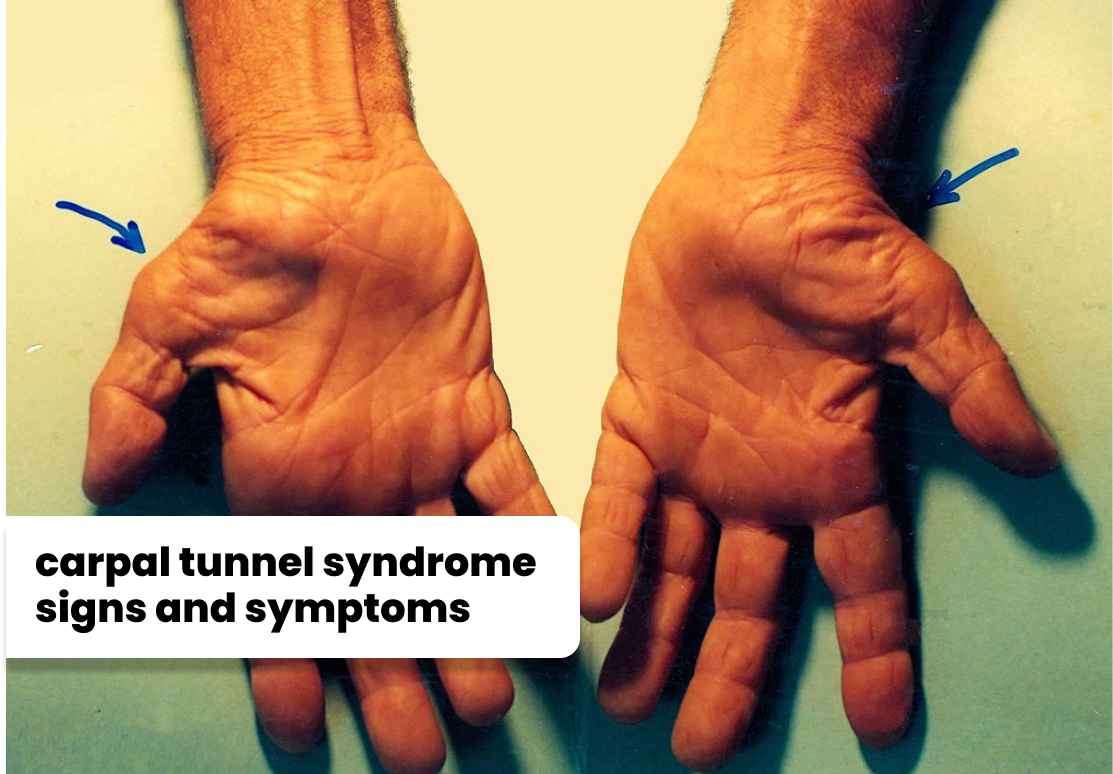
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a condition that affects the hand and wrist.
Call us to book a appointment with the best Ortho specialist near you.
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm to the hand, becomes compressed or squeezed as it passes through the carpal tunnela narrow passageway in the wrist. This compression can result in various symptoms, such as pain, tingling, numbness, and weakness in the hand and fingers. In some cases, the syndrome can affect both hands simultaneously, leading to bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome.
.jpg)
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm to the hand, becomes compressed or squeezed as it passes through the carpal tunnela narrow passageway in the wrist. This compression can result in various symptoms, such as pain, tingling, numbness, and weakness in the hand and fingers. In some cases, the syndrome can affect both hands simultaneously, leading to bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome.
Bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome can be caused by several factors. Repetitive hand movements, especially those involving the use of vibrating tools or the performance of tasks requiring a tight grip, can contribute to the development of the syndrome. Other potential causes include wrist injuries, arthritis, diabetes, hormonal changes during pregnancy, and certain health conditions like hypothyroidism.

Bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome can be caused by several factors. Repetitive hand movements, especially those involving the use of vibrating tools or the performance of tasks requiring a tight grip, can contribute to the development of the syndrome. Other potential causes include wrist injuries, arthritis, diabetes, hormonal changes during pregnancy, and certain health conditions like hypothyroidism.

