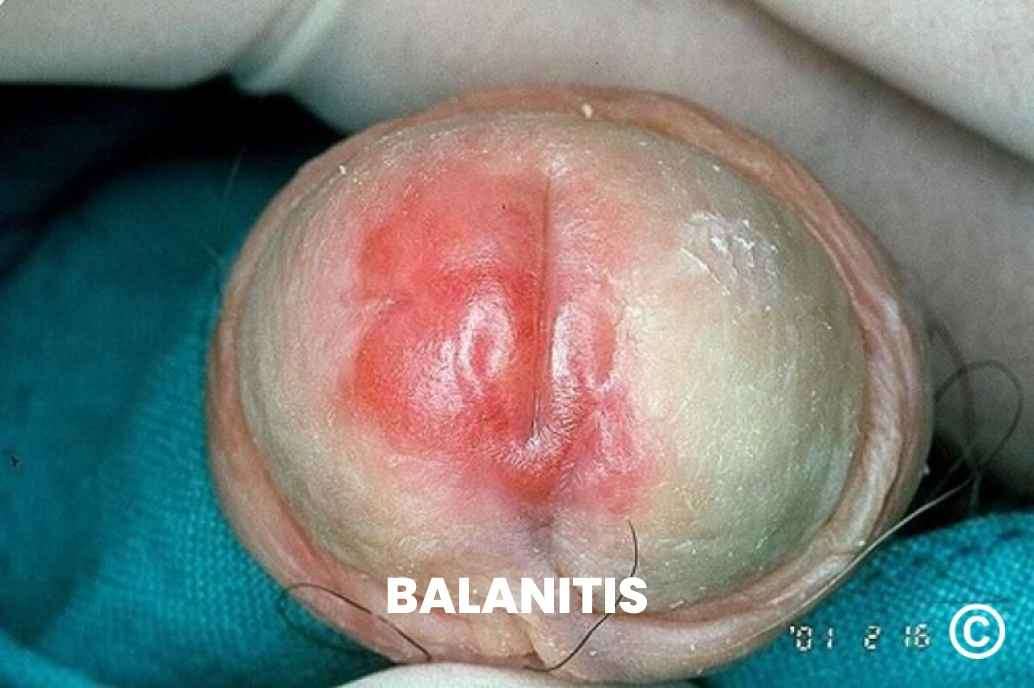
Balanitis is a common condition characterized by the inflammation and swelling of the head of the penis (glans) and the foreskin. It can cause discomfort and various symptoms that may affect the quality of life.
The symptoms of balanitis may vary depending on the underlying cause, but common signs include: 1. Redness and swelling of the glans and foreskin. 2. Itching or a burning sensation in the affected area. 3. Pain or discomfort during urination or sexual activity. 4. Discharge from the penis. 5. Odor or foul smell. 6. Tight or difficult foreskin retraction.

The symptoms of balanitis may vary depending on the underlying cause, but common signs include:
1. Redness and swelling of the glans and foreskin.
2. Itching or a burning sensation in the affected area.
3. Pain or discomfort during urination or sexual activity.
4. Discharge from the penis.
5. Odor or foul smell.
6. Tight or difficult foreskin retraction.
Balanitis can be caused by various factors, including: 1. Poor Hygiene: Inadequate cleaning of the genital area can lead to the accumulation of bacteria, fungi, and other irritants, resulting in inflammation and infection. 2. Candida Balanitis: Candida, a type of yeast, is a common cause of balanitis. It can overgrow in the warm and moist environment under the foreskin, leading to irritation and inflammation. 3. Circinate Balanitis: This form of balanitis is associated with autoimmune conditions such as reactive arthritis or psoriasis. It manifests as raised, red, and scaly patches on the glans or foreskin. 4. Fungal or Bacterial Infections: Fungal or bacterial overgrowth, often due to poor hygiene or exposure to irritants, can contribute to the development of balanitis.
Balanitis can be caused by various factors, including:
1. Poor Hygiene: Inadequate cleaning of the genital area can lead to the accumulation of bacteria, fungi, and other irritants, resulting in inflammation and infection.
2. Candida Balanitis: Candida, a type of yeast, is a common cause of balanitis. It can overgrow in the warm and moist environment under the foreskin, leading to irritation and inflammation.
3. Circinate Balanitis: This form of balanitis is associated with autoimmune conditions such as reactive arthritis or psoriasis. It manifests as raised, red, and scaly patches on the glans or foreskin.
4. Fungal or Bacterial Infections: Fungal or bacterial overgrowth, often due to poor hygiene or exposure to irritants, can contribute to the development of balanitis.
