Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop within or on the surface of the ovaries. While most ovarian cysts are benign and resolve on their own without causing any symptoms or complications, some cysts can cause pain and discomfort, requiring medical attention.
Functional cysts: The majority of ovarian cysts fall into this category and are typically related to the normal functioning of the ovaries during the menstrual cycle. The two main types of functional cysts are:
Follicular cysts: These cysts form when a follicle (a sac containing an egg) doesn't release the egg during ovulation or doesn't dissolve after the egg is released.
Corpus luteum cysts: These cysts develop when the follicle releases the egg but doesn't properly shrink afterward.
Dermoid cysts: Also known as mature cystic teratomas, these cysts are formed from embryonic cells and can contain various types of tissue, including hair, skin, teeth, or even bone.
Cystadenomas: These cysts form from the outer surface of the ovary and can be filled with a watery or mucous-like fluid. They are usually benign but can grow quite large.
Endometriomas: These cysts develop as a result of endometriosis, a condition in which the tissue that normally lines the uterus grows outside the uterus. Endometriomas are filled with old blood and can cause pain.
Visit www.doctorsapp.in to know more
Ovarian cysts may manifest with different signs and symptoms, depending on their size, type, and location. Some women may experience the following: Ovarian pain location: The pain associated with ovarian cysts is typically felt on one side of the lower abdomen or pelvis, depending on which ovary is affected. Twisted ovarian cyst: In some cases, an ovarian cyst can become twisted, leading to intense abdominal pain and potential complications. This condition, known as ovarian torsion, requires immediate medical attention. Ruptured cyst symptoms: A ruptured ovarian cyst can cause sudden, severe pain in the lower abdomen. Other symptoms may include vaginal bleeding, nausea, and dizziness.
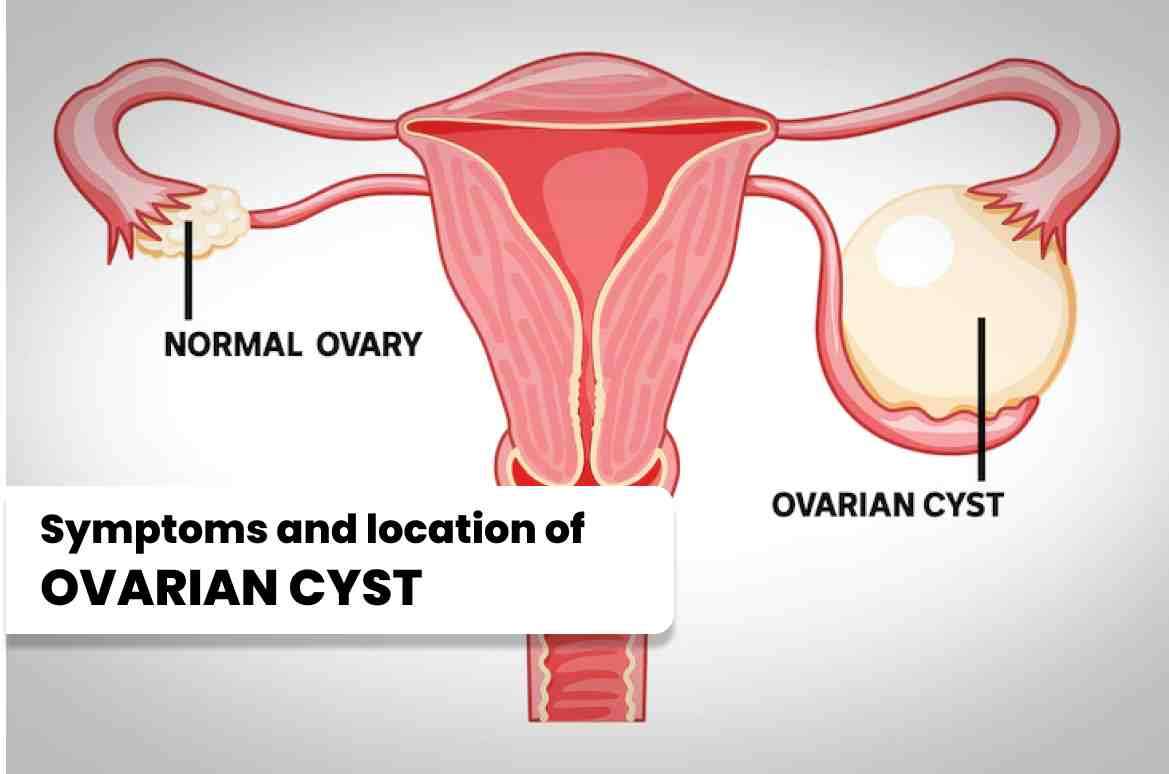
Ovarian cysts may manifest with different signs and symptoms, depending on their size, type, and location. Some women may experience the following:
Ovarian pain location: The pain associated with ovarian cysts is typically felt on one side of the lower abdomen or pelvis, depending on which ovary is affected.