Fortunately, there are various treatment options available for managing bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms and the underlying causes. Here are some commonly used approaches: 1. Surgical Therapies for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery: In cases where conservative measures have failed to provide relief, carpal tunnel release surgery may be recommended. This surgical procedure involves cutting the ligament that forms the roof of the carpal tunnel, thus relieving pressure on the median nerve. Bilateral carpal tunnel release surgery may be performed simultaneously or staged, with one hand operated on at a time. 2. Non-Surgical Therapies for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Non-surgical therapies are often the first line of treatment for bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome. These may include: a. Wrist Splints for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Wearing wrist splints can help keep the wrists in a neutral position, reducing pressure on the median nerve and providing relief from symptoms. Splints are commonly worn during sleep or activities that aggravate the condition. b. Stretching Exercises for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Certain stretching exercises can improve flexibility and reduce discomfort associated with carpal tunnel syndrome. These exercises target the muscles and tendons in the hands and wrists, helping to alleviate compression on the median nerve. c. Self-Care Techniques for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Practicing self-care techniques such as taking regular breaks during repetitive activities, applying cold packs to reduce inflammation, and maintaining proper ergonomics can also contribute to symptom relief. 3. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome during Pregnancy: Pregnancy-related carpal tunnel syndrome often resolves on its own after childbirth. In the meantime, non-surgical approaches like splinting, exercises, and modifications in daily activities can provide relief. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any treatment during pregnancy.
Fortunately, there are various treatment options available for managing bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms and the underlying causes. Here are some commonly used approaches:
1. Surgical Therapies for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery: In cases where conservative measures have failed to provide relief, carpal tunnel release surgery may be recommended. This surgical procedure involves cutting the ligament that forms the roof of the carpal tunnel, thus relieving pressure on the median nerve. Bilateral carpal tunnel release surgery may be performed simultaneously or staged, with one hand operated on at a time.
2. Non-Surgical Therapies for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
Non-surgical therapies are often the first line of treatment for bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome. These may include:
a. Wrist Splints for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Wearing wrist splints can help keep the wrists in a neutral position, reducing pressure on the median nerve and providing relief from symptoms. Splints are commonly worn during sleep or activities that aggravate the condition.
b. Stretching Exercises for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Certain stretching exercises can improve flexibility and reduce discomfort associated with carpal tunnel syndrome. These exercises target the muscles and tendons in the hands and wrists, helping to alleviate compression on the median nerve.
