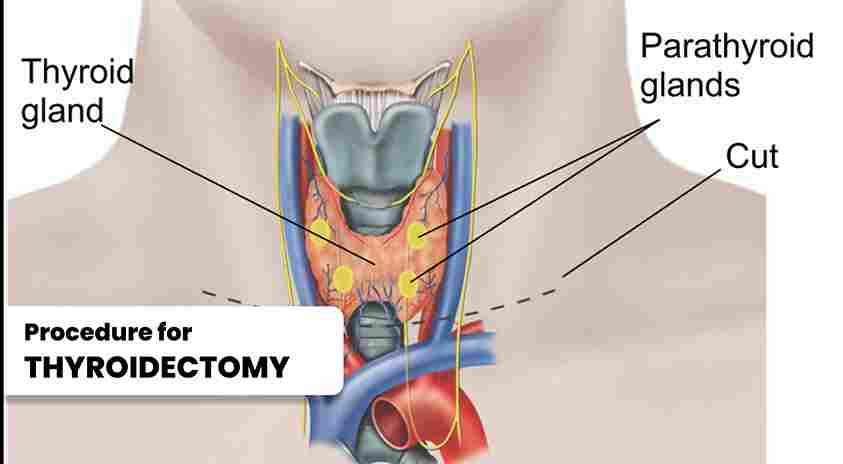
Thyroidectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the partial or total removal of the thyroid gland.
It is essential to consult with an endocrinologist or a surgeon specializing in thyroid surgery. Call us to book a appointment with the best Endocrinologist specialist near you.
Understanding Thyroidectomy Thyroidectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of part (subtotal thyroidectomy) or the entire thyroid gland (total thyroidectomy). The specific extent of the surgery depends on the underlying condition and the surgeon's assessment. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient's comfort and safety.
Thyroidectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of part (subtotal thyroidectomy) or the entire thyroid gland (total thyroidectomy). The specific extent of the surgery depends on the underlying condition and the surgeon's assessment. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient's comfort and safety.
Thyroidectomy may be recommended for various reasons, including: Thyroid Cancer: Thyroidectomy is often the primary treatment for thyroid cancer. It involves removing the affected thyroid lobe or the entire thyroid gland, along with any affected lymph nodes in the neck. Benign Thyroid Nodules: Large or symptomatic benign thyroid nodules that cause discomfort or difficulty swallowing may be surgically removed. Hyperthyroidism: In cases of hyperthyroidism that do not respond to medication or other treatments, thyroidectomy may be performed to remove the overactive thyroid gland. Goiter removal: When the thyroid gland becomes enlarged, causing symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swallowing, or speaking, thyroidectomy may be necessary to alleviate these symptoms.

Thyroidectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of part (subtotal thyroidectomy) or the entire thyroid gland (total thyroidectomy). The specific extent of the surgery depends on the underlying condition and the surgeon's assessment. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient's comfort and safety.
Thyroidectomy may be recommended for various reasons, including:
Thyroid Cancer: Thyroidectomy is often the primary treatment for thyroid cancer. It involves removing the affected thyroid lobe or the entire thyroid gland, along with any affected lymph nodes in the neck.
Benign Thyroid Nodules: Large or symptomatic benign thyroid nodules that cause discomfort or difficulty swallowing may be surgically removed.
Hyperthyroidism: In cases of hyperthyroidism that do not respond to medication or other treatments, thyroidectomy may be performed to remove the overactive thyroid gland.
Goiter removal: When the thyroid gland becomes enlarged, causing symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swallowing, or speaking, thyroidectomy may be necessary to alleviate these symptoms.
After thyroidectomy, patients are typically observed in the hospital for a day or two to monitor their recovery and ensure that the calcium levels remain stable. Most patients experience mild to moderate pain or discomfort in the neck area, which can be managed with pain medications. The surgeon may prescribe thyroid hormone replacement medication to maintain normal thyroid hormone levels in the body. It is important to follow the post-operative instructions provided by the surgeon, including wound care, activity restrictions, and any necessary dietary modifications.
After thyroidectomy, patients are typically observed in the hospital for a day or two to monitor their recovery and ensure that the calcium levels remain stable. Most patients experience mild to moderate pain or discomfort in the neck area, which can be managed with pain medications. The surgeon may prescribe thyroid hormone replacement medication to maintain normal thyroid hormone levels in the body. It is important to follow the post-operative instructions provided by the surgeon, including wound care, activity restrictions, and any necessary dietary modifications.
Regular follow-up visits with the surgeon are crucial after thyroidectomy. These visits allow for monitoring of the surgical site, assessment of hormone levels, and evaluation of overall recovery. Depending on the specific condition, some patients may require lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy to maintain normal thyroid function. The dosage and frequency of hormone replacement will be determined by the physician based on blood tests and individual needs.

Regular follow-up visits with the surgeon are crucial after thyroidectomy. These visits allow for monitoring of the surgical site, assessment of hormone levels, and evaluation of overall recovery. Depending on the specific condition, some patients may require lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy to maintain normal thyroid function. The dosage and frequency of hormone replacement will be determined by the physician based on blood tests and individual needs.