Twisted ovarian cyst: In some cases, an ovarian cyst can become twisted, leading to intense abdominal pain and potential complications. This condition, known as ovarian torsion, requires immediate medical attention.
Ruptured cyst symptoms: A ruptured ovarian cyst can cause sudden, severe pain in the lower abdomen. Other symptoms may include vaginal bleeding, nausea, and dizziness.
Signs and symptoms of ovarian cyst during pregnancy: Ovarian cysts can occur during pregnancy and may present with similar symptoms. However, the presence of an ovarian cyst during pregnancy requires close monitoring by healthcare professionals.
If a healthcare provider suspects the presence of an ovarian cyst, they may recommend several diagnostic tests, including: Pelvic examination: A physical examination of the pelvis can help detect the presence of ovarian cysts or any abnormalities. Imaging tests: Ultrasound imaging is commonly used to visualize and assess the size, shape, and composition of ovarian cysts. Laparoscopy: In some cases, a laparoscopy, a minimally invasive surgical procedure, may be performed to directlyvisualize and diagnose ovarian cysts.
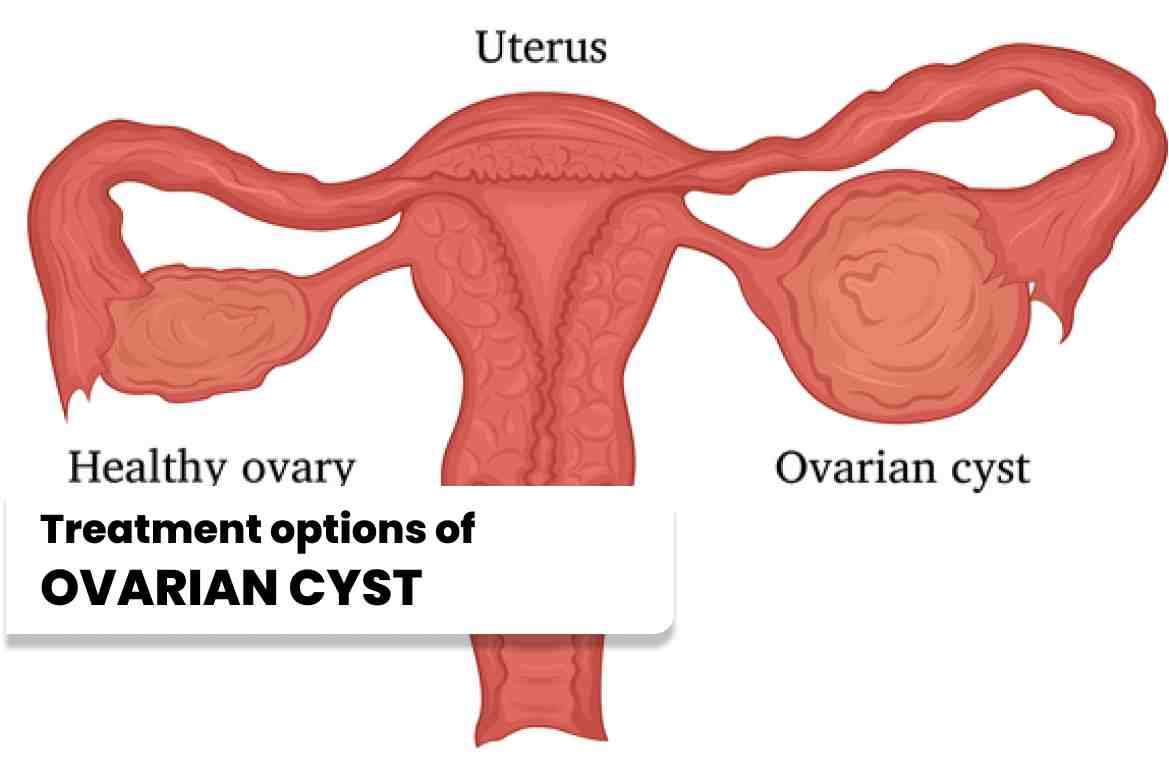
Ovarian Cysts Treatment options
Observation: Small, asymptomatic cysts may simply be monitored over time to ensure they resolve on their own without intervention. Medication: Hormonal contraceptives or other medications can help regulate hormone levels and prevent the formation of new cysts. Ovarian cyst removal: If the cyst is large, causing severe symptoms, or is potentially cancerous, surgical removal may be recommended. This procedure, known as an ovarian laparoscopic cystectomy, can be performed using laparoscopic techniques.
If a healthcare provider suspects the presence of an ovarian cyst, they may recommend several diagnostic tests, including:
Pelvic examination: A physical examination of the pelvis can help detect the presence of ovarian cysts or any abnormalities.
