Turbinate reduction, also known as turbinate surgery or turbinate
resection, is a surgical procedure performed to alleviate nasal
congestion and improve nasal breathing.
Call us to book an appointment with the best Otolaryngologist-Ear, Nose,
and Throat (ENT) specialist or a Sinus Surgeon near you.
Turbinate reduction is a surgical procedure aimed at addressing nasal turbinate issues and improving nasal airflow. The turbinates are structures located inside the nasal passages that help regulate airflow and humidify the air we breathe. However, when the turbinates become enlarged or swollen due to various factors, they can cause nasal congestion, breathing difficulties, and other related symptoms. Turbinate hypertrophy refers to the condition where the inferior turbinates, the structures located on the sides of the nasal passages, become enlarged. This enlargement can be caused by several factors, including allergies, chronic sinusitis, nasal polyps, or structural abnormalities in the nasal passages. When the inferior turbinates are enlarged, they can obstruct airflow, leading to nasal congestion, difficulty breathing through the nose, snoring, and disrupted sleep patterns.
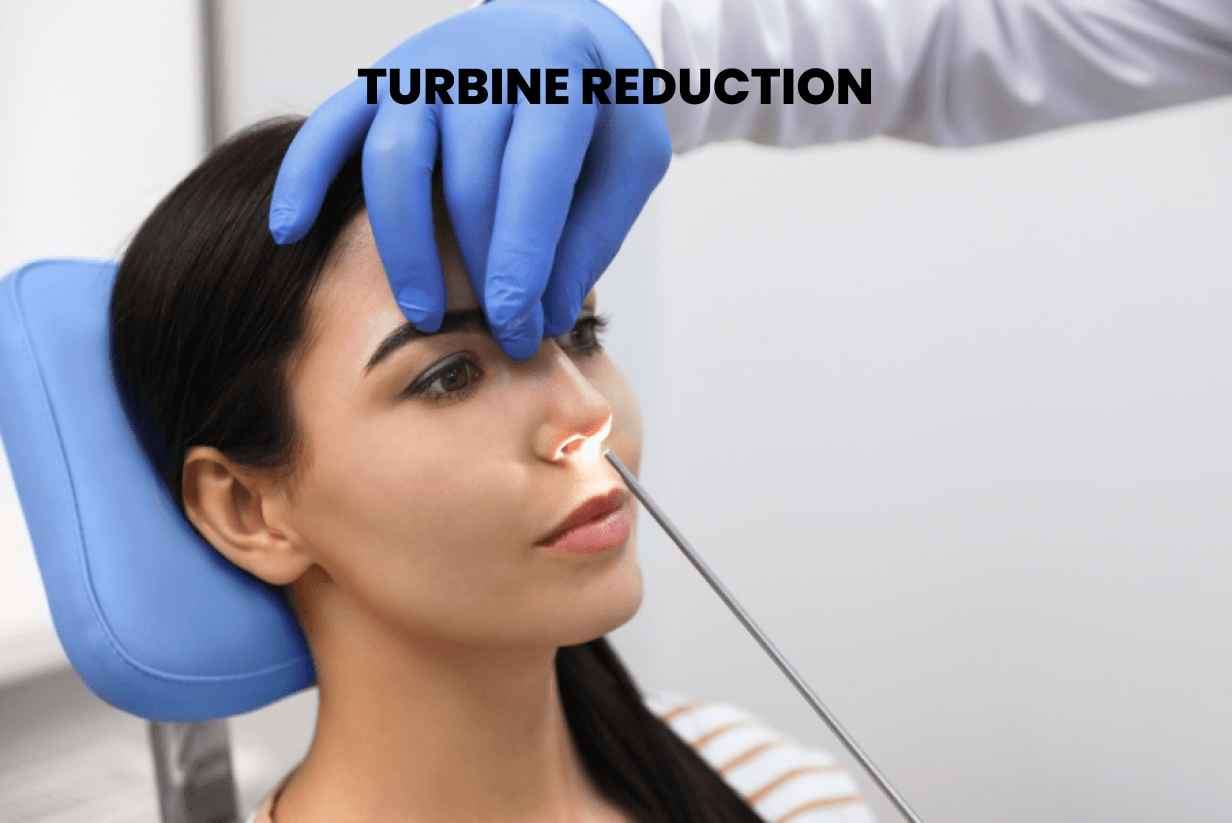
Turbinate reduction is a surgical procedure aimed at addressing nasal turbinate issues and improving nasal airflow. The turbinates are structures located inside the nasal passages that help regulate airflow and humidify the air we breathe. However, when the turbinates become enlarged or swollen due to various factors, they can cause nasal congestion, breathing difficulties, and other related symptoms.
Turbinate hypertrophy refers to the condition where the inferior turbinates, the structures located on the sides of the nasal passages, become enlarged. This enlargement can be caused by several factors, including allergies, chronic sinusitis, nasal polyps, or structural abnormalities in the nasal passages. When the inferior turbinates are enlarged, they can obstruct airflow, leading to nasal congestion, difficulty breathing through the nose, snoring, and disrupted sleep patterns.
1. Submucosal Turbinate Reduction: This technique involves making incisions inside the nasal passages to access the underlying turbinate tissue. The surgeon then removes a portion of the tissue or uses radiofrequency ablation or other energy-based devices to shrink the turbinates. The goal is to reduce the size of the turbinates while preserving their essential functions.