The treatment for balanitis depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Here are some common approaches: 1. Balanitis Cream: Topical creams or ointments may be prescribed to reduce inflammation, relieve itching, and promote healing. Antifungal creams, corticosteroids, or a combination of both may be used based on the cause and severity of balanitis. 2. Balanitis Medication: In cases of fungal or bacterial balanitis, oral medications such as antifungal or antibiotic drugs may be prescribed to combat the underlying infection. Follow your healthcare professional's instructions regarding dosage and duration. 3. Good Hygiene Practices: Maintaining proper hygiene is crucial in preventing and managing balanitis. Clean the genital area with warm water and mild soap, gently retracting the foreskin, if possible, and rinsing thoroughly. Avoid harsh soaps or excessive scrubbing. 4. Balanitis Antibiotics: In bacterial infections or severe cases of balanitis, oral antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate the infection and reduce inflammation. Take the prescribed antibiotics as directed by your healthcare professional. 5. Balanoposthitis Treatment: Balanoposthitis, which involves inflammation of the glans and foreskin, often accompanies balanitis. Treatment for balanoposthitis usually follows similar approaches, including hygiene practices, topical creams, or oral medications. 6. Candidal Balanoposthitis: Candidal balanoposthitis, caused by Candida yeast, may require antifungal medications, either as topical creams or oral formulations, to eliminate the infection and prevent recurrence. 7. Follow-up Care: After treatment, it is important to attend follow-up appointments with your healthcare professional to monitor the condition's progress and ensure complete resolution.
The treatment for balanitis depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Here are some common approaches:
1. Balanitis Cream: Topical creams or ointments may be prescribed to reduce inflammation, relieve itching, and promote healing. Antifungal creams, corticosteroids, or a combination of both may be used based on the cause and severity of balanitis.
2. Balanitis Medication: In cases of fungal or bacterial balanitis, oral medications such as antifungal or antibiotic drugs may be prescribed to combat the underlying infection. Follow your healthcare professional's instructions regarding dosage and duration.
3. Good Hygiene Practices: Maintaining proper hygiene is crucial in preventing and managing balanitis. Clean the genital area with warm water and mild soap, gently retracting the foreskin, if possible, and rinsing thoroughly. Avoid harsh soaps or excessive scrubbing.
4. Balanitis Antibiotics: In bacterial infections or severe cases of balanitis, oral antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate the infection and reduce inflammation. Take the prescribed antibiotics as directed by your healthcare professional.
5. Balanoposthitis Treatment: Balanoposthitis, which involves inflammation of the glans and foreskin, often accompanies balanitis. Treatment for balanoposthitis usually follows similar approaches, including hygiene practices, topical creams, or oral medications.
6. Candidal Balanoposthitis: Candidal balanoposthitis, caused by Candida yeast, may require antifungal medications, either as topical creams or oral formulations, to eliminate the infection and prevent recurrence.
7. Follow-up Care: After treatment, it is important to attend follow-up appointments with your healthcare professional to monitor the condition's progress and ensure complete resolution.
|
Serial No |
City |
Minimum Cost (INR) |
Average Cost (INR) |
|
1 |
Mumbai |
2,000 |
7,000 |
|
2 |
Delhi |
1,800 |
6,500 |
|
3 |
Bangalore |
1,500 |
5,000 |
|
4 |
Chennai |
1,500 |
5,000 |
|
5 |
Kolkata |
1,200 |
4,500 |
|
6 |
Hyderabad |
1,200 |
4,500 |
|
7 |
Pune |
1,000 |
3,500 |
|
8 |
Ahmedabad |
1,000 |
3,500 |
|
9 |
Jaipur |
900 |
3,000 |
|
10 |
Chandigarh |
900 |
3,000 |
|
11 |
Lucknow |
800 |
2,500 |
|
12 |
Indore |
800 |
2,500 |
|
13 |
Kochi |
700 |
2,000 |
|
14 |
Coimbatore |
700 |
2,000 |
|
15 |
Bhopal |
600 |
1,800 |
|
16 |
Nagpur |
600 |
1,800 |
|
17 |
Goa |
500 |
1,500 |
|
18 |
Mangalore |
500 |
1,500 |
|
19 |
Trivandrum |
400 |
1,200 |
|
20 |
Guwahati |
400 |
1,200 |
|
Serial No |
Hospital Name |
City |
Contact Number |
|
1 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) |
Multiple Cities |
+91-11-26588500 |
|
2 |
Safdarjung Hospital |
Delhi |
+91-11-2673-0000 |
|
3 |
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research |
Chandigarh |
+91-172-275-6565 |
|
4 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) |
Nagpur |
+91-712-270-1646 |
|
5 |
King George's Medical University (KGMU) |
Lucknow |
+91-522-2257450 |
|
6 |
Madras Medical College |
Chennai |
+91-44-2530-5000 |
|
7 |
Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research |
Kolkata |
+91-33-2204-1000 |
|
8 |
SMS Medical College |
Jaipur |
+91-141-251-8121 |
|
9 |
Government General Hospital |
Vijayawada |
+91-866-257-6000 |
Please Wait..