Imaging tests: Ultrasound imaging is commonly used to visualize and assess the size, shape, and composition of ovarian cysts.
Laparoscopy: In some cases, a laparoscopy, a minimally invasive surgical procedure, may be performed to directlyvisualize and diagnose ovarian cysts.
Ovarian Cysts Treatment options
Observation: Small, asymptomatic cysts may simply be monitored over time to ensure they resolve on their own without intervention.
Medication: Hormonal contraceptives or other medications can help regulate hormone levels and prevent the formation of new cysts.
Ovarian cyst removal: If the cyst is large, causing severe symptoms, or is potentially cancerous, surgical removal may be recommended. This procedure, known as an ovarian laparoscopic cystectomy, can be performed using laparoscopic techniques.
While ovarian cyst removal is generally safe, there are potential risks and side effects associated with the procedure. These may include: Infection Bleeding Injury to surrounding structures Adhesions (scar tissue formation) Recurrence of cysts It is important for individuals to discuss the potential risks and benefits of ovarian cyst removal with their healthcare provider before making a decision.

While ovarian cyst removal is generally safe, there are potential risks and side effects associated with the procedure. These may include:
Infection
Bleeding
Injury to surrounding structures
Adhesions (scar tissue formation)
Recurrence of cysts
It is important for individuals to discuss the potential risks and benefits of ovarian cyst removal with their healthcare provider before making a decision.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that can cause the formation of multiple cysts on the ovaries. It is characterized by symptoms such as irregular periods, excessive hair growth, acne, and fertility issues. Poly cystic ovaries require comprehensive management, including lifestyle changes, medication, and sometimes assisted reproductive techniques.
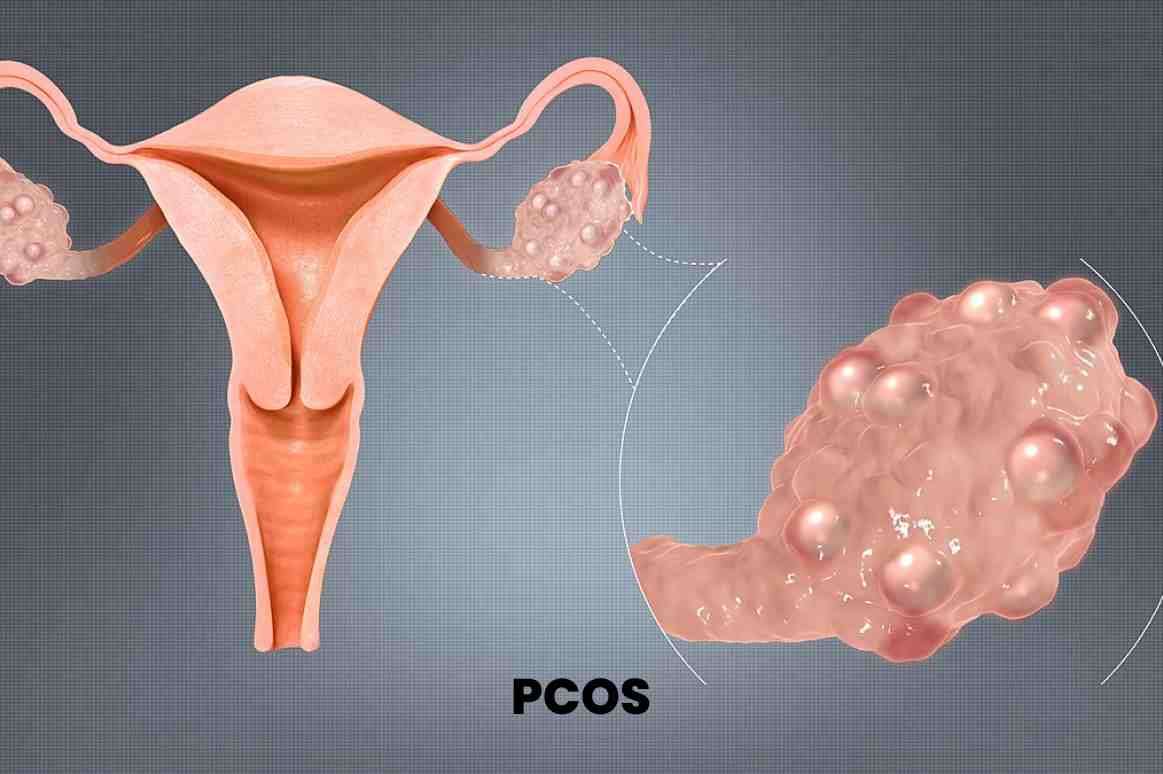
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that can cause the formation of multiple cysts on the ovaries. It is characterized by symptoms such as irregular periods, excessive hair growth, acne, and fertility issues. Poly cystic ovaries require comprehensive management, including lifestyle changes, medication, and sometimes assisted reproductive techniques.
Please Wait..