c. Self-Care Techniques for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Practicing self-care techniques such as taking regular breaks during repetitive activities, applying cold packs to reduce inflammation, and maintaining proper ergonomics can also contribute to symptom relief.
3. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome during Pregnancy: Pregnancy-related carpal tunnel syndrome often resolves on its own after childbirth. In the meantime, non-surgical approaches like splinting, exercises, and modifications in daily activities can provide relief. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any treatment during pregnancy.
To minimize the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome or prevent its recurrence, individuals can adopt certain self-care measures: a. Maintain good posture and ergonomics while performing tasks involving repetitive hand movements. b. Take frequent breaks to rest and stretch the hands and wrists. c. Avoid excessive force or prolonged gripping of objects.
d. Keep the wrists in a neutral position during activities, avoiding extreme flexion or extension.
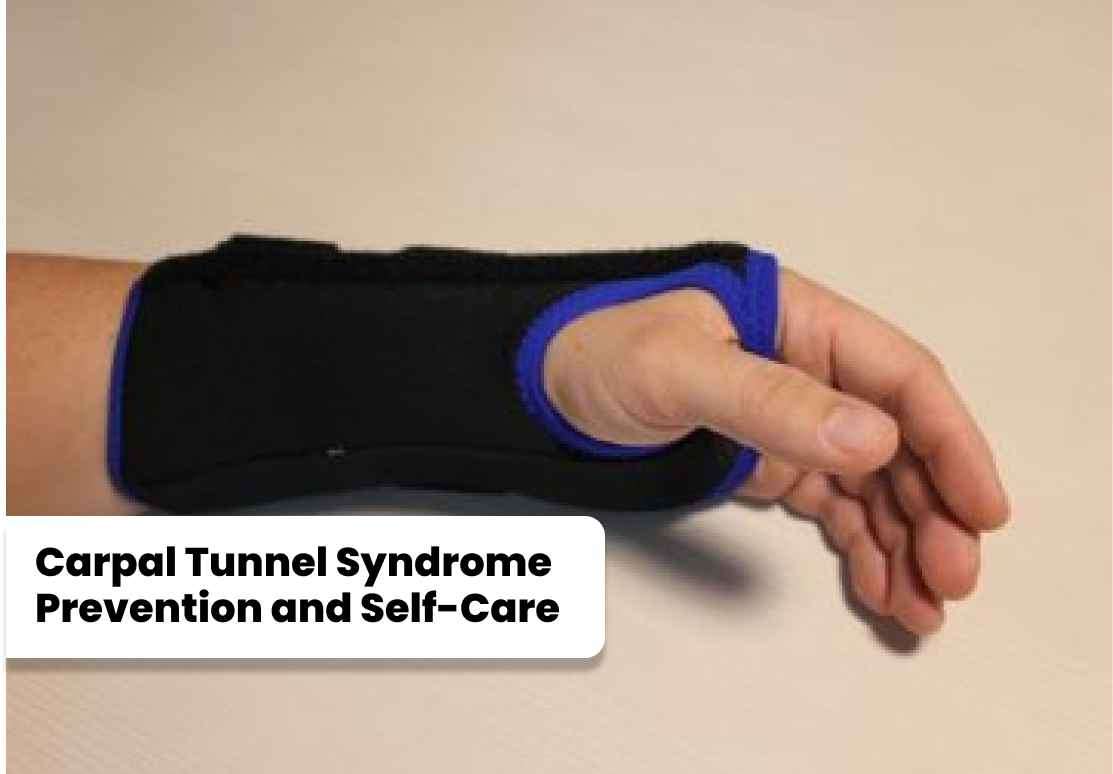
To minimize the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome or prevent its recurrence, individuals can adopt certain self-care measures:
a. Maintain good posture and ergonomics while performing tasks involving repetitive hand movements.
b. Take frequent breaks to rest and stretch the hands and wrists.
c. Avoid excessive force or prolonged gripping of objects.
d. Keep the wrists in a neutral position during activities, avoiding extreme flexion or extension.
|
Serial No |
City |
Minimum Cost (INR) |
Average Cost (INR) |
|
1 |
Mumbai |
20,000 |
45,000 |
|
2 |
Delhi |
18,000 |
40,000 |
|
3 |
Bangalore |
15,000 |
35,000 |
|
4 |
Chennai |
15,000 |
35,000 |
|
5 |
Kolkata |
14,000 |
30,000 |
|
6 |
Hyderabad |
14,000 |
30,000 |
|
7 |
Pune |
14,000 |
30,000 |
|
8 |
Ahmedabad |
12,000 |
25,000 |
|
9 |
Jaipur |
12,000 |
25,000 |
|
10 |
Chandigarh |
12,000 |
25,000 |
|
11 |
Lucknow |
10,000 |
22,000 |
|
12 |
Indore |
10,000 |
22,000 |
|
13 |
Kochi |
10,000 |
20,000 |
|
14 |
Coimbatore |
10,000 |
20,000 |
|
15 |
Bhopal |
9,000 |
18,000 |
|
16 |
Nagpur |
9,000 |
18,000 |
|
17 |
Goa |
8,000 |
16,000 |
|
18 |
Mangalore |
8,000 |
16,000 |
|
19 |
Trivandrum |
8,000 |
16,000 |
|
20 |
Guwahati |
7,000 |
14,000 |
|
Serial No |
Hospital Name |
Address |
Contact Number |
|
1 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) |
Ansari Nagar, Aurobindo Marg, New Delhi - 110029 |
+91-11-26588500 |
|
2 |
Safdarjung Hospital |
Safdarjung Campus, Ansari Nagar, New Delhi - 110029 |
+91-11-26165060 |
|
3 |
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER) |
Sector-12, Chandigarh - 160012 |
+91-172-2747585 |
|
4 |
King George's Medical University (KGMU) |
Chowk, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226003 |
+91-522-2257450 |
|
5 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) |
Saket Nagar, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh - 462020 |
+91-755-2672355 |
|
6 |
Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences (NIMS) |
Punjagutta, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500082 |
+91-40-23489000 |
|
7 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) |
Sector 32, Chandigarh - 160030 |
+91-172-2601023 |
|
8 |
Institute of Medical Sciences (IMS), Banaras Hindu University (BHU) |
Lanka, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh - 221005 |
+91-542-2367568 |
|
9 |
Osmania General Hospital |
Afzal Gunj, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500012 |
+91-40-24600146 |
|
10 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) |
Sector 32, Chandigarh - 160030 |
+91-172-2601023 |
Please Wait..