2. Turbinate Cauterization: In this procedure, the surgeon uses a heated instrument, such as a cautery or laser, to reduce the size of the turbinate tissue. The heat energy is applied to the turbinate, causing controlled tissue damage and subsequent reduction in size. 3. Partial Turbinate Resection: In cases where the turbinates are significantly enlarged, a portion of the turbinate tissue may be surgically removed. This procedure is typically reserved for severe cases or when other conservative measures have not provided sufficient relief. Before undergoing turbinate reduction surgery, it is crucial to have a thorough evaluation by an otolaryngologist or ENT specialist. The surgeon will assess the individual's nasal anatomy, perform diagnostic tests if necessary, and discuss the potential benefits and risks of the procedure. After turbinate reduction surgery, individuals often experience a significant improvement in nasal airflow and a reduction in nasal congestion. Breathing through the nose becomes easier, leading to better sleep quality and an overall improvement in the quality of life. It is important to note that the results of turbinate reduction can vary from person to person, and full recovery may take some time. Before undergoing turbinate reduction surgery, it is common for individuals to have a nasal passage that is obstructed and narrowed due to enlarged turbinates. This can lead to chronic nasal congestion and difficulty breathing through the nose. However, after the surgery, the reduced size of the turbinates allows for improved airflow, reduced congestion, and easier nasal breathing. The recovery period after turbinate reduction surgery can vary depending on the individual and the extent of the procedure. It is common to experience some temporary swelling, congestion, and mild discomfort in the first few weeks after surgery. The surgeon may prescribe pain medication and recommend nasal saline rinses to help alleviate these symptoms and promote healing.

1. Submucosal Turbinate Reduction: This technique involves making incisions inside the nasal passages to access the underlying turbinate tissue. The surgeon then removes a portion of the tissue or uses radiofrequency ablation or other energy-based devices to shrink the turbinates. The goal is to reduce the size of the turbinates while preserving their essential functions.
2. Turbinate Cauterization: In this procedure, the surgeon uses a heated instrument, such as a cautery or laser, to reduce the size of the turbinate tissue. The heat energy is applied to the turbinate, causing controlled tissue damage and subsequent reduction in size.
3. Partial Turbinate Resection: In cases where the turbinates are significantly enlarged, a portion of the turbinate tissue may be surgically removed. This procedure is typically reserved for severe cases or when other conservative measures have not provided sufficient relief.
Before undergoing turbinate reduction surgery, it is crucial to have a thorough evaluation by an otolaryngologist or ENT specialist. The surgeon will assess the individual's nasal anatomy, perform diagnostic tests if necessary, and discuss the potential benefits and risks of the procedure.
After turbinate reduction surgery, individuals often experience a significant improvement in nasal airflow and a reduction in nasal congestion. Breathing through the nose becomes easier, leading to better sleep quality and an overall improvement in the quality of life. It is important to note that the results of turbinate reduction can vary from person to person, and full recovery may take some time.
Before undergoing turbinate reduction surgery, it is common for individuals to have a nasal passage that is obstructed and narrowed due to enlarged turbinates. This can lead to chronic nasal congestion and difficulty breathing through the nose. However, after the surgery, the reduced size of the turbinates allows for improved airflow, reduced congestion, and easier nasal breathing.
The recovery period after turbinate reduction surgery can vary depending on the individual and the extent of the procedure. It is common to experience some temporary swelling, congestion, and mild discomfort in the first few weeks after surgery. The surgeon may prescribe pain medication and recommend nasal saline rinses to help alleviate these symptoms and promote healing.
|
Serial No |
City |
Minimum Cost (INR) |
Average Cost (INR) |
|
1 |
Mumbai |
20,000 |
60,000 |
|
2 |
Delhi |
18,000 |
50,000 |
|
3 |
Bangalore |
15,000 |
45,000 |
|
4 |
Chennai |
14,000 |
40,000 |
|
5 |
Kolkata |
12,000 |
35,000 |
|
6 |
Hyderabad |
12,000 |
35,000 |
|
7 |
Pune |
10,000 |
30,000 |
|
8 |
Ahmedabad |
10,000 |
30,000 |
|
9 |
Jaipur |
8,000 |
25,000 |
|
10 |
Chandigarh |
8,000 |
25,000 |
|
11 |
Lucknow |
7,000 |
20,000 |
|
12 |
Indore |
7,000 |
20,000 |
|
13 |
Kochi |
6,000 |
18,000 |
|
14 |
Coimbatore |
6,000 |
18,000 |
|
15 |
Bhopal |
5,000 |
15,000 |
|
16 |
Nagpur |
5,000 |
15,000 |
|
17 |
Goa |
4,000 |
12,000 |
|
18 |
Mangalore |
4,000 |
12,000 |
|
19 |
Trivandrum |
3,000 |
10,000 |
|
20 |
Guwahati |
3,000 |
10,000 |
|
Serial No |
Hospital Name |
City |
Contact Number |
|
1 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) |
Multiple Cities |
+91-11-26588500 |
|
2 |
Safdarjung Hospital |
Delhi |
+91-11-2673-0000 |
|
3 |
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research |
Chandigarh |
+91-172-275-6565 |
|
4 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) |
Nagpur |
+91-712-270-1646 |
|
5 |
King George's Medical University (KGMU) |
Lucknow |
+91-522-2257450 |
|
6 |
Madras Medical College |
Chennai |
+91-44-2530-5000 |
|
7 |
Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research |
Kolkata |
+91-33-2204-1000 |
|
8 |
SMS Medical College |
Jaipur |
+91-141-251-8121 |
|
9 |
Government General Hospital |
Vijayawada |
+91-866-257-6000 |
Please Wait..