Total Thyroidectomy: Procedure, the entire thyroid gland is removed. It is typically performed to treat thyroid cancer, large goiters, Graves' disease, or when there is a high risk of thyroid cancer. Partial Thyroidectomy/Hemithyroidectomy: This surgery involves the removal of one lobe (half) of the thyroid gland. It is commonly performed when there is a benign tumor or nodules present in one lobe, or in cases where only one lobe is affected by thyroid cancer. Subtotal Thyroidectomy: Also known as near-total thyroidectomy, this procedure involves the removal of almost all of the thyroid gland, leaving a small amount of thyroid tissue behind. It is sometimes performed in cases of large goiters or when there are multiple nodules or tumors in both lobes. Lobectomy: Lobectomy involves the removal of a single lobe of the thyroid gland. It is typically performed when there is a solitary thyroid nodule or a suspicious tumor confined to one lobe.
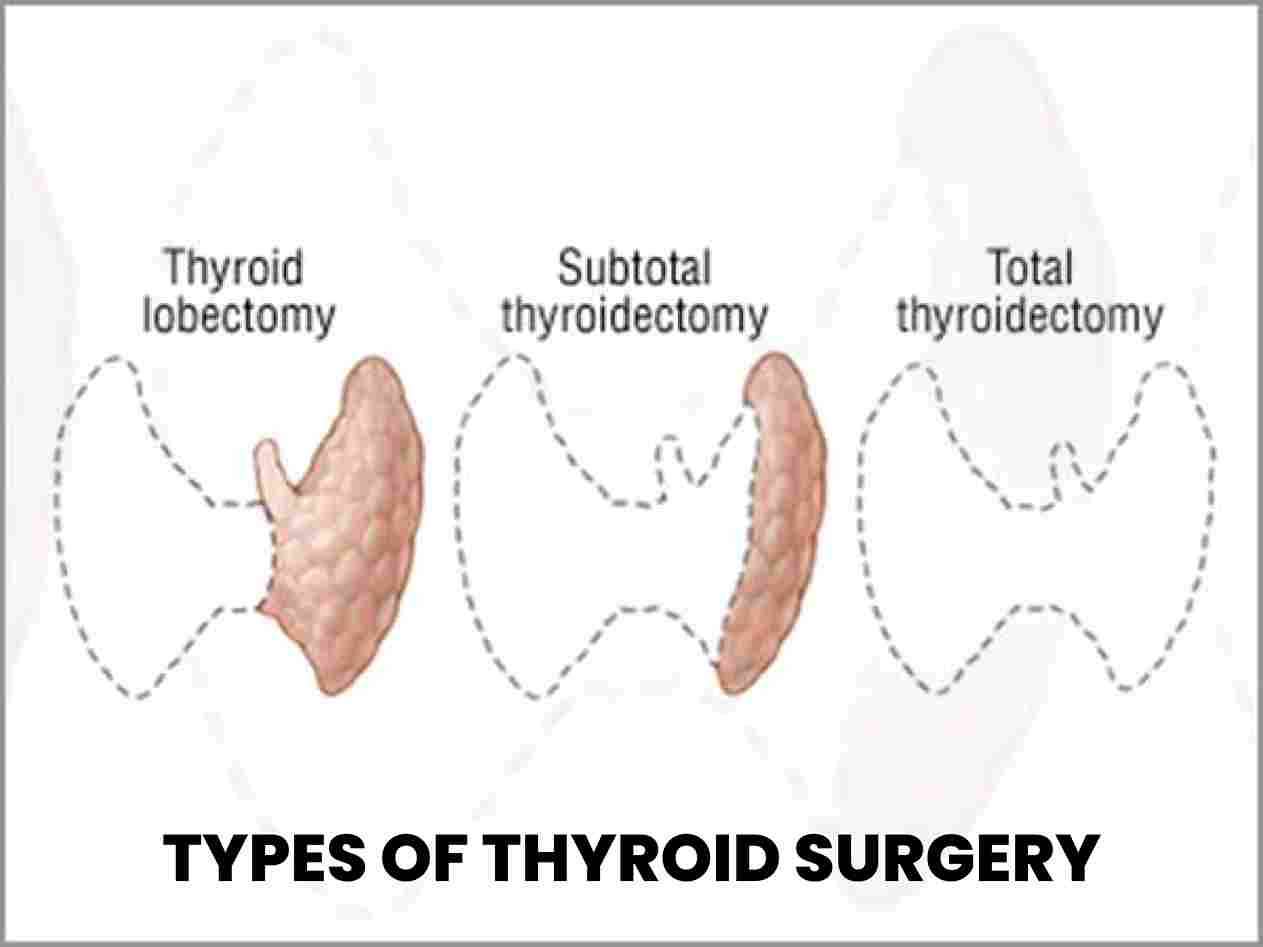
Total Thyroidectomy:
Procedure, the entire thyroid gland is removed. It is typically performed to treat thyroid cancer, large goiters, Graves' disease, or when there is a high risk of thyroid cancer.
Partial Thyroidectomy/Hemithyroidectomy:
This surgery involves the removal of one lobe (half) of the thyroid gland. It is commonly performed when there is a benign tumor or nodules present in one lobe, or in cases where only one lobe is affected by thyroid cancer.
Subtotal Thyroidectomy:
Also known as near-total thyroidectomy, this procedure involves the removal of almost all of the thyroid gland, leaving a small amount of thyroid tissue behind. It is sometimes performed in cases of large goiters or when there are multiple nodules or tumors in both lobes.
Lobectomy:
Lobectomy involves the removal of a single lobe of the thyroid gland. It is typically performed when there is a solitary thyroid nodule or a suspicious tumor confined to one lobe.
Please Wait..